Realism captures the world with striking accuracy, focusing on everyday life and genuine human experiences. This artistic and literary movement avoids fantasy, highlighting ordinary characters and situations to reflect society truly. Discover how Realism continues to influence culture and why it remains relevant to Your understanding of art and literature in the full article.
Table of Comparison
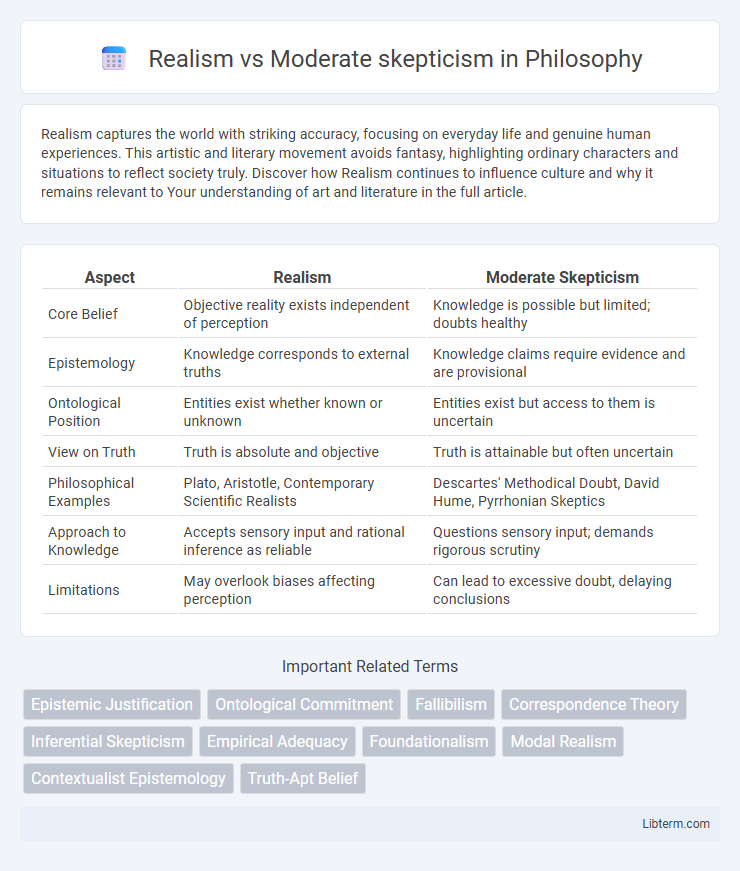
| Aspect | Realism | Moderate Skepticism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Objective reality exists independent of perception | Knowledge is possible but limited; doubts healthy |
| Epistemology | Knowledge corresponds to external truths | Knowledge claims require evidence and are provisional |
| Ontological Position | Entities exist whether known or unknown | Entities exist but access to them is uncertain |
| View on Truth | Truth is absolute and objective | Truth is attainable but often uncertain |
| Philosophical Examples | Plato, Aristotle, Contemporary Scientific Realists | Descartes' Methodical Doubt, David Hume, Pyrrhonian Skeptics |
| Approach to Knowledge | Accepts sensory input and rational inference as reliable | Questions sensory input; demands rigorous scrutiny |
| Limitations | May overlook biases affecting perception | Can lead to excessive doubt, delaying conclusions |
Defining Realism: Core Principles
Realism asserts that an objective reality exists independently of human perception and that knowledge can accurately represent this reality through empirical observation and scientific methods. Core principles of realism emphasize the existence of mind-independent facts and the possibility of obtaining true knowledge about the world. This philosophical stance contrasts with moderate skepticism, which questions the certainty and completeness of human knowledge while still allowing for some degree of justified belief.
Understanding Moderate Skepticism
Moderate skepticism challenges the absolute certainty claimed by realism by asserting that while knowledge of the external world is possible, it remains inherently limited and fallible. This epistemological stance emphasizes cautious inquiry and the provisional acceptance of beliefs based on evidence, promoting ongoing questioning rather than definitive conclusions. Understanding moderate skepticism involves recognizing its role in refining knowledge claims through critical examination and reducing dogmatism in philosophical and scientific discourse.
