Constructionism emphasizes learning through hands-on building and creating, allowing learners to construct knowledge actively rather than passively receiving information. This approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper understanding by engaging individuals in real-world projects and collaborative activities. Discover how constructionism can transform your educational experience and enhance learning outcomes by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
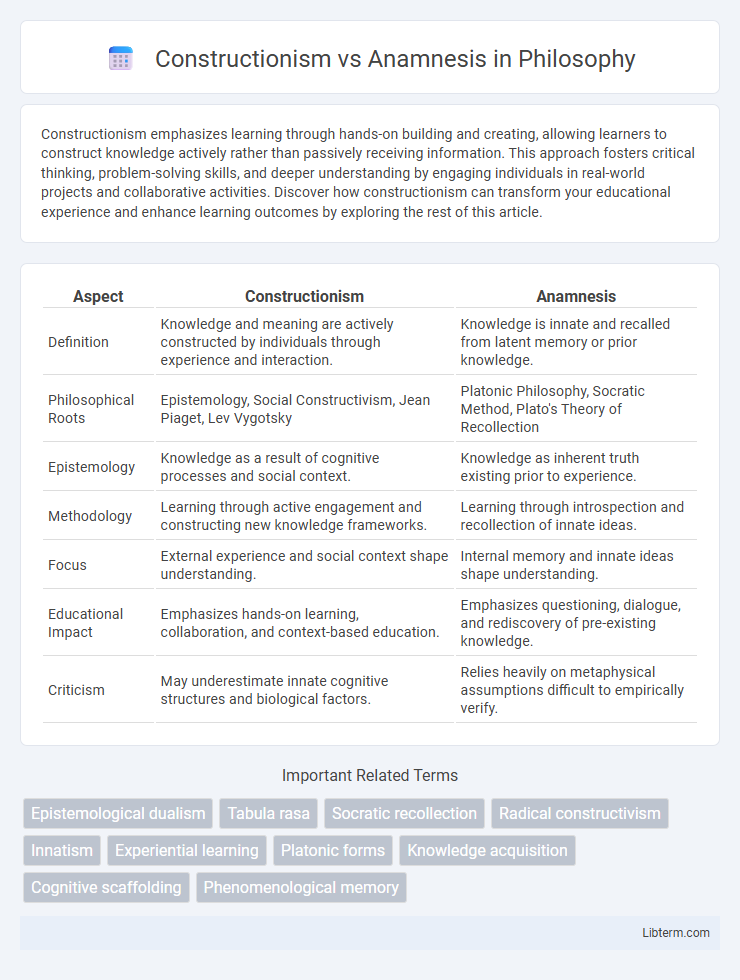
| Aspect | Constructionism | Anamnesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Knowledge and meaning are actively constructed by individuals through experience and interaction. | Knowledge is innate and recalled from latent memory or prior knowledge. |
| Philosophical Roots | Epistemology, Social Constructivism, Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky | Platonic Philosophy, Socratic Method, Plato's Theory of Recollection |
| Epistemology | Knowledge as a result of cognitive processes and social context. | Knowledge as inherent truth existing prior to experience. |
| Methodology | Learning through active engagement and constructing new knowledge frameworks. | Learning through introspection and recollection of innate ideas. |
| Focus | External experience and social context shape understanding. | Internal memory and innate ideas shape understanding. |
| Educational Impact | Emphasizes hands-on learning, collaboration, and context-based education. | Emphasizes questioning, dialogue, and rediscovery of pre-existing knowledge. |
| Criticism | May underestimate innate cognitive structures and biological factors. | Relies heavily on metaphysical assumptions difficult to empirically verify. |
Introduction to Constructionism and Anamnesis
Constructionism emphasizes learning through building tangible objects and active experimentation, fostering deep understanding by engaging learners in creating artifacts. Anamnesis, rooted in Platonic philosophy, involves recollecting innate knowledge through reflective questioning, aiming to awaken pre-existing understanding within the learner. These contrasting educational theories highlight hands-on creation versus introspective memory recall as core methods for acquiring knowledge.
