The cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance--serve as foundational principles guiding moral behavior and ethical decision-making. These virtues help you cultivate a balanced character by promoting wisdom, fairness, courage, and self-control in everyday life. Explore the rest of the article to discover how embracing these virtues can transform your personal and social relationships.
Table of Comparison
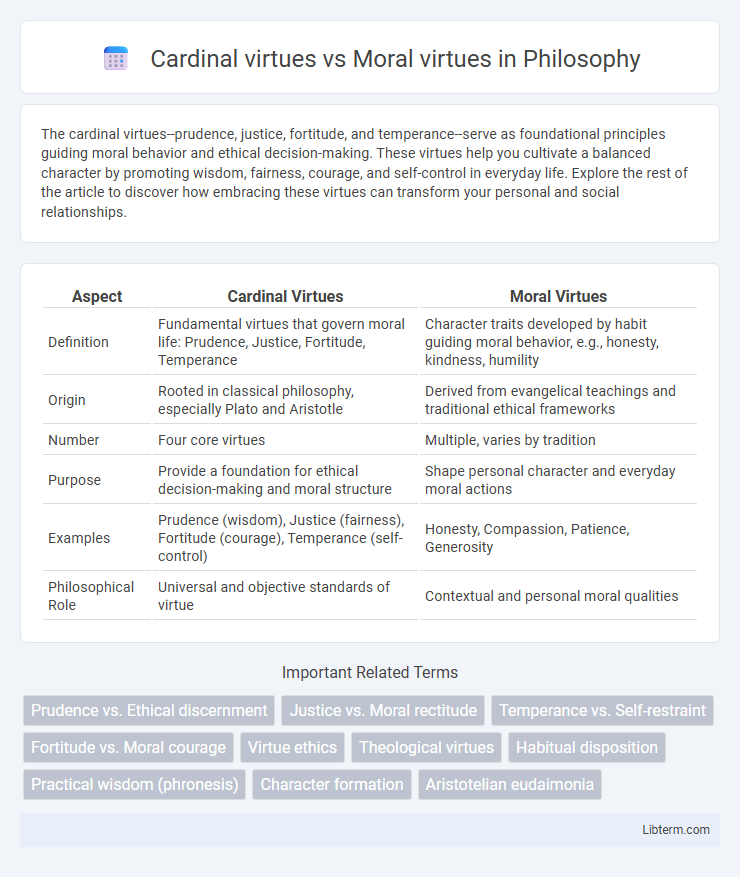
| Aspect | Cardinal Virtues | Moral Virtues |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fundamental virtues that govern moral life: Prudence, Justice, Fortitude, Temperance | Character traits developed by habit guiding moral behavior, e.g., honesty, kindness, humility |
| Origin | Rooted in classical philosophy, especially Plato and Aristotle | Derived from evangelical teachings and traditional ethical frameworks |
| Number | Four core virtues | Multiple, varies by tradition |
| Purpose | Provide a foundation for ethical decision-making and moral structure | Shape personal character and everyday moral actions |
| Examples | Prudence (wisdom), Justice (fairness), Fortitude (courage), Temperance (self-control) | Honesty, Compassion, Patience, Generosity |
| Philosophical Role | Universal and objective standards of virtue | Contextual and personal moral qualities |
Introduction to Cardinal and Moral Virtues
Cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, temperance, and fortitude--form the foundational qualities that govern ethical behavior and rational decision-making. Moral virtues, including honesty, kindness, and humility, derive from these cardinal virtues and guide individuals in developing good character through habitual right actions. Understanding the distinction clarifies how cardinal virtues provide the structural framework, while moral virtues express personal ethical conduct in daily life.
Defining Cardinal Virtues
Cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance--serve as foundational moral qualities guiding ethical behavior and decision-making. These virtues are considered pivotal because they regulate human passions and ensure actions aligned with reason and societal good. Unlike moral virtues, which are specific habits developed through practice, cardinal virtues function as essential principles underpinning all virtuous behavior.
Understanding Moral Virtues
Moral virtues, rooted in the ethical behavior that shapes character, guide individuals to act rightly through practiced habits like honesty, courage, and temperance. Unlike cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, temperance, and fortitude--which serve as foundational principles for ethical living, moral virtues focus on personal development in everyday decision-making and relationships. Understanding moral virtues involves recognizing their role in fostering integrity, responsibility, and empathy within social contexts.
Historical Origins of Cardinal Virtues
The cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, temperance, and fortitude--originate from ancient Greek philosophy, notably articulated by Plato and Aristotle as essential qualities for ethical living. These virtues were later adopted and integrated into Christian theology by St. Ambrose and St. Augustine, establishing their central role in medieval moral teachings. Unlike the cardinal virtues, moral virtues derive more broadly from individual character traits developed through habitual action and cultural context.
The Role of Moral Virtues in Ethics
Moral virtues, such as honesty, courage, and compassion, play a crucial role in ethics by guiding individuals to act in morally commendable ways that reflect good character. Unlike cardinal virtues, which serve as fundamental principles (prudence, justice, temperance, and fortitude), moral virtues are dispositions developed through habit that shape ethical decision-making and behavior in everyday life. The cultivation of moral virtues fosters personal integrity and social harmony, reinforcing ethical standards within communities.
Differences Between Cardinal and Moral Virtues
Cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance--serve as fundamental principles underpinning ethical behavior, whereas moral virtues refer to specific character traits developed through habituation, such as honesty, kindness, and humility. Cardinal virtues are considered universal and foundational, guiding the formation of moral virtues that manifest in concrete actions and decisions. The key difference lies in cardinal virtues providing the essential framework for virtuous living, while moral virtues are the practical expressions shaped by cultural and individual experiences.
Interrelation of Cardinal and Moral Virtues
Cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance--serve as foundational ethical principles that guide moral virtues like honesty, courage, and humility. Moral virtues are particular habits that perfect human actions in accordance with cardinal virtues, creating a dynamic interplay where cardinal virtues inform and shape the practice of moral virtues in daily life. This interrelation ensures the development of a coherent moral character, enabling individuals to make prudent decisions and act justly with strength and moderation.
Practical Examples of Each Virtue
Prudence, one of the cardinal virtues, guides a person to make wise decisions, such as planning a budget to avoid financial troubles, while moral virtues like honesty manifest in everyday actions like returning lost property. Justice, another cardinal virtue, is demonstrated through fair treatment at work or in legal situations, whereas temperance is seen in self-control examples like moderating food intake for health. Fortitude, exemplified by enduring hardships with courage, contrasts with moral virtues such as kindness, reflected in simple deeds like helping neighbors in need.
Importance of Virtues in Modern Society
Cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance--serve as foundational ethical principles guiding rational decision-making and social harmony in modern society. Moral virtues, such as honesty, compassion, and integrity, build upon these core principles to shape individual character and promote interpersonal trust. Emphasizing both cardinal and moral virtues fosters ethical behavior, strengthens community bonds, and supports sustainable societal development in contemporary contexts.
Conclusion: Harmonizing Virtuous Living
Cardinal virtues--prudence, justice, temperance, and fortitude--serve as foundational principles guiding moral virtues, which are specific habits cultivated through practice and intention. Harmonizing virtuous living requires aligning these cardinal virtues with moral virtues such as honesty, kindness, and courage to achieve ethical consistency and personal integrity. This integration fosters balanced character development essential for navigating complex moral decisions and promoting overall well-being.
Cardinal virtues Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com