Desire drives human motivation, influencing goals and behaviors across various aspects of life. Understanding the psychological and emotional roots of desire can help you harness its power for personal growth and fulfillment. Explore the rest of this article to discover how to channel your desires effectively.
Table of Comparison
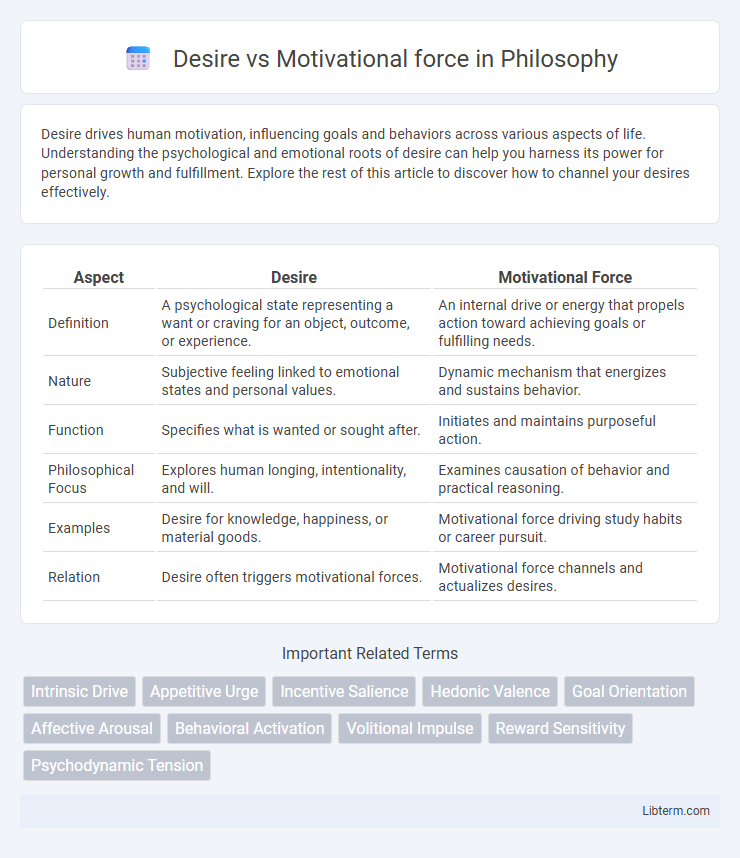
| Aspect | Desire | Motivational Force |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A psychological state representing a want or craving for an object, outcome, or experience. | An internal drive or energy that propels action toward achieving goals or fulfilling needs. |
| Nature | Subjective feeling linked to emotional states and personal values. | Dynamic mechanism that energizes and sustains behavior. |
| Function | Specifies what is wanted or sought after. | Initiates and maintains purposeful action. |
| Philosophical Focus | Explores human longing, intentionality, and will. | Examines causation of behavior and practical reasoning. |
| Examples | Desire for knowledge, happiness, or material goods. | Motivational force driving study habits or career pursuit. |
| Relation | Desire often triggers motivational forces. | Motivational force channels and actualizes desires. |
Understanding Desire: Definition and Characteristics
Desire is a psychological state characterized by a strong feeling of wanting or craving something specific, often driven by emotional or instinctual needs. It differs from motivational force in that desire represents the internal longing or attraction towards a goal, while motivational force encompasses the energy or drive that propels actions to achieve that goal. Key characteristics of desire include its emotional intensity, persistence over time, and ability to influence decision-making processes significantly.
What is Motivational Force? Key Concepts
Motivational force refers to the internal drive that propels individuals toward specific goals or behaviors, integrating both desire and expectancy with the perceived value of an outcome. Key concepts include expectancy theory, which highlights the belief that effort leads to performance, and instrumentality, the perception that performance will result in desired rewards. This concept underscores that motivation is a dynamic interplay between personal desire and rational evaluation of effort-to-reward relationships, shaping behavioral choices.
The Psychological Roots of Desire
Desire originates from intricate psychological roots, intertwining basic human needs with deep emotional drives and cognitive evaluations. It acts as a potent motivational force by channeling internal urges into goal-directed behavior that fulfills both survival and self-actualization needs. This process is heavily influenced by subconscious mechanisms, past experiences, and perceived value, shaping how desire propels motivation and decision-making.
How Motivational Force Drives Action
Motivational force drives action by translating internal desires into tangible behaviors through a combination of psychological energy and goal-directed effort. It activates the neural circuits responsible for decision-making, persistence, and overcoming obstacles, thereby transforming abstract aspirations into concrete results. This dynamic interplay ensures sustained commitment and progress toward desired outcomes in both personal and professional contexts.
Desire vs Motivational Force: Core Differences
Desire represents an internal longing or wish for a specific outcome, often fueled by emotions and personal values, whereas motivational force embodies the measurable energy or drive that propels an individual toward action. Desire is primarily psychological and subjective, reflecting what one wants, while motivational force translates this want into behavior through goals, effort, and persistence. Understanding the core difference highlights that desire sparks interest, but motivational force sustains the actions required to achieve tangible results.
The Interplay Between Desire and Motivation
Desire acts as the emotional catalyst that triggers motivational forces, driving individuals toward specific goals by creating an internal longing. The strength of motivation is directly influenced by the intensity and clarity of one's desire, shaping the persistence and direction of efforts. This dynamic interplay ensures that desire fuels motivation, while motivation channels desire into focused, goal-oriented actions essential for achievement.
Factors Influencing Desire and Motivational Forces
Desire is primarily influenced by intrinsic factors such as personal values, emotional needs, and past experiences, which shape the intensity and direction of an individual's wants. Motivational forces, on the other hand, encompass both intrinsic and extrinsic elements including rewards, social recognition, and environmental stimuli that drive goal-oriented behavior. Understanding these factors allows for targeted interventions in enhancing commitment and performance by aligning desires with effective motivational strategies.
Real-Life Examples: Distinguishing Desire from Motivation
Desire often represents a passive longing for outcomes such as wanting to lose weight or earn more money, whereas motivational force drives active behavior like consistent gym attendance or pursuing additional work shifts to achieve those goals. For instance, a student may desire academic success but only when motivation kicks in through setting study schedules and seeking help do they improve grades. In workplaces, employees may desire promotions, but motivation manifests through proactive projects and skill development that lead to tangible advancement.
Enhancing Motivation: Strategies to Channel Desire
Enhancing motivation involves strategically channeling desire into sustainable actions by setting clear, achievable goals and fostering intrinsic motivation through personal relevance. Techniques such as visualization, positive reinforcement, and structured feedback increase motivational force, transforming vague desires into focused energy that drives consistent progress. Understanding the neurological basis of desire and motivation further enables the development of customized strategies to maintain engagement and overcome obstacles.
Balancing Desire and Motivation for Success
Balancing desire and motivational force is crucial for achieving sustained success, as desire ignites passion while motivation fuels consistent action. High desire without sufficient motivation can lead to frustration, whereas strong motivation with unclear desire may result in lack of direction. Integrating clear goals with intrinsic motivation enhances focus, perseverance, and the ability to overcome obstacles effectively.
Desire Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com