Essence captures the core nature and fundamental qualities that define a person, object, or concept, influencing how we perceive and relate to it deeply. Understanding essence helps you grasp the true meaning behind appearances or superficial elements, leading to more meaningful insights. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how essence shapes your understanding and experiences.
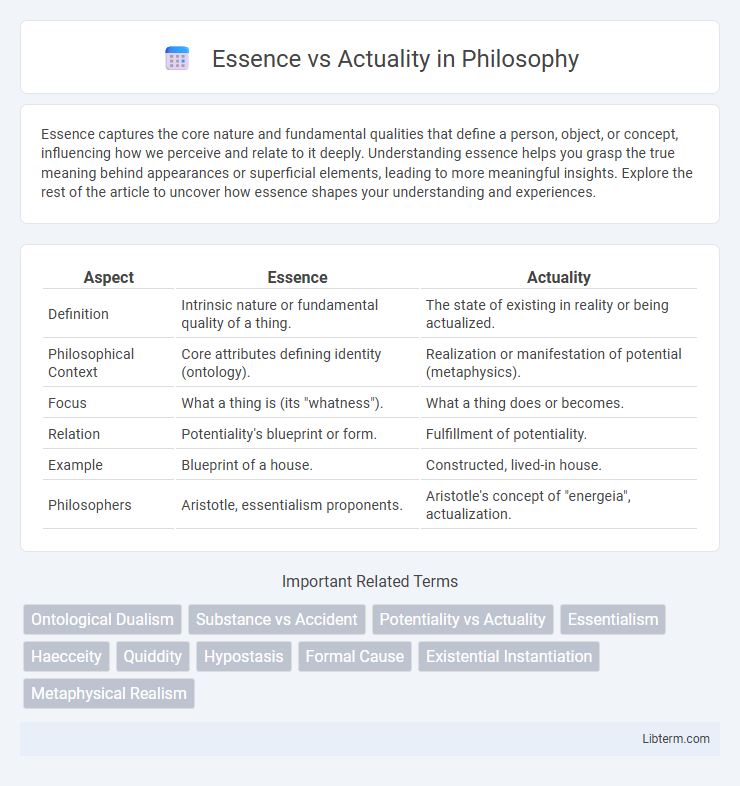
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Essence | Actuality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intrinsic nature or fundamental quality of a thing. | The state of existing in reality or being actualized. |
| Philosophical Context | Core attributes defining identity (ontology). | Realization or manifestation of potential (metaphysics). |
| Focus | What a thing is (its "whatness"). | What a thing does or becomes. |
| Relation | Potentiality's blueprint or form. | Fulfillment of potentiality. |
| Example | Blueprint of a house. | Constructed, lived-in house. |
| Philosophers | Aristotle, essentialism proponents. | Aristotle's concept of "energeia", actualization. |
Defining Essence and Actuality
Essence refers to the intrinsic nature or fundamental qualities that define what a thing is, independent of its existence or manifestation. Actuality signifies the state of being real or existing in fact, where the essence is fully realized or manifested in concrete form. The distinction highlights that essence represents potential or conceptual identity, while actuality embodies the expression or fulfillment of that essence in reality.
Historical Perspectives on Essence vs Actuality
Medieval philosophers like Thomas Aquinas distinguished essence as "what a thing is" and actuality as "that a thing is," establishing a foundational metaphysical framework. Aristotle's concept of potentiality and actuality influenced Scholastic debates by emphasizing substance and existence as interrelated yet distinct principles. Renaissance thinkers further refined this distinction, integrating it with emerging scientific methodologies to explore the dynamic interplay between an entity's essential nature and its realized state.
Philosophical Foundations: Aristotle and Beyond
Essence, defined as the intrinsic nature or indispensable quality of a thing, contrasts with actuality, which refers to the concrete existence or realization of potential within Aristotle's metaphysical framework. Aristotle's distinction between essence (what a thing is) and actuality (that a thing is) forms the foundation of classical ontology, influencing subsequent philosophers such as Aquinas and Heidegger who expanded on the interplay between potentiality and realization in being. This conceptual dichotomy remains central to discussions in metaphysics, ontology, and existential philosophy, shaping interpretations of existence and identity across philosophical traditions.
The Role of Essence in Metaphysics
Essence in metaphysics defines the fundamental nature or intrinsic properties that make an entity what it is, distinguishing it from mere existence or actuality. It provides the criteria for identity and classification, allowing philosophers to understand what must be true for something to be considered that specific thing. By exploring essence, metaphysics addresses questions of necessity, possibility, and the underlying reality beyond mere appearances.
Actuality: Manifestation of Potential
Actuality represents the realization of essence by manifesting inherent potential into tangible existence. It underscores the transition from mere possibility to concrete reality, where potentialities are fully actualized and observable. This concept is pivotal in understanding how latent qualities or capacities become operative and effective within a given context.
Essence vs Actuality in Human Identity
Essence in human identity refers to the intrinsic qualities and fundamental nature that define a person's being, whereas actuality represents the lived experience and manifestation of those qualities through actions and choices. The dynamic interplay between essence and actuality shapes individual self-awareness and personal growth by balancing inherent potential with realized existence. Understanding this relationship enhances philosophical insights into identity formation and the continuous process of becoming.
Real-World Applications: Science and Ethics
Essence and actuality are fundamental concepts in metaphysics that influence real-world applications in science and ethics by distinguishing potential states from realized states. In science, understanding the essence of phenomena guides hypothesis formation, while actual data validates theories, enabling precise experimentation and technological innovation. Ethical frameworks use this differentiation to assess the inherent nature of moral principles (essence) versus their real-world implementation (actuality), shaping policies that align ideals with societal practices.
Contrasts in Eastern and Western Philosophies
Essence and actuality contrast sharply in Eastern and Western philosophies, where Western thought, influenced by Aristotle, emphasizes essence as the defining nature of a thing and actuality as its realized state, while Eastern philosophies, such as Daoism and Buddhism, often blur the distinction, focusing on impermanence and the fluid interplay between potential and manifestation. In Western metaphysics, essence is fixed and precedes existence, whereas in Eastern traditions, the concept of essence is dynamic, intertwined with existence and subject to constant transformation. This fundamental divergence reflects broader ontological differences, with Western philosophy prioritizing static identity and Eastern philosophy embracing process and change.
Contemporary Debates and Interpretations
Contemporary debates on Essence vs Actuality explore the distinction between an entity's inherent nature (essence) and its realized state (actuality) within metaphysical frameworks. Philosophers like Kit Fine emphasize the modal aspects of essence, arguing that essence determines an entity's necessary properties regardless of its current actualization. Recent interpretations integrate this dichotomy into discussions on identity, existence, and ontological dependence, influencing analytic metaphysics and philosophy of mind.
Essence and Actuality: Implications for the Future
Essence represents the fundamental nature or defining characteristics of a concept, while actuality refers to its realization or existence in concrete form. Understanding the interplay between essence and actuality enables predictive insights into innovation, as potential ideas (essence) transition into tangible applications (actuality). Future technological advancements hinge on effectively bridging this gap, ensuring conceptual breakthroughs are actualized into impactful solutions.
Essence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com