Possibility opens doors to new opportunities and drives innovation in every aspect of life. Embracing the potential within challenges allows you to explore creative solutions and unlock hidden pathways to success. Discover how harnessing the power of possibility can transform your future by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
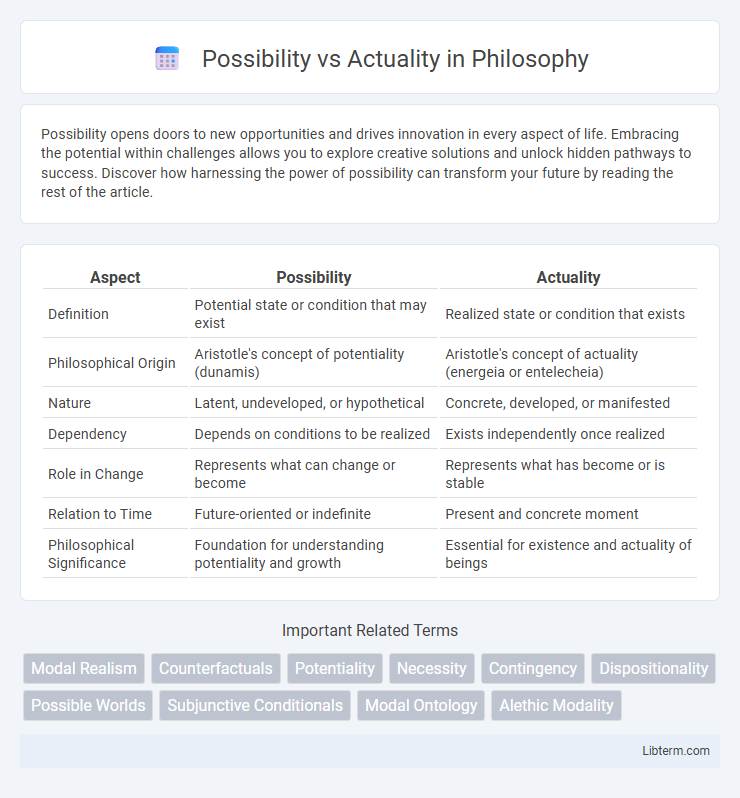
| Aspect | Possibility | Actuality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Potential state or condition that may exist | Realized state or condition that exists |
| Philosophical Origin | Aristotle's concept of potentiality (dunamis) | Aristotle's concept of actuality (energeia or entelecheia) |
| Nature | Latent, undeveloped, or hypothetical | Concrete, developed, or manifested |
| Dependency | Depends on conditions to be realized | Exists independently once realized |
| Role in Change | Represents what can change or become | Represents what has become or is stable |
| Relation to Time | Future-oriented or indefinite | Present and concrete moment |
| Philosophical Significance | Foundation for understanding potentiality and growth | Essential for existence and actuality of beings |
Understanding the Concept of Possibility
Possibility refers to the potential for events or conditions to occur, existing as a state that is logically or physically feasible but not yet realized. It encompasses various degrees, from theoretical constructs in philosophy to practical probabilities in everyday decision-making and scientific predictions. Understanding possibility involves distinguishing it from actuality--what is real and confirmed--by exploring hypothetical scenarios, potential outcomes, and the parameters that enable something to be considered possible within a given context.
Defining Actuality in Context
Actuality refers to the state of being real and existing in fact, rather than merely potential or possible. In philosophical terms, it denotes the realized condition of an entity or event when potential possibilities have been fully actualized. Understanding actuality involves examining concrete occurrences and tangible evidence that distinguish what is truly present from what could merely happen.
Key Differences Between Possibility and Actuality
Possibility refers to the potential for an event or condition to occur, existing within the realm of what can happen or be imagined, while actuality denotes the state of something that has already happened or is currently true in reality. The key difference lies in possibility's nature of uncertainty and potentiality versus actuality's definitiveness and factual existence. Understanding this distinction is crucial in fields like philosophy, decision-making, and science where potential outcomes must be differentiated from confirmed states.
The Role of Probability in Possibility
Probability quantifies the likelihood that a possible event will transition to actuality, providing a measurable framework to evaluate uncertainty. It bridges the gap between abstract possibility and concrete realization by assigning numerical values to potential outcomes. This role of probability is fundamental in decision-making, risk assessment, and predictive modeling across various disciplines.
How Potential Becomes Actual
Potential becomes actual through the process of intentional action and external conditions aligning to realize latent capacities. The transformation hinges on factors like motivation, opportunity, and environmental support that enable the shift from possibility to concrete existence. Philosophically, this transition reflects Aristotle's principle where actuality is the fulfillment of a thing's inherent potentialities.
Philosophical Perspectives on Possibility vs Actuality
Philosophical perspectives on possibility vs actuality often examine the relationship between potential states and their manifestation in reality, as articulated in Aristotle's metaphysics where possibility (dunamis) exists as the capacity for change, while actuality (energeia) represents realized existence. Contemporary modal logic builds upon this by formalizing possible worlds semantics to differentiate necessary truths from contingent actual facts. Debates continue on whether possibilities are mere abstractions or have ontological status independent of actualized events.
Real-World Examples Illustrating Both Concepts
Possibility is exemplified by the concept of space exploration, where multiple missions like Mars rovers and planned human colonization represent potential achievements, while actuality is demonstrated by the successful Apollo moon landings, which materialized as concrete human accomplishments. In technology, the possibility of artificial intelligence surpassing human cognition exists theoretically, but the actuality is seen in current AI applications such as natural language processing and autonomous vehicles operating effectively today. Medical advancements also highlight these concepts, with possibilities including gene editing to eradicate inherited diseases, contrasted by the actuality of vaccines currently preventing widespread illnesses worldwide.
Impact on Decision-Making and Planning
Possibility and actuality influence decision-making by distinguishing between theoretical options and actionable realities, shaping strategic priorities and resource allocation. Understanding possibilities expands the scope of potential outcomes, while focusing on actuality ensures plans are grounded in feasible conditions, reducing risks. Effective planning balances these concepts to optimize flexibility and responsiveness in dynamic environments.
Possibility vs Actuality in Science and Innovation
In science and innovation, possibility represents theoretical concepts and potential discoveries that have yet to be realized, while actuality refers to proven facts and implemented technologies. Scientific research explores possibilities through hypotheses and simulations, but actual breakthroughs require empirical validation and practical application. The dynamic interplay between possibility and actuality drives technological advancement by transforming innovative ideas into concrete solutions.
Navigating Uncertainty: Bridging Possibility to Actuality
Navigating uncertainty involves transforming potential outcomes into concrete realities by assessing risks and leveraging strategic decision-making frameworks. Understanding the interplay between possibility and actuality requires continuous evaluation of available information and adaptive responses to emerging challenges. Effective execution depends on aligning resources with clear objectives to bridge conceptual opportunities and tangible results.
Possibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com