Objective value represents the optimal result achieved from an optimization problem, reflecting the best solution according to the defined criteria. Understanding how to interpret and apply the objective value can significantly enhance your decision-making process in various fields such as economics, engineering, and data science. Explore the rest of this article to learn how objective values influence outcomes and strategies in complex problem-solving.
Table of Comparison
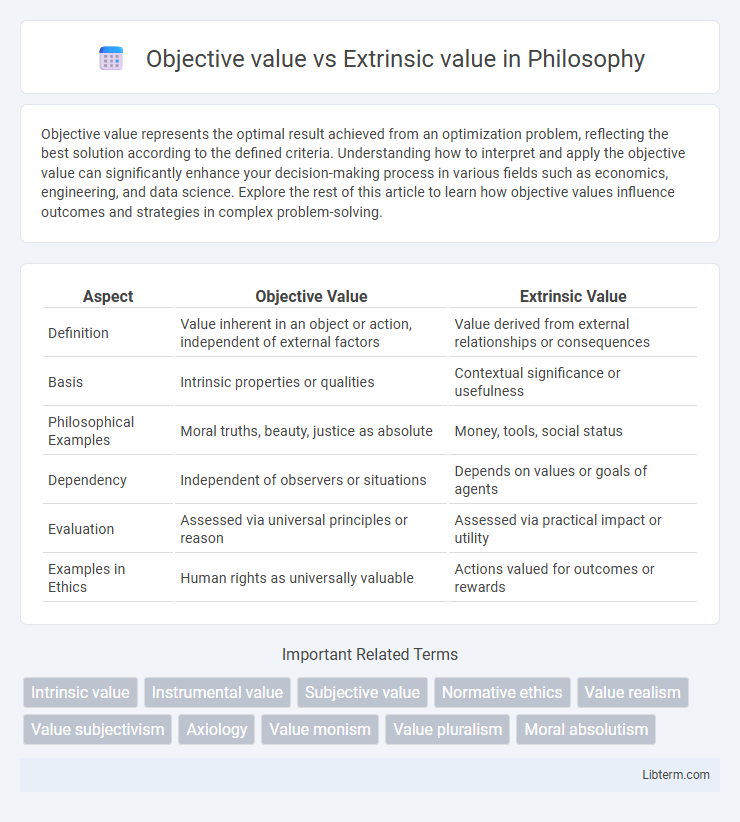
| Aspect | Objective Value | Extrinsic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Value inherent in an object or action, independent of external factors | Value derived from external relationships or consequences |
| Basis | Intrinsic properties or qualities | Contextual significance or usefulness |
| Philosophical Examples | Moral truths, beauty, justice as absolute | Money, tools, social status |
| Dependency | Independent of observers or situations | Depends on values or goals of agents |
| Evaluation | Assessed via universal principles or reason | Assessed via practical impact or utility |
| Examples in Ethics | Human rights as universally valuable | Actions valued for outcomes or rewards |
Introduction to Value Theory
Objective value refers to the intrinsic worth of an entity or action based on universal standards, independent of individual preferences or feelings. Extrinsic value, often called instrumental value, is determined by the usefulness or utility an entity provides as a means to achieve an end. Value theory explores these distinctions to understand how different types of value influence ethical decision-making and human motivation.
Defining Objective Value
Objective value refers to the intrinsic worth of an object or action, determined by universal standards independent of individual preferences or emotions. It emphasizes measurable, quantifiable criteria such as functionality, utility, or ethical principles that remain constant across different contexts. In contrast, extrinsic value depends on external factors, including subjective assessments and situational influences that affect perceived importance or desirability.
Understanding Extrinsic Value
Extrinsic value represents the portion of an option's price that exceeds its intrinsic value, reflecting factors such as time until expiration and market volatility. It is crucial for traders to understand extrinsic value because it quantifies the premium investors pay for the potential of future profitability beyond the current intrinsic worth. Analyzing extrinsic value helps in assessing the time decay impact and the likelihood of an option finishing in the money.
Key Differences Between Objective and Extrinsic Value
Objective value refers to the inherent worth of an object or action based on universal principles or facts, independent of individual feelings. Extrinsic value, on the other hand, depends on external factors and the utility or benefits that an object or action provides to a person or group. The key differences lie in objectivity versus subjectivity, with objective value being intrinsic and universally valid, while extrinsic value varies according to context and personal or societal preferences.
Philosophical Foundations of Value
Objective value refers to the belief that certain values exist independently of human feelings or opinions, grounded in metaphysical or moral realism as studied in classical philosophy. Extrinsic value, in contrast, is derived from the usefulness or consequences of an object or action, emphasizing its relational or instrumental significance rather than inherent worth. Philosophical foundations distinguish these concepts by debating whether value is an intrinsic property of things or merely contingent upon external factors and subjective evaluations.
Real-world Examples of Objective Value
Objective value refers to the inherent worth of an asset or item based on measurable factors such as cost, utility, or material composition, distinct from subjective perceptions. For example, gold has objective value due to its scarcity, durability, and industrial uses, regardless of individual preferences. In real estate, the objective value of a property is determined by quantifiable aspects like location, square footage, and comparable sales data.
Real-world Examples of Extrinsic Value
Extrinsic value reflects the worth that an asset derives from external factors and market perceptions rather than its inherent qualities, such as a stock option's premium influenced by time until expiration or market volatility. Real-world examples include brand-name products like luxury watches, whose value exceeds the materials due to reputation, and currency, where face value differs from collector interest or exchange demand. Unlike objective value based on tangible attributes, extrinsic value hinges on external demand, scarcity, and investor sentiment.
Implications in Ethics and Decision Making
Objective value, grounded in universal moral principles, provides a consistent framework for evaluating actions irrespective of personal preferences, ensuring ethical decisions are made based on inherent rightness or wrongness. Extrinsic value depends on external outcomes or consequences, influencing decision making by prioritizing practical benefits and situational advantages. Understanding the distinction between these values is crucial in ethics, as it shapes whether decisions emphasize absolute moral duties or flexible, context-dependent considerations.
Debates and Critiques in Value Theory
Debates in value theory contrast objective value, which asserts intrinsic worth independent of individual beliefs, with extrinsic value, determined by external factors or usefulness. Critics argue objective value lacks empirical verification, making it susceptible to subjective interpretation, while extrinsic value is challenged for reducing worth to mere instrumental or relational criteria. These critiques fuel ongoing discourse on value objectivity, grounding ethical, aesthetic, and economic evaluations in philosophical inquiry.
Conclusion: Objective vs Extrinsic Value
Objective value refers to intrinsic worth based on inherent properties or universal principles, while extrinsic value depends on external factors and subjective preferences. In evaluating decisions, objective value provides a stable foundation grounded in measurable criteria, whereas extrinsic value reflects context-dependent utility and personal significance. Balancing these distinctions helps clarify ethical judgments, economic assessments, and philosophical interpretations of value.
Objective value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com