Hermeneutic refers to the art and science of interpretation, especially of texts, language, and symbolic expressions. It plays a crucial role in understanding literary works, historical documents, and philosophical texts by uncovering deeper meanings beyond the surface. Discover how hermeneutic methods can transform your reading experience by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
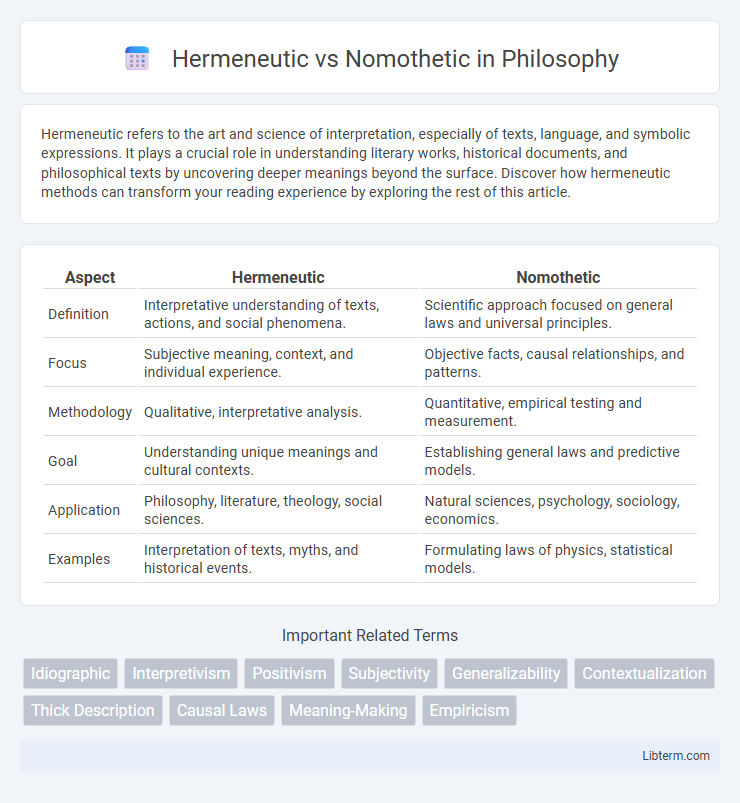
| Aspect | Hermeneutic | Nomothetic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpretative understanding of texts, actions, and social phenomena. | Scientific approach focused on general laws and universal principles. |
| Focus | Subjective meaning, context, and individual experience. | Objective facts, causal relationships, and patterns. |
| Methodology | Qualitative, interpretative analysis. | Quantitative, empirical testing and measurement. |
| Goal | Understanding unique meanings and cultural contexts. | Establishing general laws and predictive models. |
| Application | Philosophy, literature, theology, social sciences. | Natural sciences, psychology, sociology, economics. |
| Examples | Interpretation of texts, myths, and historical events. | Formulating laws of physics, statistical models. |
Introduction to Hermeneutic and Nomothetic Approaches
Hermeneutic approaches emphasize understanding the meaning and context of human experiences through qualitative analysis, focusing on individual cases and subjective interpretations. Nomothetic approaches seek to identify general laws and patterns by applying quantitative methods to large data sets, aiming for objective and replicable results. These contrasting methodologies highlight the tension between in-depth, contextual insights and broad, generalized knowledge in social sciences research.
Defining Hermeneutic Methodology
Hermeneutic methodology centers on interpreting and understanding human experiences and texts by exploring meaning within specific contexts, emphasizing subjective perspectives. Unlike the nomothetic approach, which seeks general laws through empirical observation and quantification, hermeneutics employs qualitative analysis to reveal depth and complexity in social and cultural phenomena. Key techniques include iterative interpretation, thematic analysis, and uncovering implicit assumptions in communication.
Understanding the Nomothetic Approach
The nomothetic approach seeks to establish general laws and principles through objective, quantitative methods often used in natural and social sciences. It emphasizes the identification of patterns, correlations, and causal relationships across large populations to explain behaviors and phenomena. This approach contrasts with the hermeneutic method by prioritizing measurable data and statistical analysis over subjective interpretation and contextual understanding.
Historical Origins and Philosophical Foundations
Hermeneutic approaches originate from ancient Greek philosophy, particularly Aristotle's emphasis on interpretation and understanding human experience through context and meaning. Nomothetic methods trace back to Enlightenment thinkers like Newton and Comte, emphasizing universal laws and objective knowledge through empirical observation and generalization. The philosophical foundation of hermeneutics is rooted in phenomenology and existentialism, focusing on subjective understanding, whereas nomothetic philosophy is grounded in positivism and empiricism, prioritizing quantifiable data and predictability.
Key Differences: Hermeneutic vs Nomothetic
Hermeneutic approaches emphasize understanding individual meanings and contexts through qualitative analysis, focusing on subjective interpretations and rich, detailed data. Nomothetic methods prioritize generalizable laws by using quantitative techniques to identify patterns and relationships across large populations. The key difference lies in hermeneutics' aim for depth and nuance versus nomothetics' goal of broad applicability and prediction.
Applications in Social Sciences and Humanities
Hermeneutic approaches in social sciences and humanities emphasize deep interpretation of texts, cultural artifacts, and social phenomena to understand meaning within specific contexts. Nomothetic methods prioritize identifying general laws and patterns through quantitative data analysis, enabling broad predictions across populations. These contrasting methodologies complement each other by providing both richly contextualized insights and generalizable frameworks in fields such as anthropology, sociology, and history.
Strengths and Limitations of Hermeneutic Analysis
Hermeneutic analysis excels in providing deep, context-rich interpretations of human experiences, capturing subjective meanings and cultural nuances often overlooked by quantitative methods. Its strength lies in flexibility and adaptability to diverse texts and scenarios, enabling researchers to uncover complex layers of understanding. Limitations include potential researcher bias, challenges in replicability, and difficulties in generalizing findings beyond specific contexts.
Advantages and Criticisms of Nomothetic Research
Nomothetic research provides the advantage of identifying general laws and patterns through quantifiable data, enabling broad applicability and predictability across populations. Its emphasis on objectivity and replication supports scientific rigor and comparability between studies. Criticisms focus on its potential to oversimplify complex human behaviors and social phenomena by neglecting individual nuances and contextual depth that qualitative approaches like hermeneutics prioritize.
Integrating Both Approaches: Mixed Methods Perspective
Integrating hermeneutic and nomothetic approaches through a mixed methods perspective enhances research by combining qualitative insight with quantitative rigor. This fusion allows for a comprehensive analysis where rich contextual understanding from hermeneutics complements the generalizable patterns identified by nomothetic methods. Employing both approaches facilitates a holistic exploration of complex phenomena, improving validity and depth in social science studies.
Future Directions in Hermeneutic and Nomothetic Research
Future directions in hermeneutic research emphasize integrating advanced qualitative methodologies with digital tools like AI-driven text analysis to deepen interpretative frameworks. Nomothetic research is increasingly leveraging large-scale data analytics and machine learning algorithms to refine predictive models and identify universal patterns across diverse populations. Combining hermeneutic contextual insights with nomothetic generalizations promises innovative hybrid approaches that enhance both understanding and prediction in social science and humanities studies.
Hermeneutic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com