Humanism emphasizes the value and agency of human beings, focusing on reason, ethics, and justice rather than supernatural beliefs. It encourages critical thinking and a secular approach to solving social and moral issues. Discover how humanism can influence your worldview and contribute to a more thoughtful society in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
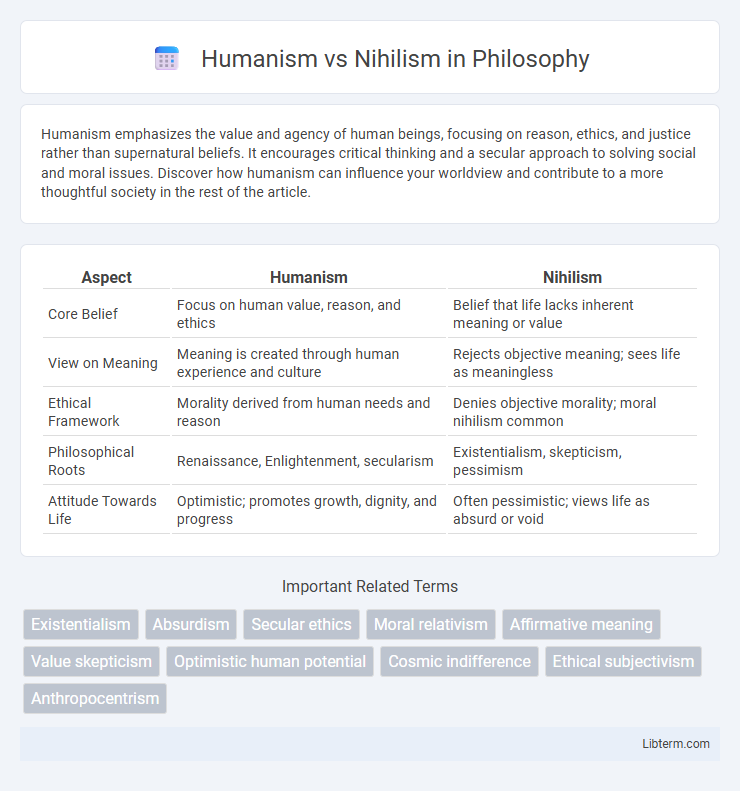
| Aspect | Humanism | Nihilism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Focus on human value, reason, and ethics | Belief that life lacks inherent meaning or value |
| View on Meaning | Meaning is created through human experience and culture | Rejects objective meaning; sees life as meaningless |
| Ethical Framework | Morality derived from human needs and reason | Denies objective morality; moral nihilism common |
| Philosophical Roots | Renaissance, Enlightenment, secularism | Existentialism, skepticism, pessimism |
| Attitude Towards Life | Optimistic; promotes growth, dignity, and progress | Often pessimistic; views life as absurd or void |
Understanding Humanism: Core Principles and Values
Humanism centers on the inherent dignity, worth, and potential of individuals, emphasizing reason, ethics, and compassion as guides for living meaningful lives. It rejects supernatural beliefs, advocating for a secular morality grounded in human experience and scientific inquiry. Core values include autonomy, social justice, and the pursuit of knowledge to foster human flourishing and well-being.
Nihilism Explained: Origins and Key Beliefs
Nihilism, originating from the Latin word "nihil" meaning "nothing," emerged as a philosophical doctrine in the 19th century, challenging traditional values and beliefs. Key beliefs of nihilism include the rejection of inherent meaning or purpose in life, the denial of objective morality, and the belief that existence is fundamentally without value. This worldview contrasts sharply with humanism, which emphasizes human dignity, purpose, and the potential for ethical progress.
Historical Evolution: Humanism and Nihilism in Context
Humanism emerged during the Renaissance as a response to medieval scholasticism, emphasizing human potential, reason, and the value of individual experience, while nihilism gained prominence in the 19th century through philosophers like Friedrich Nietzsche, challenging established moral values and the meaning of existence. The historical evolution of humanism reflects a gradual shift towards secularism and scientific inquiry, fostering progress in arts and humanities, whereas nihilism represents a critical reaction to the perceived collapse of traditional belief systems in modernity. These contrasting philosophies provide insights into cultural transformations, influencing contemporary debates on purpose, ethics, and the role of religion in society.
Meaning and Purpose: Contrasting Worldviews
Humanism emphasizes meaning and purpose derived from human experience, reason, and ethical values, promoting the belief that individuals can create fulfilling lives through personal growth and social contribution. Nihilism denies inherent meaning or purpose in existence, asserting that life lacks objective value or significance, often leading to existential skepticism. These contrasting worldviews shape differing attitudes toward life's meaning, with Humanism fostering hope and agency, while Nihilism challenges the possibility of inherent purpose.
Ethics and Morality: Humanist vs Nihilist Perspectives
Humanism emphasizes ethics rooted in human dignity, reason, and compassion, promoting moral values based on empathy and social well-being without reliance on supernatural beliefs. Nihilism often rejects absolute moral truths, viewing ethical systems as human constructs lacking inherent meaning or objective justification. While humanists seek to build moral frameworks that enhance human flourishing, nihilists question the existence of intrinsic moral order, leading to ethical skepticism or moral relativism.
Impact on Society: Humanism and Nihilism Compared
Humanism promotes progress and social cohesion by emphasizing human dignity, ethics, and rationality, fostering education, empathy, and community development. In contrast, nihilism challenges inherent meaning or value, often leading to existential despair, social fragmentation, or apathy, which can undermine collective purpose and societal stability. The societal impact of humanism encourages constructive dialogue and moral responsibility, whereas nihilism may provoke skepticism toward established norms and institutions, influencing cultural and philosophical discourse.
Well-being and Fulfillment: Humanist vs Nihilist Approaches
Humanism emphasizes well-being through meaning, purpose, and self-actualization, highlighting human potential and ethical values as pathways to fulfillment. Nihilism, often rejecting inherent meaning or objective values, views well-being as subjective and fulfillment as potentially elusive or constructed. Humanists promote growth and community connection, while nihilists may advocate for personal freedom by recognizing life's inherent meaninglessness.
Influence on Art, Literature, and Culture
Humanism's emphasis on human potential and rationality inspired Renaissance art and literature, fostering works that celebrate individuality, emotion, and classical ideals. Nihilism's rejection of inherent meaning influenced modernist and existentialist movements, provoking themes of absurdity, disillusionment, and fragmented narrative structures in 20th-century culture. Both philosophies reshaped cultural expressions by challenging traditional values and prompting artists and writers to explore new existential and ethical dimensions.
Criticisms and Misconceptions of Humanism and Nihilism
Humanism is often criticized for its perceived anthropocentrism and naivety in assuming inherent human goodness, while nihilism faces misconceptions of promoting moral emptiness or despair rather than questioning meaning and values. Critics argue humanism sometimes overlooks systemic issues by focusing excessively on individual potential and rationality, whereas nihilism is frequently misunderstood as advocating hopelessness, despite its philosophical inquiry into the absence of intrinsic meaning. Both philosophies provoke debate on the nature of ethics and existence, challenging simplistic interpretations by highlighting complexities in human purpose and value systems.
Choosing a Path: Navigating Humanism and Nihilism Today
Choosing between humanism and nihilism today involves evaluating the intrinsic value of human experience against the belief in life's inherent meaninglessness. Humanism emphasizes the potential for growth, ethics, and purpose derived from human connections and reasoning, while nihilism challenges these by asserting the absence of objective meaning or value. Navigating these philosophies requires balancing the humanist pursuit of meaningful existence with the nihilist recognition of existential uncertainty.
Humanism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com