Essentia is a cutting-edge open-source library designed for audio analysis and music information retrieval, providing state-of-the-art algorithms for sound processing. Its versatile framework allows You to extract features, analyze rhythms, and perform real-time audio classification with ease. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Essentia can transform your audio projects and creative endeavors.
Table of Comparison
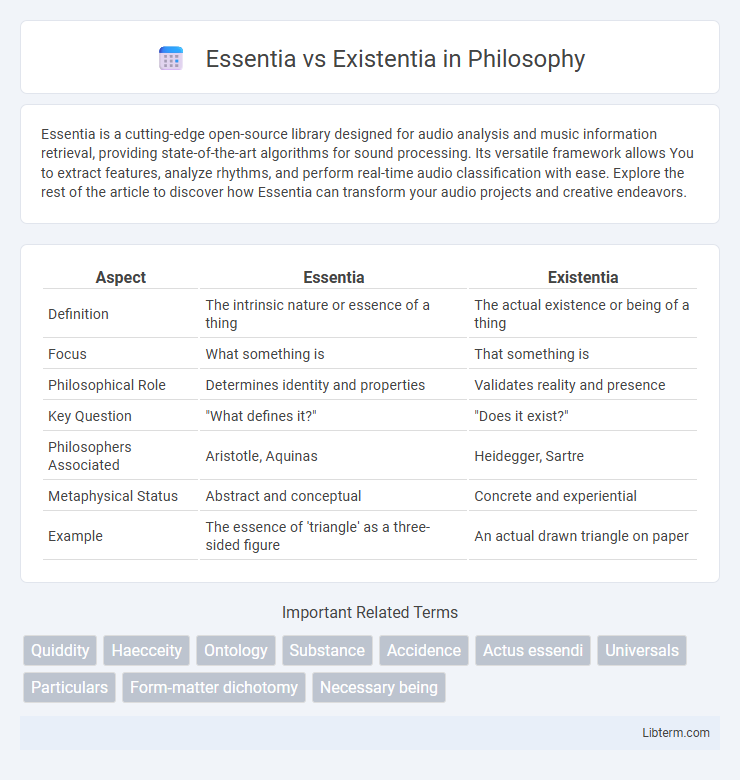
| Aspect | Essentia | Existentia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The intrinsic nature or essence of a thing | The actual existence or being of a thing |
| Focus | What something is | That something is |
| Philosophical Role | Determines identity and properties | Validates reality and presence |
| Key Question | "What defines it?" | "Does it exist?" |
| Philosophers Associated | Aristotle, Aquinas | Heidegger, Sartre |
| Metaphysical Status | Abstract and conceptual | Concrete and experiential |
| Example | The essence of 'triangle' as a three-sided figure | An actual drawn triangle on paper |
Introduction to Essentia and Existentia
Essentia and Existentia represent core metaphysical concepts originating from classical philosophy, particularly within the works of Aristotle and later scholastics. Essentia refers to the essence or intrinsic nature of a thing--what it is fundamentally--while Existentia denotes the actual existence or being of that thing in reality. Understanding the distinction between Essentia and Existentia is crucial for exploring debates on being, identity, and the relationship between potentiality and actuality in ontology.
Defining Essentia: The Essence of Being
Essentia defines the intrinsic nature or essence of a being, representing what fundamentally characterizes an entity beyond mere existence. It encompasses essential properties that make an object or concept what it truly is, independent of accidental attributes. This philosophical concept contrasts with existenti, emphasizing the core identity over the fact of being present in reality.
Understanding Existentia: Existence Explained
Existentia refers to the state of actual being or existence, emphasizing the concrete reality of entities as they manifest in the world. Unlike Essentia, which denotes the inherent essence or defining nature of a thing, Existentia focuses on the fact that something is present and perceivable in reality. Understanding Existentia involves analyzing the conditions and contexts that allow a being to exist, including its temporal and spatial presence.
Historical Roots: From Aristotle to Existentialism
Essentia and Existentia trace their historical roots to Aristotle's metaphysics, where essentia defines the inherent nature or "whatness" of a thing, while existentia concerns the fact of its being or actual existence. Medieval scholastic philosophers like Thomas Aquinas further developed this distinction, emphasizing essentia as the essence of God or creatures apart from their existence, anchoring metaphysical debates. Existentialism in the 20th century, notably through thinkers like Sartre and Heidegger, challenges and reinterprets this classical dichotomy by prioritizing existentia, placing human existence and individual experience over fixed essences.
Essentia vs Existentia: Key Philosophical Differences
Essentia refers to the inherent nature or essence of a thing, defining what it fundamentally is, whereas Existentia pertains to the actual existence or being of that thing in reality. Philosophers like Thomas Aquinas emphasized that Essentia and Existentia are distinct, with Essentia representing potentiality and Existentia actualizing that potential. This distinction underpins key metaphysical debates about the relationship between what things are and whether they actually are, influencing existential and essentialist viewpoints.
Influence on Metaphysics and Ontology
Essentia and Existentia play a critical role in shaping metaphysical and ontological debates by defining the nature of being and existence; Essentia refers to the essential characteristics that make an entity what it is, while Existentia concerns the actual occurrence or presence of that entity in reality. The distinction influences key philosophical discussions on whether essence precedes existence or vice versa, impacting theories of substance, identity, and reality. This dichotomy informs ontological frameworks by addressing how entities are categorized, understood, and distinguished within the metaphysical hierarchy.
Essentia and Existentia in Modern Thought
Essentia and Existentia in modern thought represent the foundational distinction between essence (the defining nature of a thing) and existence (the fact of being real). Contemporary philosophy engages with this dichotomy by exploring how Essentia informs identity and meaning, while Existentia emphasizes empirical reality and presence in the world. This interplay influences existentialism, phenomenology, and metaphysics, shaping discussions on human nature, being, and ontology.
Real-World Implications of the Debate
Essentia, referring to the essential nature or essence of a being, versus Existentia, focusing on existence itself, has profound real-world implications in philosophy, theology, and psychology. This debate influences ethical decision-making by questioning whether identity is rooted in inherent qualities or the act of existing and evolving in reality. Legal frameworks and mental health treatments often wrestle with these concepts, shaping how personal identity and human rights are understood and applied.
Notable Philosophers on Essentia and Existentia
Notable philosophers on essentia include Thomas Aquinas, who emphasized the distinction between essence (essentia) and existence (existentia) in his metaphysical framework, and Duns Scotus, who nuanced this differentiation with his concept of haecceity. Existentialist thinkers such as Jean-Paul Sartre challenged traditional notions by asserting that existence precedes essence, highlighting the primacy of existence in defining human identity. Martin Heidegger's analysis of Dasein further explores the interplay between essentia and existentia, focusing on being and existence as foundational philosophical themes.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Relevance of the Distinction
The distinction between essentia and existentia remains crucial in contemporary metaphysics and ontology, providing foundational insight into the nature of beings and their existence. Essentia, or essence, defines what a thing is, while existentia, or existence, confirms that it is actualized in reality. This differentiation continues to influence debates on the nature of being, existence, and identity in philosophical and theological contexts.
Essentia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com