Individualism emphasizes personal independence and the importance of self-expression in shaping one's identity and choices. This philosophy champions your unique perspective, encouraging autonomy in decision-making and valuing personal responsibility. Explore the rest of the article to understand how individualism impacts societal structures and your everyday life.
Table of Comparison
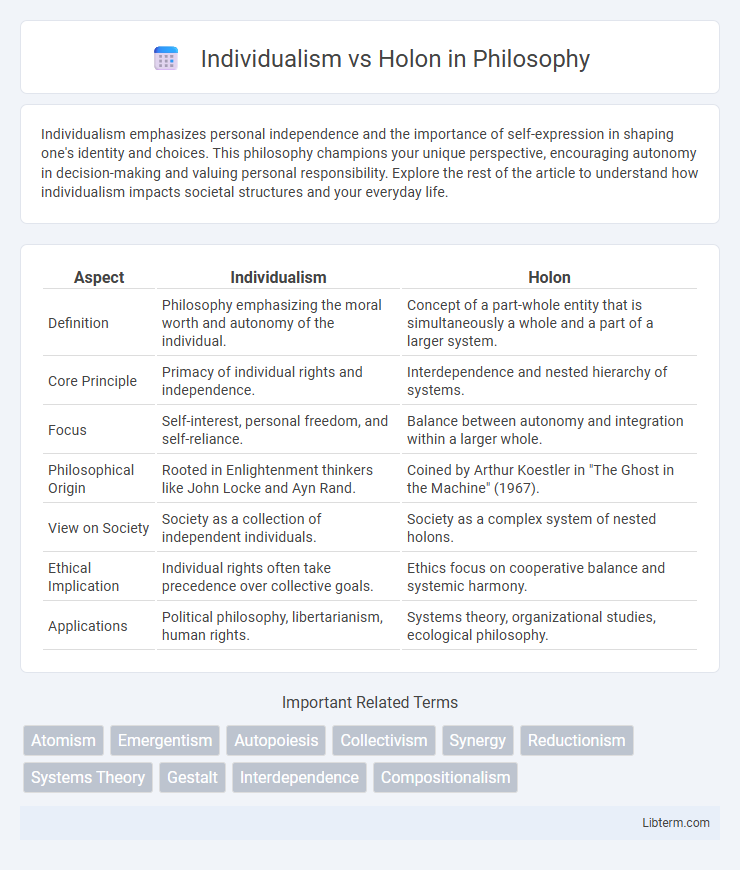
| Aspect | Individualism | Holon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophy emphasizing the moral worth and autonomy of the individual. | Concept of a part-whole entity that is simultaneously a whole and a part of a larger system. |
| Core Principle | Primacy of individual rights and independence. | Interdependence and nested hierarchy of systems. |
| Focus | Self-interest, personal freedom, and self-reliance. | Balance between autonomy and integration within a larger whole. |
| Philosophical Origin | Rooted in Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke and Ayn Rand. | Coined by Arthur Koestler in "The Ghost in the Machine" (1967). |
| View on Society | Society as a collection of independent individuals. | Society as a complex system of nested holons. |
| Ethical Implication | Individual rights often take precedence over collective goals. | Ethics focus on cooperative balance and systemic harmony. |
| Applications | Political philosophy, libertarianism, human rights. | Systems theory, organizational studies, ecological philosophy. |
Understanding Individualism: Core Principles
Individualism centers on the belief that each person is a distinct entity with inherent rights, autonomy, and self-reliance, emphasizing personal freedom and individual choice. It advocates for the priority of individual goals and values over collective or group interests, promoting independent thought and responsibility. Core principles include self-ownership, personal accountability, and the pursuit of unique identity, shaping societal structures that support individual liberties and diversity.
Defining Holon: Beyond the Individual
Holon represents a concept where entities function simultaneously as wholes and parts within larger systems, emphasizing interconnectedness beyond individual existence. Unlike strict individualism that highlights autonomy and self-sufficiency, holons embody integration and interdependence across multiple levels of organization. This framework enhances understanding of complex systems by illustrating how individual units contribute to and derive meaning from collective structures.
Historical Roots of Individualism and Holon
The historical roots of individualism trace back to the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, emphasizing personal autonomy, self-expression, and the intrinsic value of the individual in Western philosophy. In contrast, the concept of the holon, introduced by Arthur Koestler in the 20th century, originates from systems theory and Eastern holistic traditions, highlighting entities as both wholes and parts within larger systems. These foundational differences reveal individualism's focus on independent agency, whereas holons emphasize interdependence and nested hierarchies in social and natural structures.
Key Differences: Individual Identity vs Collective Integration
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, prioritizing unique identity and independent decision-making. In contrast, the holon concept integrates individuals as parts of larger, self-regulating wholes, where collective needs and interdependence shape identity. Key differences lie in balancing self-interest against system harmony, with individualism valuing distinctiveness and holon emphasizing seamless integration within broader systems.
The Role of Individualism in Modern Society
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and self-expression, driving innovation and cultural diversity in modern society. It fosters accountability and freedom, allowing individuals to pursue unique goals and contribute distinct perspectives to social development. This focus on individual rights balances collective needs, shaping democratic principles and economic systems in contemporary life.
Holon in Nature, Culture, and Systems
Holons represent entities that are simultaneously wholes and parts within nature, culture, and systems, embodying interconnectedness and hierarchy. In natural ecosystems, holons function as organisms made of cells or communities of species maintaining balance and resilience. Culturally, holon theory explains social structures where individuals act as autonomous units within larger social systems, promoting cooperation and systemic harmony.
Benefits of Embracing Individualism
Embracing individualism fosters creativity, innovation, and personal accountability by encouraging unique perspectives and self-expression. It empowers individuals to take ownership of their actions and decisions, driving motivation and productivity in both personal and professional contexts. This approach also cultivates diverse problem-solving skills, enhancing adaptability in dynamic environments.
Advantages of the Holonic Perspective
The holonic perspective enhances system efficiency by integrating individual autonomy with collective coordination, allowing components to operate independently yet contribute to the whole. This approach improves scalability and adaptability in complex environments, as holons dynamically adjust roles based on contextual demands. Such synergy between individual units and the larger system leads to robust decision-making and resilience against disruptions.
Synergy or Conflict: Can Individualism and Holon Coexist?
Individualism emphasizes personal autonomy and distinct identity, while holon theory highlights entities functioning as both wholes and parts within larger systems. Synergy emerges when individual contributions within a holon are recognized and integrated, fostering collective innovation and adaptability. Conflict arises when excessive individualism undermines the cohesion or interdependence necessary for holon stability and collaborative success.
Toward a Balanced Future: Integrating Both Approaches
Balancing individualism and holon theory fosters a future where personal autonomy coexists with collective harmony, promoting sustainable decision-making and innovation. Emphasizing individual contributions within interconnected systems enhances adaptability and resilience in social, economic, and environmental spheres. Integrating these approaches cultivates a holistic framework that supports both unique identities and collaborative progress.
Individualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com