Historical Roots of Realism and Skepticism
Realism traces its historical roots to ancient Greek philosophers such as Plato, who emphasized the existence of objective reality independent of perception, while Moderate Skepticism emerged from Pyrrhonian skepticism but was refined by thinkers like Sextus Empiricus who argued for doubt without complete denial of knowledge. The development of Realism was further shaped by medieval scholastics like Thomas Aquinas, reinforcing the belief in an external reality accessible through reason. Moderate Skepticism, distinct in its cautious approach, insists on withholding absolute certainty while accepting practical knowledge, reflecting an epistemological balance stemming from Hellenistic philosophical traditions.
Key Philosophical Differences
Realism holds that an external world exists independently of our perceptions, asserting that objects possess properties regardless of human observation. Moderate skepticism questions the certainty of our knowledge about this external world, allowing for doubt but stopping short of denying its existence entirely. The key philosophical difference lies in realism's commitment to objective truth versus moderate skepticism's caution about the limits of human knowledge and belief justification.
Realism: Strengths and Criticisms
Realism asserts that an objective reality exists independently of our perceptions, providing a firm foundation for scientific inquiry and knowledge accumulation. Its strength lies in enabling consistent and predictive explanations of natural phenomena, fostering technological and intellectual progress. Criticisms target its sometimes rigid stance, arguing that it underestimates the impact of subjective experience and the complexities introduced by theoretical frameworks in shaping our understanding of reality.
The Appeal of Moderate Skepticism
Moderate skepticism appeals by striking a balance between absolute certainty and radical doubt, acknowledging the limitations of human knowledge while still accepting some reliable beliefs. It encourages critical examination without dismissing empirical evidence or common sense, fostering intellectual humility and openness. This approach is favored for its practical applicability in everyday reasoning and scientific inquiry, promoting a thoughtful yet cautious stance toward truth claims.
Realism vs Moderate Skepticism in Epistemology
Realism in epistemology asserts that knowledge corresponds to an objective reality independent of human perceptions, whereas moderate skepticism questions the certainty of such knowledge claims without outright denying the existence of knowledge. Realists argue that through reliable cognitive faculties and empirical evidence, humans can attain true beliefs about the external world. Moderate skeptics accept the possibility of knowledge but maintain cautious doubt regarding absolute certainty, emphasizing the limitations and fallibility of human cognition.
Practical Implications in Modern Thought
Realism asserts the existence of an objective reality independent of human perception, influencing scientific methodologies and technological advancements by promoting empirical evidence as the foundational truth. Moderate skepticism, which questions the certainty of knowledge while accepting probable truths, encourages critical thinking and adaptive learning approaches, fostering innovation through continuous inquiry and cautious acceptance. In modern thought, these perspectives shape educational frameworks and policy-making by balancing confidence in facts with openness to revision based on new evidence.
Bridging the Divide: Is Reconciliation Possible?
Realism and moderate skepticism present contrasting epistemological views, where realism asserts the independent existence of an objective reality while moderate skepticism questions the certainty of knowledge about that reality. Bridging the divide involves exploring epistemic humility and acknowledging the provisional nature of human understanding, allowing for a pragmatic middle ground that respects empirical evidence without claiming absolute certainty. Reconciliation is possible through dialogue that emphasizes fallibilism and the continuous refinement of knowledge, fostering cooperation between these paradigms in scientific and philosophical inquiry.
Current Debates and Future Perspectives
Current debates between Realism and Moderate Skepticism focus on the extent to which knowledge claims can be justified amidst epistemic uncertainty and the reliability of perceptual and scientific evidence. Realism asserts that an external reality exists independently of our beliefs, whereas Moderate Skepticism challenges the certainty of such knowledge without dismissing it entirely, advocating for a cautious and provisional acceptance. Future perspectives emphasize integrating cognitive science findings and developing epistemic frameworks that balance objective truth claims with acknowledgment of perceptual limitations and cognitive biases.
Realism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com