Pragmatic approaches focus on practical solutions that deliver tangible results, emphasizing functionality over theoretical ideals. This mindset helps streamline decision-making processes by prioritizing effectiveness and adaptability in real-world scenarios. Discover how adopting a pragmatic perspective can enhance your problem-solving skills throughout the rest of the article.
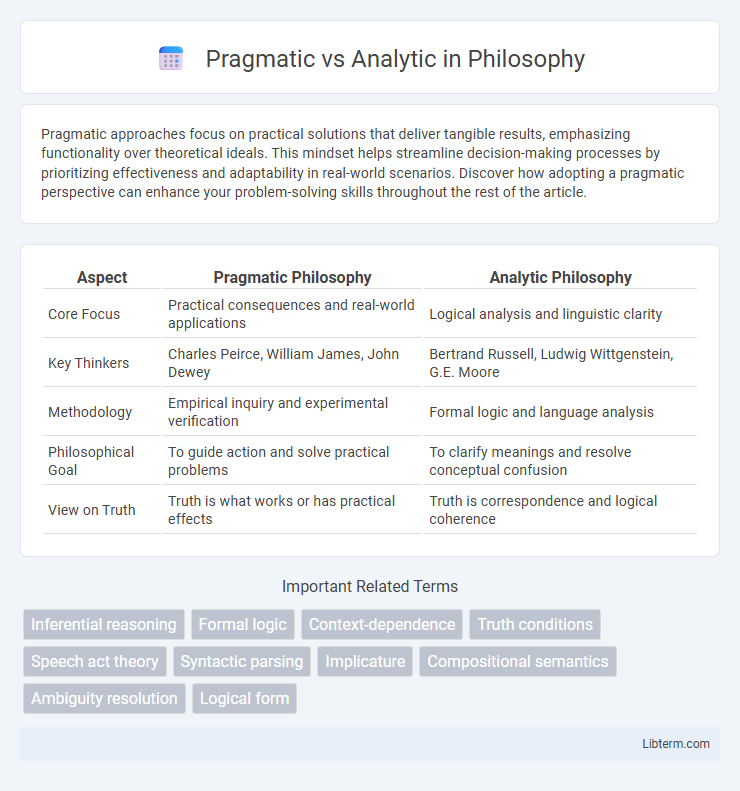
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pragmatic Philosophy | Analytic Philosophy |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Practical consequences and real-world applications | Logical analysis and linguistic clarity |
| Key Thinkers | Charles Peirce, William James, John Dewey | Bertrand Russell, Ludwig Wittgenstein, G.E. Moore |
| Methodology | Empirical inquiry and experimental verification | Formal logic and language analysis |
| Philosophical Goal | To guide action and solve practical problems | To clarify meanings and resolve conceptual confusion |
| View on Truth | Truth is what works or has practical effects | Truth is correspondence and logical coherence |
Understanding Pragmatism and Analytic Approaches
Pragmatic approaches emphasize practical outcomes and real-world applications to solve problems efficiently, often prioritizing flexibility and context-specific solutions. Analytic approaches focus on breaking down complex issues into fundamental components using systematic, logical reasoning and structured methodologies. Understanding pragmatism involves recognizing its adaptability and outcome-driven mindset, while analytic approaches require grasping formal logic, data analysis, and systematic evaluation processes.
Historical Origins of Pragmatic and Analytic Philosophy
Pragmatic philosophy originated in the late 19th century United States, with key figures such as Charles Sanders Peirce, William James, and John Dewey emphasizing practical consequences and experiential learning. In contrast, analytic philosophy emerged in the early 20th century in Europe, particularly in Britain, with foundational thinkers like Bertrand Russell, G.E. Moore, and Ludwig Wittgenstein focusing on language analysis, logic, and clarity of argument. Both traditions addressed different philosophical problems: pragmatism rooted in American intellectual contexts aiming at application and utility, while analytic philosophy concentrated on linguistic precision and formal logic derived from European academic institutions.
Core Principles of Pragmatic Thinking
Pragmatic thinking centers on actionable strategies, emphasizing practical problem-solving and adaptability in dynamic environments. Core principles include focusing on real-world results, continuously updating mental models based on experience, and prioritizing clarity in communication to facilitate efficient decision-making. This mindset values simplicity, iterative learning, and the ability to pivot quickly to optimize outcomes effectively.
Key Features of Analytic Reasoning
Analytic reasoning emphasizes structured problem-solving through logical steps, pattern recognition, and systematic evaluation of components. It relies on deductive and inductive methods to break down complex information into smaller, manageable parts for clearer understanding. Key features include critical thinking, evidence-based analysis, and the ability to identify relationships and infer conclusions from data.
Pragmatism vs. Analytic Philosophy: Main Differences
Pragmatism emphasizes practical consequences and real-world applications as the basis for meaning and truth, focusing on experience and action rather than abstract principles. Analytic philosophy prioritizes logical clarity, argumentative rigor, and linguistic analysis, often addressing metaphysical and epistemological questions through formal reasoning. The primary difference lies in pragmatism's outcome-oriented approach versus analytic philosophy's emphasis on conceptual precision and language structure.
Practical Applications of Pragmatic Methods
Pragmatic methods emphasize practical solutions by prioritizing real-world outcomes over theoretical models, making them ideal for industries like software development, healthcare, and education where flexibility and immediate problem-solving are critical. These approaches enable rapid iteration, user-focused design, and adaptive strategies that improve efficiency and effectiveness in dynamic environments. Embracing pragmatic strategies enhances decision-making by leveraging empirical evidence and context-specific data rather than relying solely on abstract analyses typical of analytic methods.
Analytic Techniques in Modern Problem-Solving
Analytic techniques in modern problem-solving leverage data-driven approaches such as statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, and predictive modeling to uncover patterns and inform decision-making. These methods prioritize logic and structured reasoning, enabling precise identification of root causes and evaluation of potential solutions based on quantitative evidence. The integration of tools like data visualization and computational simulations enhances the depth and accuracy of analytic processes across diverse industries.
Advantages and Limitations of Pragmatic Approaches
Pragmatic approaches in language learning emphasize practical communication skills and contextual understanding, enabling learners to interact effectively in real-life situations. They offer the advantage of adaptability across diverse cultural and conversational settings but may lack systematic structure, making it challenging to master grammatical accuracy. Limitations include potential inconsistencies in language rules and difficulty in achieving deep theoretical knowledge compared to analytic methods.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Analytic Strategies
Analytic strategies emphasize breaking down complex problems into smaller components, enabling precise data analysis and clearer understanding of causal relationships. Benefits include enhanced accuracy in decision-making and the ability to identify specific optimization opportunities, while drawbacks involve potential overlooking of contextual factors and reduced flexibility in adapting to ambiguous or evolving situations. These limitations can lead to slower response times and challenges in addressing problems requiring holistic or intuitive approaches.
Choosing between Pragmatic and Analytic Perspectives
Choosing between pragmatic and analytic perspectives depends on the problem context and desired outcomes. Pragmatic approaches prioritize practical solutions and adaptability, often leveraging real-world applications and iterative testing. Analytic perspectives emphasize systematic reasoning, data-driven insights, and theoretical frameworks to ensure accuracy and in-depth understanding.
Pragmatic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com