Consistency is the foundation of achieving lasting success in any endeavor, reinforcing positive habits and building trust over time. Maintaining regular efforts, even when motivation wanes, ensures steady progress and measurable results. Discover how consistency can transform your goals by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
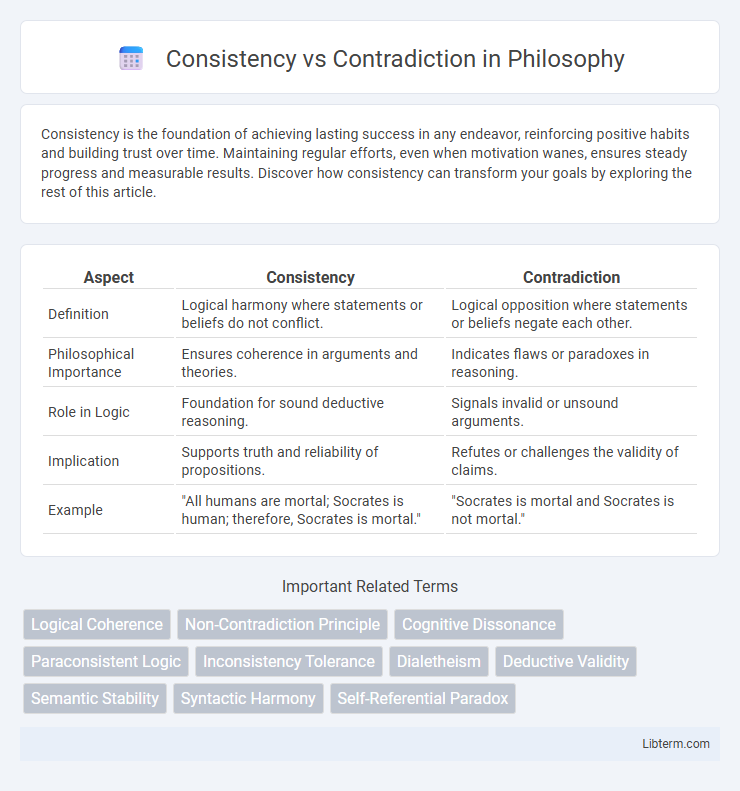
| Aspect | Consistency | Contradiction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Logical harmony where statements or beliefs do not conflict. | Logical opposition where statements or beliefs negate each other. |
| Philosophical Importance | Ensures coherence in arguments and theories. | Indicates flaws or paradoxes in reasoning. |
| Role in Logic | Foundation for sound deductive reasoning. | Signals invalid or unsound arguments. |
| Implication | Supports truth and reliability of propositions. | Refutes or challenges the validity of claims. |
| Example | "All humans are mortal; Socrates is human; therefore, Socrates is mortal." | "Socrates is mortal and Socrates is not mortal." |
Understanding Consistency and Contradiction
Understanding consistency involves recognizing the alignment and coherence of information or actions within a system, ensuring reliability and predictability. Contradiction highlights opposing or conflicting elements that disrupt harmony and challenge the validity of statements or behaviors. Analyzing these concepts aids in evaluating logical coherence, decision-making, and effective communication across disciplines.
The Importance of Consistency in Communication
Consistency in communication reinforces trust and credibility by ensuring messages are clear, reliable, and predictable across different platforms and interactions. Brands and individuals that maintain consistent tone, style, and information reduce confusion, making their communication more effective and memorable. Contradictions in messaging create doubt and diminish audience confidence, highlighting the critical role of consistency for successful communication strategies.
How Contradiction Shapes Critical Thinking
Contradiction is a fundamental driver of critical thinking, as it challenges existing beliefs and prompts deeper analysis. Encountering conflicting information encourages individuals to evaluate evidence rigorously, identify biases, and refine their reasoning processes. This dynamic tension between opposing ideas fosters intellectual growth and enhances problem-solving skills by demanding precise argumentation and openness to alternative perspectives.
Psychological Roots of Consistent and Contradictory Behavior
Consistent behavior often stems from cognitive stability and the desire to maintain a coherent self-image, driven by psychological theories such as cognitive dissonance and self-perception. Contradictory behavior may arise from internal conflicts, shifting priorities, or external stressors that challenge an individual's belief system and adaptive strategies. Understanding these psychological roots helps explain why people sometimes act predictably and other times inconsistently, reflecting the complexity of human cognition and emotional regulation.
Consequences of Consistency in Personal and Professional Life
Consistency in personal and professional life enhances trustworthiness and reliability, fostering stronger relationships and career growth. Regularly meeting commitments and maintaining a steady performance level contribute to a positive reputation and increased opportunities. Long-term consistency also promotes discipline and efficiency, reducing stress and avoiding conflict caused by erratic behavior.
Positive Roles of Contradiction in Innovation
Contradiction plays a crucial role in driving innovation by challenging existing norms and encouraging diverse perspectives that foster creative problem-solving. The tension created by contradictory ideas stimulates critical thinking and experimentation, leading to breakthrough technologies and novel solutions. Embracing contradictions enables organizations to adapt dynamically and sustain competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets.
Common Sources of Contradiction in Arguments
Common sources of contradiction in arguments often stem from ambiguous definitions, inconsistent evidence, and logical fallacies such as false dilemmas or straw man tactics. Misinterpretation of key terms or selective use of data can create conflicting conclusions that undermine overall consistency. Identifying and addressing these sources enhances the clarity and reliability of argumentative discourse.
Balancing Consistency and Contradiction for Growth
Balancing consistency and contradiction is crucial for fostering growth, as consistency provides stability and predictable outcomes while contradiction sparks innovation and critical thinking. Businesses and individuals that maintain core values consistently yet embrace diverse perspectives and challenges can adapt effectively to changing environments. This dynamic interplay drives continuous improvement, helping organizations evolve without losing their foundational identity.
Case Studies: Consistency vs Contradiction in Real Life
Case studies highlighting consistency versus contradiction reveal how organizations that maintain consistent messaging and actions achieve stronger brand loyalty and operational efficiency. For example, Apple's unwavering commitment to sleek design and user experience reinforces customer trust, while contradictory marketing messaging from brands like Pepsi during the Kendall Jenner ad controversy led to public backlash and diminished brand credibility. Analyzing real-life scenarios illustrates that consistency in values, communication, and execution directly impacts consumer perception and business success.
Strategies for Managing Consistency and Contradiction
Effective strategies for managing consistency and contradiction involve implementing robust communication frameworks and fostering an open organizational culture that encourages transparency. Utilizing data reconciliation techniques alongside conflict resolution tools helps identify and address discrepancies early, ensuring alignment across teams and processes. Prioritizing continuous feedback loops and adaptive policy adjustments maintains coherence while accommodating necessary changes in dynamic environments.
Consistency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com