Hermeticism is a philosophical tradition rooted in the writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, focusing on the interconnectedness of the cosmos, mind, and spirit. It encompasses principles of alchemy, astrology, and mysticism, aiming to unlock hidden knowledge and spiritual transformation. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of Hermeticism's ancient wisdom and relevance today.
Table of Comparison
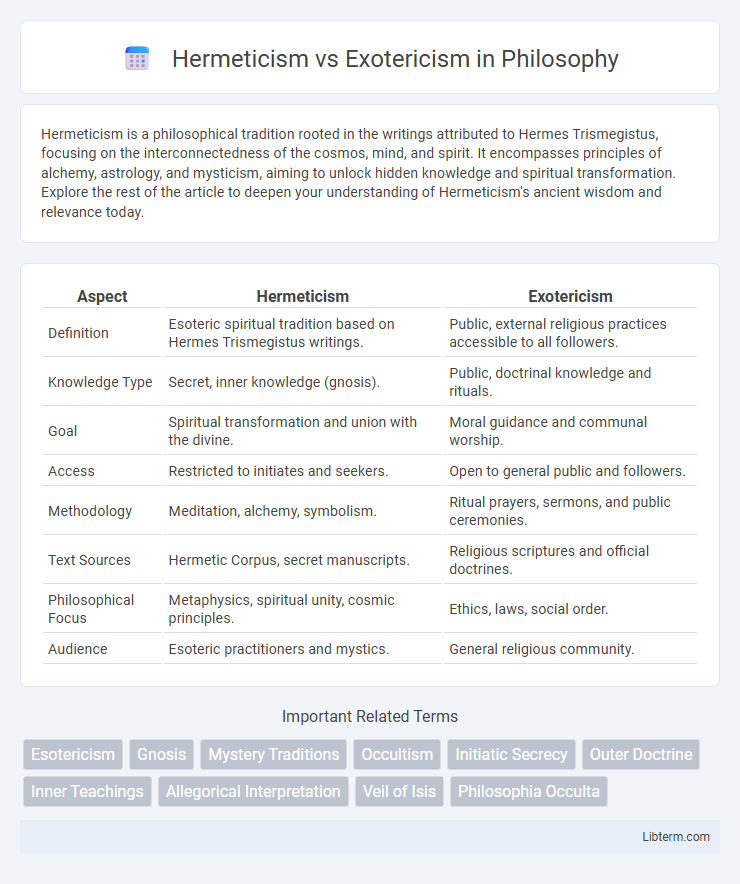
| Aspect | Hermeticism | Exotericism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Esoteric spiritual tradition based on Hermes Trismegistus writings. | Public, external religious practices accessible to all followers. |
| Knowledge Type | Secret, inner knowledge (gnosis). | Public, doctrinal knowledge and rituals. |
| Goal | Spiritual transformation and union with the divine. | Moral guidance and communal worship. |
| Access | Restricted to initiates and seekers. | Open to general public and followers. |
| Methodology | Meditation, alchemy, symbolism. | Ritual prayers, sermons, and public ceremonies. |
| Text Sources | Hermetic Corpus, secret manuscripts. | Religious scriptures and official doctrines. |
| Philosophical Focus | Metaphysics, spiritual unity, cosmic principles. | Ethics, laws, social order. |
| Audience | Esoteric practitioners and mystics. | General religious community. |
Understanding Hermeticism: Origins and Core Principles
Hermeticism originates from ancient texts attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, emphasizing esoteric knowledge and the unity of the divine, cosmos, and human spirit. Core principles include the belief in "As above, so below," highlighting the interconnectedness of all realms, and the pursuit of spiritual transformation through hidden wisdom. Unlike Exotericism, which promotes outward religious practices accessible to the general public, Hermeticism centers on inner enlightenment and secret teachings reserved for initiates.
Defining Exotericism: Meaning and Historical Context
Exotericism refers to the outward, public teachings and practices of a religious or philosophical tradition accessible to the general population, contrasting with the hidden, inner knowledge characteristic of Hermeticism. Historically, exoteric doctrines emerged as formalized belief systems intended for communal worship and societal order, often codified in scriptures and rituals visible to all adherents. This public dimension facilitated the transmission of moral codes and cosmological views, anchoring collective identity while preserving esoteric wisdom for select initiates.