Historical Origins and Philosophical Background
Constructionism traces its historical origins to the works of Jean Piaget and Seymour Papert, emphasizing knowledge acquisition through active learning and experience-based construction. Anamnesis, rooted in Platonic philosophy, originates from Plato's theory of recollection, proposing that learning is a process of remembering innate knowledge from the soul's past existence. The philosophical background of Constructionism centers on cognitive development and social interaction, while Anamnesis focuses on metaphysical concepts of innate ideas and the soul's immortality.
Key Concepts Defined: Constructionism
Constructionism emphasizes knowledge as a product of active learning where individuals build new understandings through experiences and social interactions. It highlights the role of context, collaboration, and reflection in shaping cognitive development and knowledge construction. Unlike passive absorption, constructionism views learners as creators of meaning, continuously integrating new information with prior knowledge.
Key Concepts Defined: Anamnesis
Anamnesis in philosophy refers to the recollection or innate knowledge that the soul possesses prior to birth, emphasizing the retrieval of eternal truths through introspection. This concept, rooted in Platonic thought, contrasts with constructionism by asserting that knowledge is discovered rather than constructed. Key elements include innate ideas, memory as a form of knowledge access, and the soul's pre-existence.
Comparison of Core Principles
Constructionism emphasizes knowledge as actively built through personal experience and social interaction, valuing learner-centered environments and collaborative meaning-making. In contrast, Anamnesis centers on knowledge as innate recollection, drawing from Platonic philosophy where learning is the process of remembering eternal truths inherent within the soul. The core comparison reveals Constructionism's focus on external knowledge construction, while Anamnesis prioritizes internal, pre-existing knowledge retrieval.
Applications in Education and Learning
Constructionism emphasizes learning through making, where students build tangible objects or digital projects to internalize knowledge, fostering creativity and problem-solving skills in educational settings. Anamnesis, rooted in Socratic dialogue, promotes recollection and deep reflection, encouraging learners to connect current knowledge with prior understanding for enhanced critical thinking. Integrating constructionism's hands-on methodologies with anamnesis's reflective inquiry can create a dynamic learning environment that supports active engagement and meaningful knowledge retention.
The Role of Memory and Experience
Constructionism posits that memory and experience are actively constructed through social interaction and cultural context, shaping knowledge by integrating personal and collective histories. Anamnesis views memory as a process of recollection where true knowledge is retrieved from innate understanding or past existence, emphasizing the awakening of latent wisdom. Both theories highlight memory's pivotal role but differ in framing experience as either constructed in the present or recollected from an inherent source.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Constructionism excels in promoting active learning and critical thinking by encouraging learners to build knowledge through experience and social interaction, though it may struggle with providing structured guidance for complex subjects. Anamnesis leverages the recollection of innate knowledge and past experiences, facilitating deep understanding and self-awareness, but it risks reliance on subjective memory which can lead to biased or incomplete insights. Balancing constructionism's collaborative, hands-on strengths with anamnesis's introspective reflection can address their individual limitations in educational or philosophical contexts.
Influences on Modern Thought and Practice
Constructionism reshaped modern thought by emphasizing knowledge as a process of active building through social interaction and authentic experiences, influencing educational practices that prioritize collaborative learning and critical thinking. Anamnesis, rooted in Platonic philosophy, impacts contemporary practice by encouraging introspective recollection and the uncovering of innate knowledge, shaping approaches in psychotherapy and transformative learning. Both concepts contribute to evolving epistemologies, with constructionism underpinning constructivist pedagogy and anamnesis informing methods of self-awareness and cognitive retrieval in modern psychology.
Choosing Between Constructionism and Anamnesis
Choosing between Constructionism and Anamnesis depends on the philosophical perspective on knowledge acquisition and learning. Constructionism emphasizes building new understanding through active engagement and interaction with the environment, often applied in educational technology and cognitive development. Anamnesis, rooted in Platonic thought, focuses on recollecting innate knowledge, suggesting that learning is realizing what the soul already knows rather than acquiring new information.
Constructionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com