Understanding the intuitive reason behind a concept helps bridge the gap between abstract theory and practical application, making complex ideas more accessible and easier to grasp. This clarity empowers you to apply knowledge effectively in real-world scenarios. Dive into the rest of the article to explore the intuitive explanations that simplify intricate topics.
Table of Comparison
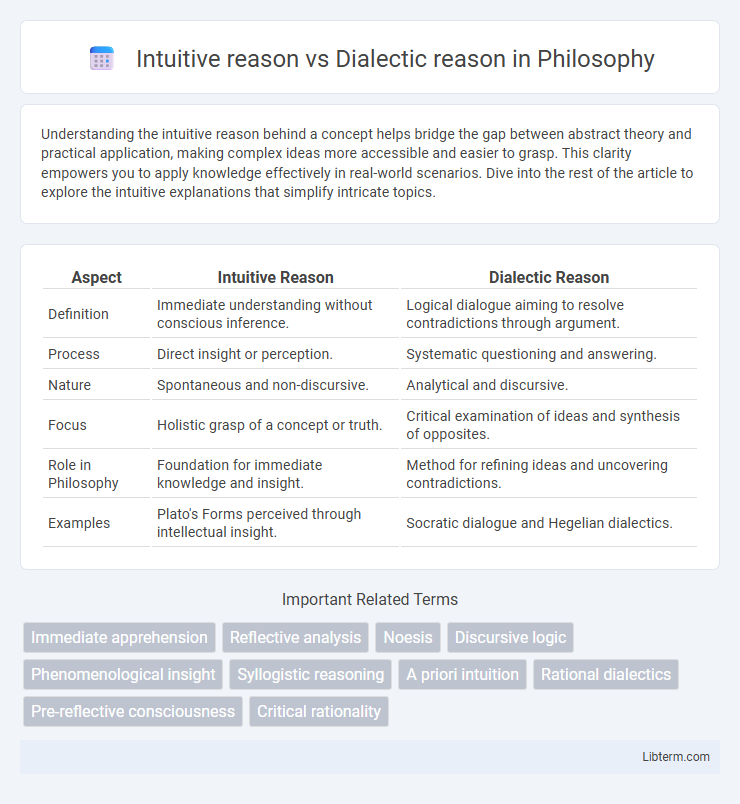
| Aspect | Intuitive Reason | Dialectic Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate understanding without conscious inference. | Logical dialogue aiming to resolve contradictions through argument. |
| Process | Direct insight or perception. | Systematic questioning and answering. |
| Nature | Spontaneous and non-discursive. | Analytical and discursive. |
| Focus | Holistic grasp of a concept or truth. | Critical examination of ideas and synthesis of opposites. |
| Role in Philosophy | Foundation for immediate knowledge and insight. | Method for refining ideas and uncovering contradictions. |
| Examples | Plato's Forms perceived through intellectual insight. | Socratic dialogue and Hegelian dialectics. |
Introduction to Intuitive and Dialectic Reason
Intuitive reason involves immediate understanding or insight without conscious analytical thought, relying on innate perception and experience. Dialectic reason, contrastingly, entails structured argumentation and logical examination of contradictory ideas to arrive at a synthesized conclusion. These reasoning modes underpin diverse cognitive processes, influencing decision-making and problem-solving in philosophical and practical contexts.
Defining Intuitive Reason: Core Characteristics
Intuitive reason operates through immediate understanding without conscious analytical processes, relying on innate or experiential knowledge to grasp concepts holistically. Core characteristics include rapid cognition, pattern recognition, and emotional resonance, enabling individuals to make judgments quickly and confidently. This form of reasoning contrasts with dialectic reason by emphasizing perception and insight over structured argumentation and logical deduction.
Understanding Dialectic Reason: Key Features
Dialectic reason involves structured dialogue and critical examination of opposing ideas to arrive at a coherent understanding or truth. Key features include the systematic evaluation of arguments, the synthesis of contradictory viewpoints, and the progression from thesis through antithesis to synthesis. This method fosters deeper insight by emphasizing logical coherence, reflective questioning, and the dynamic resolution of conflicts in thought.
Historical Perspectives on Reasoning Styles
Historical perspectives on reasoning styles distinguish intuitive reason as an immediate, non-conscious process prevalent in early human cognition, while dialectic reason emerged through classical Greek philosophy emphasizing structured dialogue and logical argumentation. Philosophers like Plato and Aristotle formalized dialectic reasoning as a method for uncovering truth through systematic questioning, contrasting with earlier, intuition-based decision-making rooted in experience and instinct. Over time, this dichotomy has influenced epistemology and cognitive science, highlighting a dynamic interplay between fast, intuitive judgments and slower, analytical thinking in human reasoning.
Cognitive Processes Behind Intuitive Reason
Intuitive reason relies on rapid, automatic cognitive processes that draw from implicit knowledge and past experiences, enabling quick judgments without conscious deliberation. This form of reasoning engages heuristic shortcuts and pattern recognition within the brain's neural networks, often involving the amygdala and the basal ganglia. Understanding these cognitive mechanisms highlights how intuition facilitates decision-making under uncertainty by bypassing slower, analytic thought pathways associated with dialectic reason.
Logical Structures in Dialectic Thinking
Dialectic reason relies on structured logical frameworks that emphasize thesis, antithesis, and synthesis to resolve contradictions and deepen understanding. This logical structure contrasts with intuitive reason, which is based on immediate, subconscious insights without formal analysis. Dialectic thinking systematically evaluates opposing ideas to generate coherent and reasoned conclusions through rational discourse.
Advantages of Intuitive Reasoning
Intuitive reasoning offers rapid decision-making by leveraging subconscious pattern recognition, enabling individuals to solve complex problems without extensive analytical processing. This form of reasoning excels in situations requiring creativity and innovation, as it taps into deep-seated knowledge and experience that may not be easily articulated. Intuition enhances adaptability and responsiveness, particularly in dynamic environments where immediate judgments are crucial.
Strengths of Dialectic Reasoning
Dialectic reasoning excels in systematically evaluating opposing viewpoints to arrive at a coherent and well-supported conclusion, enhancing critical thinking and intellectual rigor. Its strength lies in fostering deep analytical skills, enabling the identification of contradictions and synthesis of complex ideas in philosophical and practical contexts. This method promotes clarity and precision, which are essential for resolving disputes and advancing knowledge in academic and scientific disciplines.
Intuitive vs. Dialectic Reason in Decision Making
Intuitive reason in decision making relies on immediate perception and subconscious synthesis of experiences, enabling swift judgments without extensive analysis. Dialectic reason, contrastingly, involves structured argumentation and critical evaluation of opposing viewpoints to reach a logical conclusion. Balancing intuitive insight with dialectic scrutiny enhances the quality and reliability of complex decisions across various fields.
Integrating Intuitive and Dialectic Approaches
Integrating intuitive and dialectic approaches enhances decision-making by combining spontaneous insight with structured analysis, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of complex problems. Intuitive reason leverages subconscious pattern recognition and emotional intelligence, while dialectic reason relies on logical argumentation and critical evaluation of opposing viewpoints. Balancing these methods facilitates innovative solutions that are both creatively inspired and rigorously validated.
Intuitive reason Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com