Prescriptive grammar establishes rules about how language should be used, focusing on correctness and standardized forms. It guides your writing and speech by setting norms for syntax, punctuation, and word usage to maintain clarity and professionalism. Explore the rest of this article to understand how prescriptive grammar can enhance your communication skills.
Table of Comparison
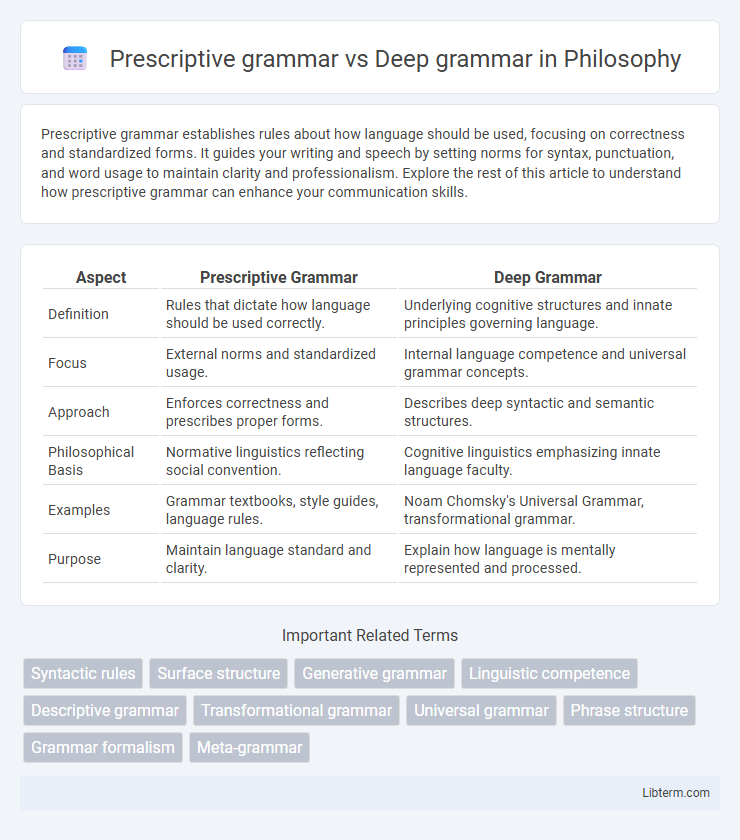
| Aspect | Prescriptive Grammar | Deep Grammar |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules that dictate how language should be used correctly. | Underlying cognitive structures and innate principles governing language. |
| Focus | External norms and standardized usage. | Internal language competence and universal grammar concepts. |
| Approach | Enforces correctness and prescribes proper forms. | Describes deep syntactic and semantic structures. |
| Philosophical Basis | Normative linguistics reflecting social convention. | Cognitive linguistics emphasizing innate language faculty. |
| Examples | Grammar textbooks, style guides, language rules. | Noam Chomsky's Universal Grammar, transformational grammar. |
| Purpose | Maintain language standard and clarity. | Explain how language is mentally represented and processed. |
Introduction to Prescriptive and Deep Grammar
Prescriptive grammar establishes rules and standards for correct language use, emphasizing syntax, punctuation, and style to guide formal and academic writing. Deep grammar refers to the underlying, cognitive structures that govern language understanding and production, focusing on how native speakers internalize and apply grammatical knowledge unconsciously. While prescriptive grammar prioritizes correctness and clarity, deep grammar explores the innate linguistic competence enabling natural language acquisition and comprehension.
Defining Prescriptive Grammar
Prescriptive grammar establishes explicit rules and standards for correct language usage, emphasizing how language should be used in formal contexts. It dictates proper syntax, punctuation, and word choice based on authoritative sources like style guides and dictionaries. This approach contrasts with descriptive grammar, which observes and records actual language use without judgment.
Understanding Deep Grammar
Deep grammar explores the underlying structures and rules that govern language use beyond surface-level correctness, emphasizing the cognitive and syntactic patterns inherent in communication. It focuses on the mental representation of grammatical knowledge, enabling speakers to generate and understand an infinite number of sentences. Understanding deep grammar facilitates insights into language acquisition, processing, and the innate linguistic competence shared by all humans.
Historical Evolution of Grammar Theories
Prescriptive grammar, emerging in the 18th century, focused on establishing standardized rules based on classical languages to guide proper language use in education and literature. Deep grammar theories, influenced by Noam Chomsky's transformational-generative grammar in the mid-20th century, shifted attention to the underlying cognitive structures that govern language acquisition and use. The historical evolution from prescriptive norms to deep grammar reflects a paradigm shift from external correctness to internal linguistic competence.
Prescriptive Grammar: Rules and Standards
Prescriptive grammar establishes strict rules and standards governing language use, dictating how sentences should be correctly structured based on traditional norms. It emphasizes proper syntax, punctuation, and word usage, aiming to maintain clarity and uniformity in written and spoken communication. This framework is essential for formal writing, academic discourse, and standardized language education, ensuring consistency and comprehension across diverse audiences.
Deep Grammar: Structure and Meaning
Deep grammar explores the underlying structure and meaning of language by analyzing syntax, semantics, and the cognitive processes involved in language comprehension. It focuses on how sentences convey meaning beyond surface rules, examining hierarchical sentence structures and their interpretation within linguistic theory. This approach contrasts with prescriptive grammar, which enforces standardized usage rather than investigating the innate mechanisms of language understanding and production.
Key Differences Between Prescriptive and Deep Grammar
Prescriptive grammar establishes strict rules governing language usage based on traditional standards, emphasizing correctness and formal structure. Deep grammar involves the underlying cognitive and syntactic structures that guide language comprehension and production naturally within the brain. Key differences include prescriptive grammar's focus on explicit rules for writing and speech versus deep grammar's analysis of implicit, mental linguistic frameworks shaping syntax and semantics.
Impacts on Language Learning and Teaching
Prescriptive grammar enforces strict language rules, guiding learners toward standardized usage and reducing errors in formal communication, which is crucial in academic and professional contexts. Deep grammar emphasizes understanding the underlying syntactic and semantic structures, enhancing learners' ability to intuitively generate correct and complex sentences, fostering language creativity and fluency. The integration of both approaches in language teaching balances rule-based accuracy with cognitive linguistic competence, improving overall language proficiency and adaptability in diverse communicative situations.
Modern Applications in Linguistics
Prescriptive grammar prescribes rules and standards for correct language use, influencing language education, editorial practices, and language policy. Deep grammar, derived from generative linguistics, models the underlying syntactic structures and cognitive processes governing language, informing natural language processing and computational linguistics. Modern applications leverage prescriptive norms for standardized communication while deep grammar frameworks enhance machine translation, syntactic parsing, and language acquisition algorithms.
Conclusion: Bridging Grammar Perspectives
Prescriptive grammar enforces standardized rules to ensure clarity and uniformity in language use, while deep grammar explores underlying cognitive structures and natural language acquisition processes. Bridging these perspectives enhances linguistic education by integrating rule-based instruction with insights from cognitive linguistics, promoting both correctness and intuitive understanding. This integrated approach optimizes language learning and communication effectiveness across diverse contexts.
Prescriptive grammar Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com