A participatory perspective emphasizes the active involvement of individuals in decision-making processes, fostering collaboration and shared responsibility. This approach enhances engagement and ensures that diverse viewpoints are considered, leading to more effective and inclusive outcomes. Discover how embracing a participatory perspective can transform your interactions and results by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
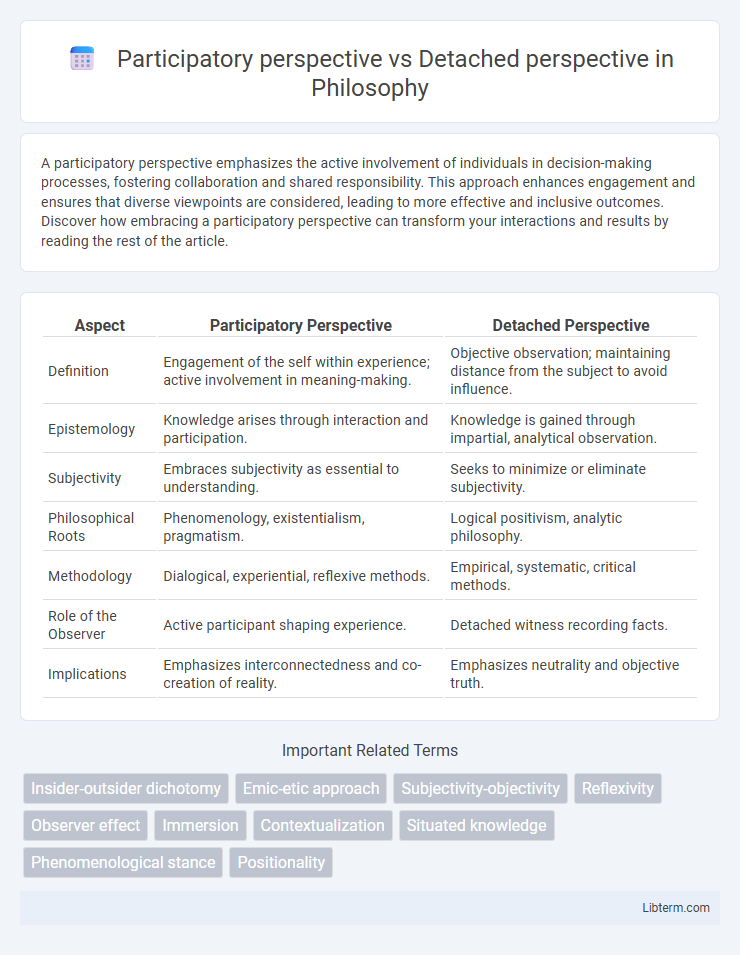
| Aspect | Participatory Perspective | Detached Perspective |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engagement of the self within experience; active involvement in meaning-making. | Objective observation; maintaining distance from the subject to avoid influence. |
| Epistemology | Knowledge arises through interaction and participation. | Knowledge is gained through impartial, analytical observation. |
| Subjectivity | Embraces subjectivity as essential to understanding. | Seeks to minimize or eliminate subjectivity. |
| Philosophical Roots | Phenomenology, existentialism, pragmatism. | Logical positivism, analytic philosophy. |
| Methodology | Dialogical, experiential, reflexive methods. | Empirical, systematic, critical methods. |
| Role of the Observer | Active participant shaping experience. | Detached witness recording facts. |
| Implications | Emphasizes interconnectedness and co-creation of reality. | Emphasizes neutrality and objective truth. |
Understanding Participatory and Detached Perspectives
Participatory perspective emphasizes active engagement and immersion within a context, allowing individuals to experience and interpret phenomena from an insider's viewpoint. Detached perspective involves maintaining objective distance, enabling unbiased observation and analysis without direct emotional or contextual involvement. Understanding these perspectives clarifies how subjective experience contrasts with empirical observation in fields like anthropology, psychology, and sociology.
