Clear and simple language improves communication by making complex ideas easier to understand and more accessible to a wider audience. Using everyday words helps avoid confusion and keeps your message relatable and straightforward. Discover more tips to enhance your writing and connect better with your readers in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
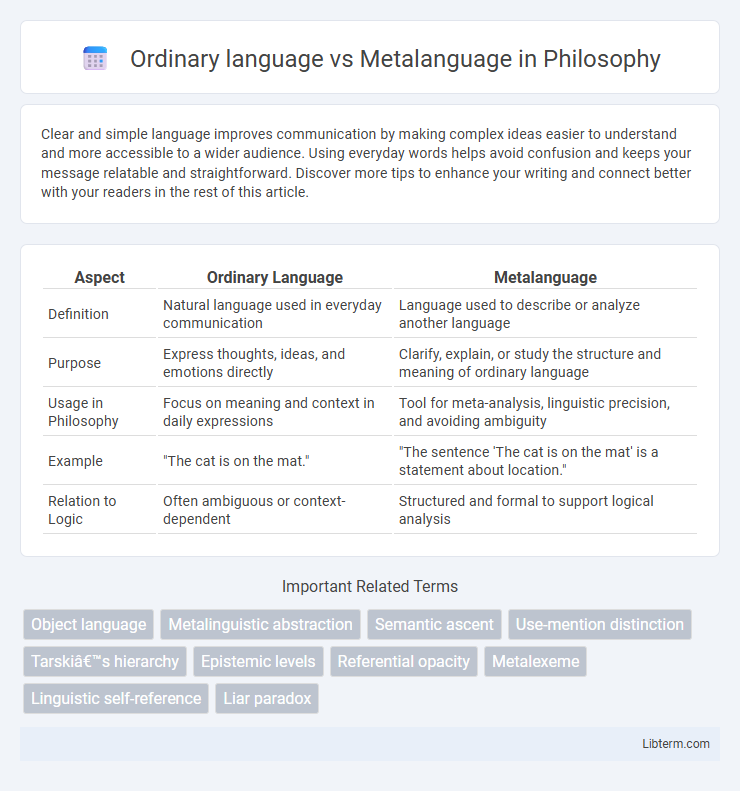
| Aspect | Ordinary Language | Metalanguage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural language used in everyday communication | Language used to describe or analyze another language |
| Purpose | Express thoughts, ideas, and emotions directly | Clarify, explain, or study the structure and meaning of ordinary language |
| Usage in Philosophy | Focus on meaning and context in daily expressions | Tool for meta-analysis, linguistic precision, and avoiding ambiguity |
| Example | "The cat is on the mat." | "The sentence 'The cat is on the mat' is a statement about location." |
| Relation to Logic | Often ambiguous or context-dependent | Structured and formal to support logical analysis |
Introduction to Ordinary Language and Metalanguage
Ordinary language refers to the everyday vocabulary and expressions used for common communication, encompassing natural speech, gestures, and contextual meanings shared by speakers. Metalanguage, by contrast, is the language used to describe, analyze, or discuss ordinary language itself, often involving technical terms, linguistic categories, and symbolic representations. Understanding the distinction between ordinary language and metalanguage facilitates clearer communication and more precise analysis in fields such as linguistics, philosophy, and computer science.
Defining Ordinary Language
Ordinary language refers to the natural, everyday communication used by people in casual conversation, encompassing common vocabulary and syntax without specialized terminology. It serves as the foundational means for expressing thoughts, emotions, and information in a straightforward and context-dependent manner. Understanding ordinary language is essential for contrasting it with metalanguage, which is the language used specifically to describe, analyze, or discuss ordinary language itself.
What is Metalanguage?
Metalanguage is a specialized linguistic system used to describe, analyze, or discuss the properties and structure of another language, known as the object language. It includes terms and symbols that enable precise explanation of grammar, syntax, and semantics, facilitating clear communication about language itself. Unlike ordinary language, which conveys everyday meanings, metalanguage functions as a tool for linguistic theory, programming languages, and formal logic.
Key Differences Between Ordinary Language and Metalanguage
Ordinary language consists of everyday words and expressions used for general communication, while metalanguage is specialized language designed to describe, analyze, or discuss language itself. Ordinary language operates at the level of content conveyance, whereas metalanguage functions at the level of linguistic reflection, enabling speakers to talk about grammar, syntax, and semantics. The key difference lies in their purpose: ordinary language transmits messages, and metalanguage provides a framework to examine or explain those messages.
Functions and Purposes of Metalanguage
Metalanguage serves primarily to describe, analyze, and clarify the features of an ordinary language by providing terms and concepts that facilitate discussion about language itself. It functions to enable precise communication about grammatical structure, semantics, and phonology, thereby supporting linguistic analysis and theory development. By offering a framework for reflection on language use, metalanguage aids in education, translation, and artificial intelligence programming.
Examples Illustrating Ordinary Language
Ordinary language consists of everyday words and phrases used for common communication, such as "The sky is blue" or "She is reading a book." These expressions convey straightforward information without reflecting on their own linguistic structure. Examples include statements like "I am hungry" or questions like "What time is it?" which simply report or inquire about real-world situations.
Illustrative Examples of Metalanguage
Metalanguage refers to a language or set of terms used to describe, analyze, or discuss another language, often employed in linguistics and logic. For example, in the sentence "The word 'dog' is a noun," the phrase "noun" functions as metalanguage because it classifies a part of speech within the ordinary language sentence "dog." Another example includes grammatical symbols such as S - NP VP, where S, NP, and VP are metalanguage elements used to explain syntactic structures of ordinary language sentences.
The Role of Context in Language and Metalanguage
Ordinary language relies heavily on contextual cues such as tone, body language, and situational factors to convey meaning, making communication dynamic and nuanced. Metalanguage, a language used to describe or analyze ordinary language, operates within a more structured context, often emphasizing clarity and precision to avoid ambiguity. The role of context in metalanguage is more explicit and controlled, enabling effective interpretation and discussion of linguistic elements without misunderstandings.
Importance of Distinguishing Metalanguage in Linguistics
Distinguishing metalanguage from ordinary language is crucial in linguistics because metalanguage provides a systematic framework for describing, analyzing, and interpreting language itself, rather than merely using language for everyday communication. Metalanguage enables precise discussion of grammar, semantics, and phonetics, facilitating objective analysis and reducing ambiguity inherent in ordinary language. Understanding this distinction supports clearer theoretical models and effective linguistic research methodologies.
Conclusion: Impact of Metalanguage on Language Understanding
Metalanguage enhances language understanding by providing tools to analyze, describe, and clarify ordinary language structures, enabling deeper comprehension of syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. It facilitates the identification of language ambiguities and supports precise communication in linguistics, philosophy, and cognitive science. The impact of metalanguage is evident in its ability to bridge natural language with formal systems, improving both language learning and linguistic theory development.
Ordinary language Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com