Analogies highlight relationships between concepts to enhance understanding and problem-solving skills by drawing comparisons. They help Your brain recognize patterns and connections across different contexts, making complex ideas more accessible. Explore the rest of this article to discover how analogies can transform your thinking and communication.
Table of Comparison
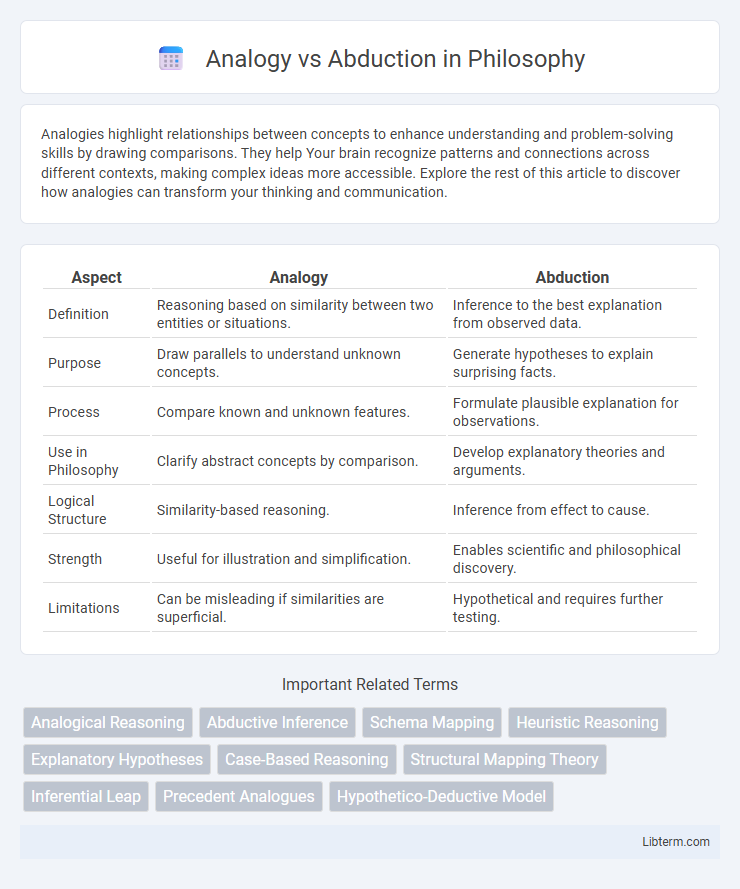
| Aspect | Analogy | Abduction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reasoning based on similarity between two entities or situations. | Inference to the best explanation from observed data. |
| Purpose | Draw parallels to understand unknown concepts. | Generate hypotheses to explain surprising facts. |
| Process | Compare known and unknown features. | Formulate plausible explanation for observations. |
| Use in Philosophy | Clarify abstract concepts by comparison. | Develop explanatory theories and arguments. |
| Logical Structure | Similarity-based reasoning. | Inference from effect to cause. |
| Strength | Useful for illustration and simplification. | Enables scientific and philosophical discovery. |
| Limitations | Can be misleading if similarities are superficial. | Hypothetical and requires further testing. |
Introduction to Analogy and Abduction
Analogy involves reasoning by drawing parallels between similar situations to infer conclusions, often used in problem-solving and learning. Abduction, or inference to the best explanation, generates the most plausible hypothesis based on incomplete observations, frequently applied in diagnostic and scientific contexts. Both forms of reasoning support decision-making but differ in their approach: analogy relies on similarity, while abduction focuses on explanatory power.
Defining Analogy: Meaning and Usage
Analogy refers to a cognitive process that identifies similarities between two different concepts or situations, allowing for understanding through comparison. It is commonly used in problem-solving, communication, and learning by mapping familiar knowledge onto unfamiliar contexts. This method facilitates reasoning by highlighting parallel structures or relationships, enhancing conceptual clarity and decision-making.
Understanding Abduction: Core Concepts
Abduction is a form of logical inference that starts with an observation and seeks the most likely explanation, distinguishing it from analogy which relies on similarity between different cases. Core concepts of abduction involve generating hypotheses that best explain the available evidence, emphasizing plausibility over certainty. This reasoning process is fundamental in fields such as diagnostic medicine, scientific discovery, and artificial intelligence for formulating testable explanations.
Historical Perspectives: Analogy vs Abduction
Historical perspectives on analogy and abduction trace back to ancient philosophy, where Aristotle emphasized analogy as a method for drawing comparisons based on similarity and proportion. Charles Sanders Peirce formalized abduction in the 19th century as a distinct mode of inference focused on generating hypotheses to explain surprising observations. These foundational developments highlight analogy as a tool for understanding through resemblance, while abduction underpins the creative formation of explanatory theories in scientific reasoning.
Key Differences Between Analogy and Abduction
Analogy involves drawing parallels between known and unknown situations to infer conclusions based on similarity, while abduction is about forming the most plausible hypothesis from incomplete or uncertain information. Analogy relies on structural or relational similarities, making it useful for problem-solving by comparing familiar cases, whereas abduction seeks to generate explanatory guesses that best fit observed data. The key difference lies in analogy emphasizing comparison for inference, and abduction focusing on hypothesis generation to explain evidence.
Roles of Analogy and Abduction in Problem Solving
Analogy plays a crucial role in problem solving by enabling the transfer of knowledge from familiar situations to new, similar contexts, facilitating pattern recognition and solution generation. Abduction involves forming the most plausible hypotheses based on incomplete information, guiding exploratory reasoning and decision-making under uncertainty. Both processes complement each other by combining analogy's strength in recognizing parallels with abduction's ability to infer explanations, enhancing creativity and adaptability in complex problem-solving scenarios.
Applications in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Analogy and abduction serve distinct roles in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, with analogy primarily aiding in pattern recognition and transfer learning by drawing parallels between known and unknown data sets. Abduction supports hypothesis generation and explanatory reasoning, enabling AI systems to infer the most plausible causes from observed evidence, which is crucial in diagnostic systems and natural language understanding. Applications of analogy include case-based reasoning and similarity search, while abduction underpins abductive inference engines and diagnostic algorithms.
Examples Illustrating Analogy and Abduction
Analogy involves drawing parallels between two similar situations, such as comparing the flow of electricity in circuits to water flowing through pipes to simplify complex concepts. Abduction, on the other hand, is reasoning to the best explanation; for example, a doctor infers a diagnosis by observing symptoms like fever and cough as signs of the flu. These examples highlight how analogy aids understanding through similarity, while abduction seeks the most plausible explanation based on available evidence.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Analogy offers strong heuristic value by enabling problem-solving through similarity mapping, promoting quick hypothesis generation in domains with well-understood patterns. However, its reliance on surface similarities can lead to misleading conclusions when underlying causal mechanisms differ significantly, limiting its applicability in novel or complex scenarios. Abduction excels at generating plausible explanations from incomplete data by inferring the best hypothesis, yet it often struggles with solution verification and can produce multiple competing hypotheses, necessitating further validation.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Analogy and Abduction
Choosing between analogy and abduction depends on the nature of the problem and the available information. Analogy excels in generating hypotheses based on similarities to known cases, making it effective for pattern recognition and transfer learning. Abduction prioritizes the best explanatory hypothesis, suitable for situations requiring inference to the most plausible cause from incomplete data.
Analogy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com