Key Philosophical Differences
Hermeticism centers on esoteric knowledge, emphasizing personal spiritual transformation and the pursuit of hidden wisdom through mystical practices and allegorical texts like the Corpus Hermeticum. Exotericism prioritizes accessible, public teachings designed for collective understanding, focusing on external rituals, moral codes, and straightforward doctrinal beliefs. Hermeticism advocates for inner enlightenment and the microcosm-macrocosm analogy, whereas exotericism emphasizes communal religious experience and adherence to established societal norms.
Esoteric vs. Exoteric Knowledge: Accessibility and Depth
Esoteric knowledge in Hermeticism is hidden, accessible only to initiates who undergo rigorous study and spiritual discipline, emphasizing profound metaphysical truths beyond ordinary perception. Exoteric knowledge, in contrast, is openly available to the general public, presented in simplified forms to guide ethical behavior and basic religious practices without revealing deeper mystical insights. This distinction highlights Hermeticism's dual approach, where exoteric teachings provide a foundation while esoteric doctrines offer transformative wisdom reserved for advanced seekers.
Symbolism and Ritual: Hermetic vs. Exoteric Practices
Hermeticism employs symbolism and ritual as profound tools for personal transformation, using esoteric symbols like the caduceus and the Hermetic principles to unlock hidden spiritual knowledge. Exoteric practices focus on accessible, communal rituals with widely recognized symbols, such as those found in mainstream religions, to foster collective worship and moral instruction. Hermetic rituals emphasize initiation and inner alchemy, while exoteric ceremonies prioritize external expressions of faith and tradition.
Inner Transformation in Hermeticism
Hermeticism emphasizes inner transformation through personal gnosis and alchemical processes aimed at spiritual enlightenment and self-realization. This esoteric tradition prioritizes the direct experience of divine truths beyond mere external rituals or teachings typical of exotericism. Inner alchemy in Hermeticism facilitates the transmutation of the soul, fostering profound metaphysical knowledge and unity with the divine essence.
Communal Belief in Exotericism
Exotericism emphasizes communal belief systems that promote shared rituals, moral codes, and public worship, fostering social cohesion and collective identity. Hermeticism, conversely, prioritizes individual spiritual knowledge and personal enlightenment rooted in esoteric teachings often accessible only to initiates. The communal aspect in exoteric traditions serves to unify diverse populations under a common framework, enhancing societal stability and cultural continuity.
Influence on Western Thought and Religion
Hermeticism, rooted in ancient Egyptian and Greco-Roman traditions, profoundly influenced Western esoteric and mystical thought, shaping Renaissance humanism, alchemy, and early modern science with its emphasis on hidden knowledge and spiritual transformation. Exotericism, characterized by accessible, orthodox religious teachings, structured mainstream Western religions like Christianity and Judaism, promoting communal beliefs and moral codes. The interplay between Hermeticism's secret wisdom and Exotericism's public doctrines has continuously impacted Western philosophy, theology, and cultural development.
Modern Interpretations and Relevance
Modern interpretations of Hermeticism emphasize esoteric knowledge, spiritual alchemy, and the pursuit of inner transformation, often influencing New Age philosophies and occult practices. Exotericism, by contrast, remains focused on accessible teachings and communal religious practices, appealing to broader audiences through institutionalized doctrines and rituals. Contemporary relevance lies in Hermeticism's role in personal mystical exploration, while Exotericism sustains collective identity and structured belief systems.
Choosing Your Path: Personal Spiritual Implications
Hermeticism emphasizes inner spiritual transformation through esoteric knowledge and mystical practices, encouraging individuals to explore hidden truths and develop personal wisdom. Exotericism focuses on outward religious practices and communal beliefs, providing structured teachings that are accessible and shared among the wider community. Choosing between Hermeticism and Exotericism affects one's spiritual journey by determining whether the emphasis lies on autonomous mystical exploration or collective adherence to established doctrines.
Hermeticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com