Biological identity is determined by the unique genetic makeup and physiological characteristics that define an individual organism. Understanding this identity involves exploring DNA sequences, cellular functions, and hereditary traits that influence health, behavior, and development. Discover how your biological identity shapes who you are by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
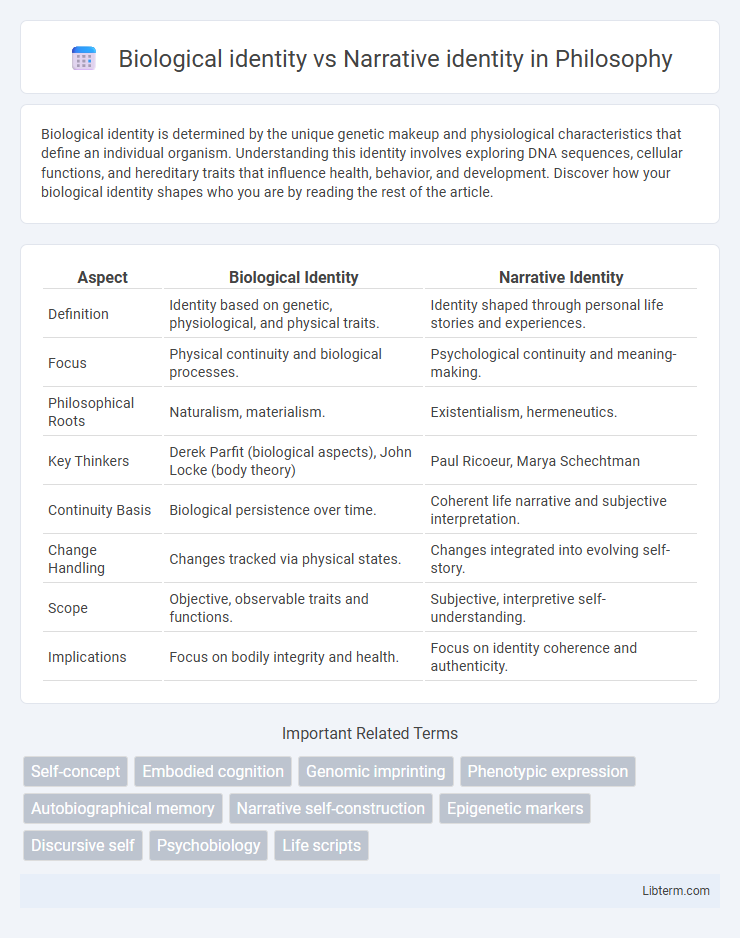
| Aspect | Biological Identity | Narrative Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identity based on genetic, physiological, and physical traits. | Identity shaped through personal life stories and experiences. |
| Focus | Physical continuity and biological processes. | Psychological continuity and meaning-making. |
| Philosophical Roots | Naturalism, materialism. | Existentialism, hermeneutics. |
| Key Thinkers | Derek Parfit (biological aspects), John Locke (body theory) | Paul Ricoeur, Marya Schechtman |
| Continuity Basis | Biological persistence over time. | Coherent life narrative and subjective interpretation. |
| Change Handling | Changes tracked via physical states. | Changes integrated into evolving self-story. |
| Scope | Objective, observable traits and functions. | Subjective, interpretive self-understanding. |
| Implications | Focus on bodily integrity and health. | Focus on identity coherence and authenticity. |
Defining Biological Identity
Biological identity refers to the genetic and physiological characteristics that define an individual, including DNA, brain structure, and biochemical processes. It encompasses innate attributes such as heredity, age, sex, and neurobiological functions that establish a person's physical and cognitive foundation. This identity is crucial for understanding distinctions between individuals on a purely biological level, separate from social, psychological, or experiential factors.
Understanding Narrative Identity
Narrative identity refers to the internalized and evolving story individuals construct about their lives, shaping their sense of self through memories and experiences. It contrasts with biological identity, which is based on physiological traits and genetic makeup. Understanding narrative identity involves exploring how personal stories provide coherence, purpose, and meaning, influencing psychological well-being and guiding future behavior.
Origins and Development of Biological Identity
Biological identity originates from genetic inheritance, encompassing DNA sequences, cellular structures, and physiological traits established at conception and continuously evolving through developmental biology. The process includes gene expression, epigenetic modifications, and neurobiological growth, which collectively shape an individual's physical and biochemical characteristics from embryogenesis to adulthood. These biological foundations interact with environmental factors but fundamentally determine the innate framework upon which narrative identity is later constructed.
The Formation of Narrative Identity
Narrative identity forms through the integration of life events into a coherent story that provides meaning and continuity across time, distinct from biological identity which is rooted in genetic and physiological characteristics. The process involves autobiographical memory, personal values, and social interactions, enabling individuals to construct and revise their life stories to reflect their evolving sense of self. Psychological theories emphasize the role of narrative identity in mental health and well-being, highlighting how individuals create meaningful connections between past experiences and future goals.
The Role of Genetics in Self-Concept
Genetics significantly shapes biological identity by determining physical traits and predispositions that form the foundation of self-awareness. Narrative identity, however, integrates genetic influences with personal experiences, memories, and cultural context to construct a coherent self-concept over time. Understanding the interplay between genetic factors and life stories reveals how biological predispositions interact with environmental narratives to influence individual identity.
Storytelling and Personal Meaning-Making
Biological identity refers to the physical and genetic aspects that define an individual, while narrative identity centers on the stories people construct to give their lives coherence and meaning. Storytelling plays a crucial role in personal meaning-making by allowing individuals to interpret past experiences, shape self-understanding, and connect with others through shared narratives. This interplay between biological facts and narrative construction enables a dynamic sense of self that evolves across time and social contexts.
Interactions Between Biology and Narratives
Biological identity, rooted in genetics and neurobiology, influences an individual's physical traits and innate predispositions, while narrative identity shapes self-understanding through personal stories and cultural context. Interactions between biology and narratives reveal how genetic factors and brain function affect memory, emotion, and cognition, thereby influencing the construction of life stories. This dynamic interplay demonstrates that biological processes and narrative meaning co-constitute identity, guiding behavior and self-perception across the lifespan.
Identity in Psychological Research
Biological identity refers to the innate and genetic aspects of the self, including physical characteristics and neurobiological processes, that form the foundation of identity in psychological research. Narrative identity involves the internalized and evolving story individuals construct about their lives, emphasizing personal meaning and psychological continuity across time. Psychological studies integrate both frameworks to understand how intrinsic biological factors and self-narratives interact to shape overall identity development and mental health.
Impacts on Mental Health and Well-being
Biological identity, rooted in genetics and physical traits, influences mental health through factors like neurochemical balance and predisposition to disorders, affecting overall well-being. Narrative identity, constructed from personal experiences and self-perception, shapes emotional resilience and coping mechanisms critical for psychological health. Interaction between these identities plays a crucial role in mental health outcomes, where congruence or conflict can impact stress levels, self-esteem, and emotional stability.
Integrating Biological and Narrative Perspectives
Integrating biological and narrative perspectives reveals how genetic, neurological, and physiological factors shape the core of one's sense of self, while personal stories provide context and meaning to these biological foundations. Advances in neurobiology demonstrate that brain structure and function influence memory and identity formation, intersecting with narrative identity's role in constructing life coherence and self-continuity. This synthesis supports a comprehensive understanding of identity as both embodied and storied, essential for fields like psychology, psychiatry, and cognitive science.
Biological identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com