The non-contradiction principle asserts that contradictory statements cannot both be true in the same context at the same time, forming a fundamental law of classical logic. This principle helps you navigate logical reasoning by ensuring consistency and avoiding paradoxes in arguments. Explore the rest of the article to understand how applying the non-contradiction principle strengthens your critical thinking skills.
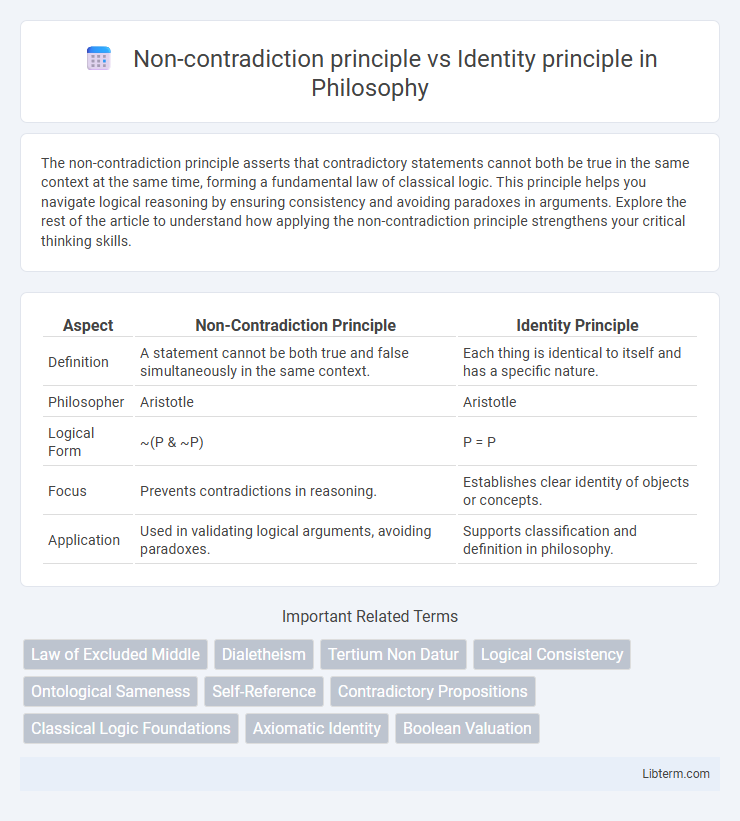
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Non-Contradiction Principle | Identity Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A statement cannot be both true and false simultaneously in the same context. | Each thing is identical to itself and has a specific nature. |
| Philosopher | Aristotle | Aristotle |
| Logical Form | ~(P & ~P) | P = P |
| Focus | Prevents contradictions in reasoning. | Establishes clear identity of objects or concepts. |
| Application | Used in validating logical arguments, avoiding paradoxes. | Supports classification and definition in philosophy. |
Introduction to Fundamental Logical Principles
The principle of non-contradiction asserts that a statement cannot be both true and false simultaneously in the same context, ensuring consistency in logical reasoning. In contrast, the principle of identity maintains that each entity is identical to itself, affirming the stability of concepts and terms throughout logical discourse. These fundamental logical principles underpin classical logic by establishing coherence and clarity in argumentation and truth evaluation.
Defining the Principle of Non-Contradiction
The Principle of Non-Contradiction states that a proposition cannot be both true and false simultaneously in the same context, serving as a fundamental rule in classical logic. It ensures consistency by preventing contradictory statements from coexisting, distinguishing it from the Principle of Identity, which asserts that each entity is identical to itself. Understanding the Principle of Non-Contradiction is crucial for logical reasoning, as it underpins valid argumentation and the coherence of truth values in formal systems.
Understanding the Principle of Identity
The Principle of Identity asserts that each entity is identical to itself, meaning an object always remains what it is without changing its nature. This foundational concept in classical logic ensures consistency by affirming that an element cannot simultaneously be something else, unlike the Principle of Non-Contradiction which prohibits a statement and its negation from both being true at the same time. Understanding the Principle of Identity is crucial for logical reasoning, as it establishes the baseline for recognizing and defining objects or propositions clearly and consistently.
Historical Roots of Both Principles
The principle of non-contradiction, articulated by Aristotle in his work "Metaphysics," asserts that contradictory statements cannot both be true simultaneously, establishing a fundamental law of classical logic. The principle of identity, also rooted in Aristotelian philosophy, states that each thing is identical to itself, forming the basis for defining entities and their properties. Both principles emerged from ancient Greek philosophical inquiries into the nature of truth and reality, laying the groundwork for Western metaphysics and formal logic.
Core Differences Between Non-Contradiction and Identity
The Non-Contradiction Principle asserts that contradictory statements cannot both be true in the same sense at the same time, emphasizing logical consistency by prohibiting a proposition and its negation from coexisting. The Identity Principle establishes that each entity is identical to itself and distinct from others, reinforcing the consistency of naming and classification in logic and philosophy. The core difference lies in Non-Contradiction addressing the impossibility of simultaneous opposites, while Identity centers on the inherent sameness and uniqueness of an object or concept.
Role in Classical Logic
The Non-contradiction principle ensures that a statement and its negation cannot both be true simultaneously, forming the backbone of consistency in classical logic. The Identity principle asserts that each entity is identical to itself, providing a foundation for clear reference and meaning in logical expressions. Together, these principles maintain coherence and clarity, enabling reliable deductive reasoning within classical logic frameworks.
Applications in Philosophy and Science
The principle of non-contradiction, asserting that contradictory statements cannot both be true simultaneously, underpins logical consistency in philosophical argumentation and scientific reasoning, ensuring coherent theories and models. The principle of identity, positing that each entity is identical to itself, supports categorical classification and the stability of concepts in both metaphysics and empirical sciences. Together, these principles enable rigorous analysis and validation of hypotheses across disciplines by maintaining clarity in definitions and preventing logical fallacies.
Common Misconceptions About Each Principle
The Non-contradiction principle, often misunderstood as forbidding any form of change or nuance, actually asserts that contradictory statements cannot both be true in the same context at the same time. The Identity principle is commonly misconceived as implying static or unchanging essence, whereas it simply states that each thing is identical to itself, promoting clarity in logical arguments. Confusion arises when these principles are conflated, leading to errors in reasoning about change, identity, and contradiction in philosophy and logic.
Interdependence and Logical Structure
The non-contradiction principle asserts that contradictory statements cannot both be true simultaneously, establishing a foundational boundary in logical systems. The identity principle maintains that each entity is identical to itself, reinforcing consistency and clarity within those systems. These principles are interdependent, as the identity principle relies on non-contradiction to prevent self-contradictory identity claims, collectively shaping a coherent logical structure.
Conclusion: Significance in Rational Thought
The Principle of Non-Contradiction ensures that contradictory statements cannot both be true simultaneously, providing a foundation for consistent reasoning. The Principle of Identity asserts that each entity is identical to itself, establishing clear reference points in logical discourse. Together, these principles underpin the coherence and reliability of rational thought, enabling clear distinctions and valid conclusions in philosophical and scientific inquiry.
Non-contradiction principle Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com