Dualism is the philosophical concept that reality consists of two fundamental, distinct substances: mind and body. This view explores how mental phenomena, such as consciousness and thoughts, interact with the physical world, posing challenges for understanding human experience and identity. Discover how dualism shapes debates in philosophy, psychology, and neuroscience throughout the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
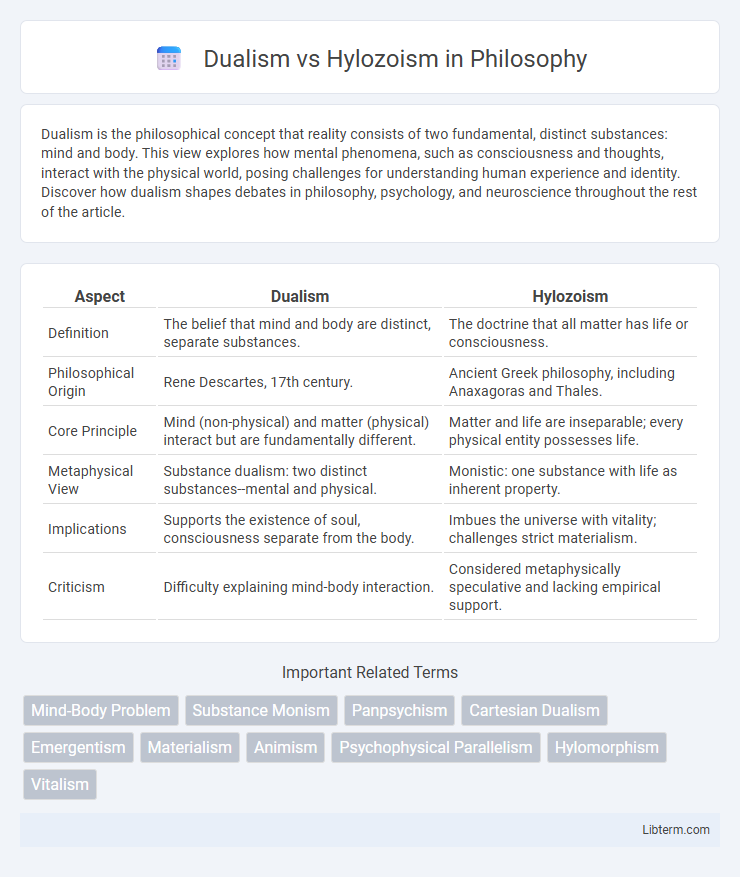
| Aspect | Dualism | Hylozoism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The belief that mind and body are distinct, separate substances. | The doctrine that all matter has life or consciousness. |
| Philosophical Origin | Rene Descartes, 17th century. | Ancient Greek philosophy, including Anaxagoras and Thales. |
| Core Principle | Mind (non-physical) and matter (physical) interact but are fundamentally different. | Matter and life are inseparable; every physical entity possesses life. |
| Metaphysical View | Substance dualism: two distinct substances--mental and physical. | Monistic: one substance with life as inherent property. |
| Implications | Supports the existence of soul, consciousness separate from the body. | Imbues the universe with vitality; challenges strict materialism. |
| Criticism | Difficulty explaining mind-body interaction. | Considered metaphysically speculative and lacking empirical support. |
Introduction to Dualism and Hylozoism
Dualism posits that reality consists of two fundamentally different substances, typically mind and body, emphasizing a clear division between mental and physical realms. Hylozoism, in contrast, asserts that all matter is alive or possessed of life, rejecting strict separations between inanimate and animate entities. These philosophical perspectives offer distinct approaches to understanding the nature of existence and the relationship between consciousness and the physical world.
Historical Origins of Dualism
The historical origins of dualism trace back to ancient Greek philosophy, notably in the works of Plato, who posited a clear distinction between the immaterial soul and the material body. This philosophical framework was further developed by Rene Descartes in the 17th century, emphasizing a fundamental separation between mind and matter. Dualism contrasts sharply with hylozoism, which asserts that all matter possesses life or spirit, an idea rooted in pre-Socratic philosophy and reflecting a holistic view of the universe.
