A descriptive critique provides a detailed and vivid depiction of a subject, focusing on its features, qualities, and overall impression. It aims to capture the essence and nuances of the topic, enabling You to form a clear mental image or understanding. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a descriptive critique enhances appreciation and insight.
Table of Comparison
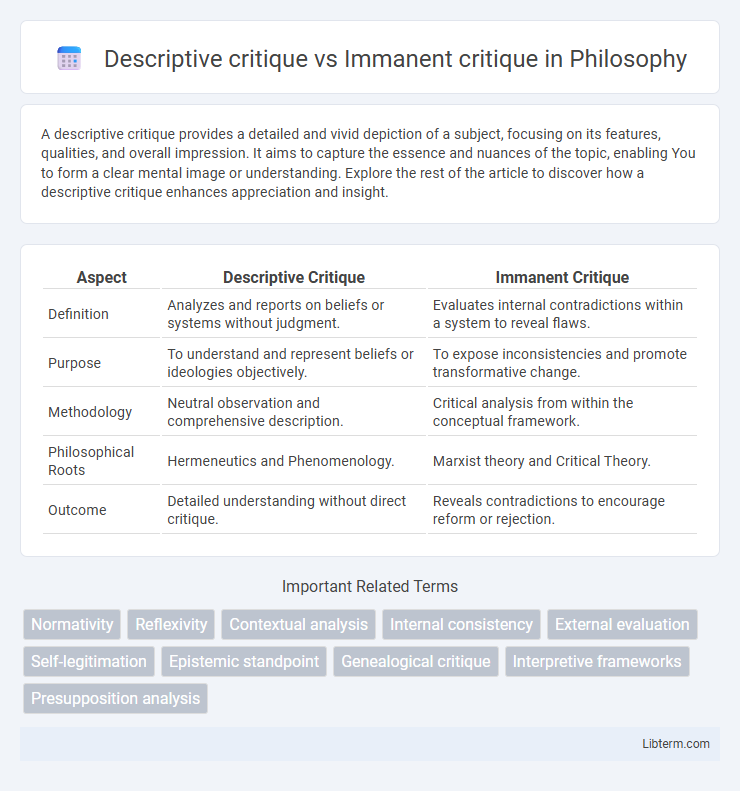
| Aspect | Descriptive Critique | Immanent Critique |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes and reports on beliefs or systems without judgment. | Evaluates internal contradictions within a system to reveal flaws. |
| Purpose | To understand and represent beliefs or ideologies objectively. | To expose inconsistencies and promote transformative change. |
| Methodology | Neutral observation and comprehensive description. | Critical analysis from within the conceptual framework. |
| Philosophical Roots | Hermeneutics and Phenomenology. | Marxist theory and Critical Theory. |
| Outcome | Detailed understanding without direct critique. | Reveals contradictions to encourage reform or rejection. |
Introduction to Critical Methodologies
Descriptive critique involves analyzing a text or concept by outlining its features and intentions without imposing external judgment, enabling a clear understanding of its internal logic. Immanent critique examines contradictions and tensions within the work itself, uncovering inconsistencies through the work's own standards and principles. These methodologies are central to critical theory, fostering nuanced evaluation by balancing objective description with internal analysis.
Defining Descriptive Critique
Descriptive critique involves objectively analyzing a work or concept by detailing its characteristics and components without imposing external judgments, aiming to understand its structure and meaning as presented. It contrasts with immanent critique, which evaluates a subject based on its internal logic, consistency, and adherence to its own principles. Defining descriptive critique centers on thorough, unbiased representation, emphasizing comprehensive observation over evaluative comparison.
Understanding Immanent Critique
Immanent critique, rooted in critical theory, involves evaluating a text or social system by exposing contradictions within its own conceptual framework, aiming to reveal internal inconsistencies that hinder its claims or practices. Unlike descriptive critique, which objectively summarizes or interprets content, immanent critique assesses the coherence of ideas based on their self-defined standards, fostering transformative reflection. This method deepens understanding by highlighting tensions that prompt revision or emancipation from prevailing ideologies.
Historical Origins and Theoretical Foundations
Descriptive critique originates from empirical traditions emphasizing objective observation and detailed documentation of social phenomena, grounded in positivist epistemology. Immanent critique, rooted in Hegelian dialectics and critical theory, analyzes contradictions within a system's own principles to reveal internal inconsistencies and potential for transformation. Historical origins of descriptive critique trace back to early sociological methods by Weber, while immanent critique is fundamentally linked to Marxist theory and the Frankfurt School's critique of ideology and culture.
Methodological Approaches: Descriptive vs Immanent
Descriptive critique employs an external, observational methodology to analyze social phenomena by systematically cataloging and interpreting data without engaging in the inherent contradictions of the subject. Immanent critique, in contrast, uses an internal methodological approach that reveals discrepancies and tensions within a system by examining its foundational principles and norms from within. While descriptive methods prioritize objective description and categorization, immanent approaches emphasize dialectical analysis to uncover latent inconsistencies and possibilities for transformation.
Key Objectives and Philosophical Aims
Descriptive critique aims to objectively outline and analyze existing ideas or systems without imposing external judgments, emphasizing clear understanding and faithful representation of the subject. Immanent critique focuses on revealing contradictions and internal tensions within a concept or ideology to drive transformative change, highlighting the dialectical processes inherent in the subject itself. Philosophically, descriptive critique seeks knowledge through detailed exposition, while immanent critique strives for progress by exposing latent inconsistencies and fostering self-reflection.
Strengths and Limitations of Descriptive Critique
Descriptive critique excels at providing detailed, context-rich analysis by closely examining texts or phenomena without imposing external judgment, allowing for a nuanced understanding of the subject's inherent characteristics. Its strength lies in capturing the authentic meaning and complexity embedded within the material, fostering empathy and deep interpretation. However, descriptive critique is limited by its tendency to avoid evaluative conclusions, which can restrict critical engagement with underlying problems or contradictions that immanent critique actively seeks to expose.
Advantages and Challenges of Immanent Critique
Immanent critique offers the advantage of analyzing a social or philosophical system from within its own principles and contradictions, enabling a deeper understanding of internal inconsistencies and potential for transformation. It encourages self-reflection and reform by highlighting gaps between ideals and realities, fostering progressive change grounded in the system's inherent logic. Challenges include the risk of bias due to insider perspective, difficulty in maintaining critical objectivity, and the potential to overlook external influences that may also shape the system's dynamics.
Practical Applications in Contemporary Analysis
Descriptive critique offers practical applications in contemporary analysis by systematically documenting and evaluating social phenomena without imposing normative judgments, facilitating objective data interpretation in fields like sociology and anthropology. Immanent critique, by contrast, is employed to reveal contradictions within a system's own values and principles, driving transformative change in political theory and cultural studies through internal consistency assessment. Both methods enhance analytical rigor by balancing empirical observation with normative reflection, optimizing critical strategies in academic and applied research settings.
Choosing the Appropriate Critique Method
Choosing between descriptive critique and immanent critique depends on the analytical goal and context. Descriptive critique offers an objective, detailed account of a work's elements and structure without judgment, ideal for initial understanding or documentation. Immanent critique is suited for revealing internal contradictions or latent tensions within a work by applying its own criteria, often used in philosophical, literary, or cultural analysis to foster deeper critical insight.
Descriptive critique Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com