Core Principles of Participatory Perspective
The Core Principles of Participatory Perspective emphasize active engagement, mutual respect, and collaborative knowledge creation, which contrasts sharply with the Detached Perspective's objective observation. This approach prioritizes inclusivity, empowering stakeholders to contribute their experiences and insights in the decision-making process. The participatory method fosters a dynamic interaction that elevates shared understanding beyond passive analysis.
Key Features of Detached Perspective
The detached perspective emphasizes objective observation and critical analysis, maintaining emotional neutrality to ensure unbiased evaluation. It prioritizes distance from the subject to avoid subjective influence, enabling a clear, systematic understanding of phenomena. Key features include emphasis on empirical evidence, analytical reasoning, and an impersonal stance that separates the observer from direct involvement.
Historical Origins and Evolution
The participatory perspective, rooted in phenomenology and experiential philosophy, emerged in the early 20th century as a response to detached, objective approaches prevalent in Enlightenment thought, emphasizing active involvement and co-creation of meaning. In contrast, the detached perspective traces back to classical empiricism and scientific method, prioritizing observation, measurement, and neutrality to achieve objective knowledge. Over time, the evolution of these perspectives reflects a dynamic interplay between subjective engagement and objective analysis in disciplines such as anthropology, psychology, and historiography.
Comparative Analysis: Involvement vs. Objectivity
The participatory perspective emphasizes active involvement and emotional engagement, fostering deeper understanding through personal experience, while the detached perspective prioritizes objectivity and impartial observation to minimize bias. Comparative analysis reveals that involvement enhances empathy and contextual insight, whereas detachment supports systematic evaluation and clearer evidence-based conclusions. Balancing both perspectives can optimize analysis by integrating subjective insights with rigorous, unbiased scrutiny.
Influence on Data Collection and Interpretation
The participatory perspective actively involves stakeholders in the research process, enhancing data richness through diverse viewpoints and fostering deeper contextual understanding during interpretation. In contrast, the detached perspective relies on objective observation by researchers, aiming to minimize bias but potentially overlooking nuanced social dynamics and subjective experiences. This difference significantly influences data validity, as participatory approaches may introduce experiential depth while detached methods emphasize replicability and neutrality.
Advantages of Participatory Perspective
The participatory perspective enhances empathy and deeper engagement by immersing individuals directly in experiences, fostering authentic understanding and connection. It promotes collaborative problem-solving and co-creation, leveraging diverse viewpoints for richer insights and innovation. This approach improves motivation and ownership, as participants actively contribute to outcomes rather than maintaining passive observation.
Benefits of Detached Perspective
A detached perspective enhances critical thinking by enabling objective analysis free from emotional bias, which fosters clearer decision-making and problem-solving. It supports mental resilience and stress reduction by promoting emotional distance from challenging situations, thus maintaining psychological well-being. Furthermore, adopting a detached viewpoint facilitates unbiased evaluation in professional and personal contexts, leading to more rational and effective outcomes.
Impacts on Research Outcomes
Participatory perspectives in research actively involve stakeholders, enhancing data relevance, contextual accuracy, and stakeholder trust, which often leads to more actionable and culturally sensitive outcomes. Detached perspectives maintain objectivity and reduce bias, but may miss nuanced insights and reduce the applicability of findings to real-world settings. The balance between these approaches significantly shapes the depth, validity, and impact of research results across social sciences and applied fields.
Choosing the Right Perspective for Your Study
Choosing the right perspective for your study depends on the research goals and the nature of the subject matter; a participatory perspective involves active engagement with participants, fostering deeper insights through collaboration and shared experiences. In contrast, a detached perspective offers objective observation, minimizing researcher influence to maintain neutrality and reduce bias in data collection. Selecting between these depends on whether the study prioritizes rich, contextual understanding or empirical objectivity for valid, generalizable results.
Participatory perspective Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com