The Foundations of Hylozoism
Hylozoism is founded on the principle that all matter possesses life or vitality, rejecting the strict mind-matter division central to dualism. This philosophy posits an intrinsic unity where physical substance and life are inseparable, contrasting with dualism's assertion of two distinct substances: mind and body. Hylozoism's emphasis on the life inherent in all material entities provides a holistic framework that challenges the Cartesian separation of consciousness from physical existence.
Key Differences Between Dualism and Hylozoism
Dualism posits a fundamental distinction between mind and matter, asserting two separate substances that interact or coexist, whereas Hylozoism claims that all matter is inherently alive, rejecting the separation of the material and spiritual. Key differences include Dualism's emphasis on mental and physical substance duality, contrasted with Hylozoism's perspective that life permeates every element of the physical world. This distinction impacts philosophical approaches to consciousness, with Dualism treating mind as a distinct entity and Hylozoism viewing life and matter as inseparable.
Dualism in Philosophical Thought
Dualism in philosophical thought asserts the existence of two fundamentally distinct substances: mind and matter, with the mind often characterized as immaterial and the body as material. This concept, prominent in the works of Rene Descartes, emphasizes that mental phenomena cannot be fully explained by physical processes alone, highlighting a clear ontological separation. Dualism influences ongoing debates in metaphysics and philosophy of mind regarding consciousness, identity, and the nature of reality.
Hylozoism and the Living Matter Perspective
Hylozoism posits that all matter possesses intrinsic life or consciousness, rejecting the strict separation between mind and body found in Dualism. This philosophy emphasizes that what appears as inert matter is inherently living, challenging mechanistic views by attributing vitality to physical substance. The living matter perspective in Hylozoism fosters an understanding of the universe as an interconnected whole, where life is a fundamental property of all material entities.
Dualism’s Influence on Religion and Science
Dualism, emphasizing the separation of mind and body, profoundly shaped religious doctrines by reinforcing beliefs in an immortal soul distinct from the physical world, influencing major faiths such as Christianity and Islam. This philosophical framework also impacted scientific inquiry, promoting a dualistic approach that separates mental phenomena from physical processes, which historically challenged the integration of consciousness into biological and neurological studies. The enduring legacy of Dualism continues to shape debates on the nature of consciousness, the mind-body problem, and the relationship between science and spirituality.
Hylozoism’s Impact on Modern Philosophy
Hylozoism, the philosophical doctrine that matter is intrinsically alive, has significantly influenced modern philosophy by challenging the strict mind-body dualism central to Cartesian thought. This perspective fosters an integrated understanding of life and consciousness, emphasizing the continuity between the material and the living, which has impacted fields like phenomenology and process philosophy. Modern thinkers explore hylozoistic ideas to reconsider the relationship between nature and mind, advancing holistic approaches to metaphysics and epistemology.
Critiques and Debates: Dualism vs Hylozoism
Critiques of dualism often target its rigid separation of mind and matter, arguing this division lacks empirical support and fails to explain their interaction effectively. Hylozoism, which posits that all matter possesses life or consciousness, faces skepticism for conflating physical properties with sentience, challenging conventional scientific understanding. The debate hinges on dualism's metaphysical clarity versus hylozoism's immanent life concept, highlighting tensions between traditional substance dualism and panpsychist or animistic perspectives in contemporary philosophy of mind.
Contemporary Relevance and Future Directions
Dualism, positing a strict separation between mind and matter, remains influential in cognitive science and philosophy of mind debates, particularly concerning consciousness and artificial intelligence. Hylozoism, which attributes life or sentience to all matter, informs emerging fields like panpsychism and ecological philosophy, shaping environmental ethics and holistic scientific approaches. Future directions suggest integrating dualistic frameworks with hylozoic perspectives to better understand consciousness as both a distinct and pervasive phenomenon in complex systems.
Dualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com