Semantics explores the meaning behind words, phrases, and sentences, revealing how language communicates ideas effectively. Understanding semantics enhances your ability to interpret context and nuances in communication. Discover more about the role semantics plays in improving language comprehension and usage in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
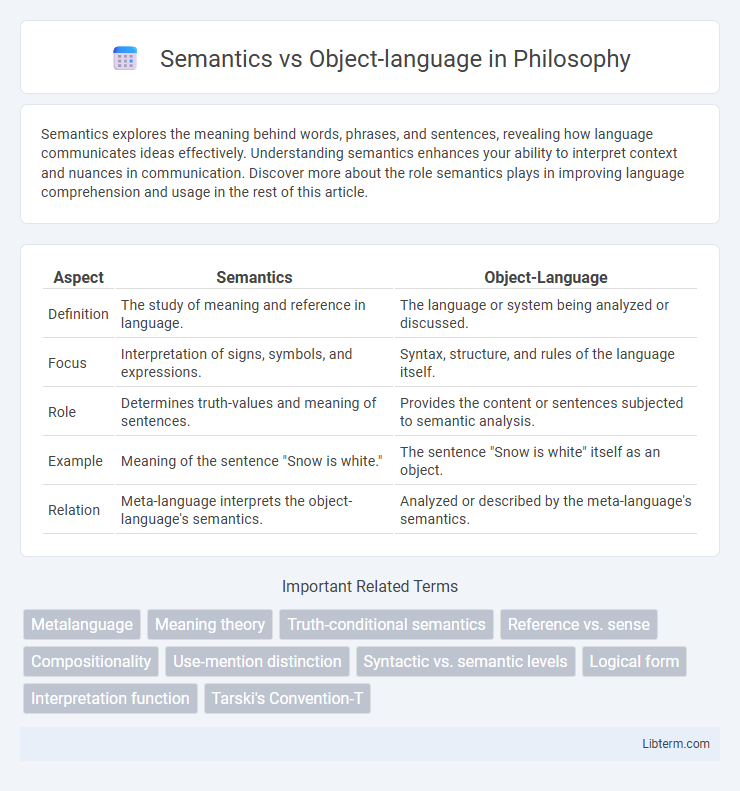
| Aspect | Semantics | Object-Language |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The study of meaning and reference in language. | The language or system being analyzed or discussed. |
| Focus | Interpretation of signs, symbols, and expressions. | Syntax, structure, and rules of the language itself. |
| Role | Determines truth-values and meaning of sentences. | Provides the content or sentences subjected to semantic analysis. |
| Example | Meaning of the sentence "Snow is white." | The sentence "Snow is white" itself as an object. |
| Relation | Meta-language interprets the object-language's semantics. | Analyzed or described by the meta-language's semantics. |
Understanding Semantics and Object-language
Semantics studies the meaning and interpretation of expressions within a language, focusing on how symbols relate to concepts and real-world references. Object-language refers to the language that is being analyzed or described, serving as the primary subject in semantic evaluation. Understanding semantics involves distinguishing between the object-language and the metalanguage used to discuss or analyze its structure and meaning.
Defining Semantics in Linguistics
Semantics in linguistics studies the meaning conveyed by words, phrases, and sentences within a natural language, emphasizing interpretation and context. Object-language refers to the actual language being analyzed or discussed, while semantics provides a framework for understanding how meaning is constructed and communicated in that object-language. Defining semantics involves exploring relationships between linguistic expressions and their referents, truth conditions, and cognitive representations.
What is Object-language?
Object-language refers to the language or system of symbols that is the subject of study or analysis within a meta-language. It consists of the terms, expressions, and rules used to construct statements and convey meaning in a particular domain. Understanding object-language is crucial for formal semantics, where the goal is to precisely describe the interpretation and truth conditions of sentences within that system.
Key Differences Between Semantics and Object-language
Semantics studies the meaning and interpretation of expressions within a language, while object-language is the language being analyzed or discussed in a metalanguage. Semantics examines truth conditions, reference, and meaning relations, whereas object-language consists of the actual symbols, syntax, and sentences subject to semantic evaluation. The key distinction lies in semantics addressing the meta-level understanding of meaning, contrasting with object-language as the primary language under scrutiny.
The Role of Semantics in Language Analysis
Semantics plays a crucial role in language analysis by providing a framework to interpret the meaning of expressions within both the object-language and its meta-language. Object-language consists of the actual language under study, while semantics offers the tools to assign truth conditions, reference, and interpretation to its symbols and sentences. This distinction enables precise examination of how meaning is constructed, enabling clearer communication, linguistic theory development, and computational language processing.
Object-language: Examples and Applications
Object-language refers to the formal language that is the subject of study or analysis within logic and semantics, typically composed of symbols, syntax, and rules for constructing valid statements. Examples of object-languages include formal systems like propositional logic, predicate logic, and programming languages such as Python or Java, where statements are precisely defined and interpreted. Applications of object-language span fields like mathematics, computer science, and linguistics, enabling rigorous theorem proving, software development, and natural language processing through structured symbolic representation.
Importance of Meta-language in Contrast
Meta-language plays a crucial role in distinguishing semantics from object-language by providing the framework to describe and analyze the properties and meanings of expressions within the object-language. It enables the formal articulation of truth conditions, reference, and interpretative rules that cannot be expressed within the object-language itself. The use of meta-language is essential for clarity and precision in semantic theory, allowing for rigorous definitions and the resolution of semantic paradoxes.
Semantics and Object-language in Formal Logic
In formal logic, semantics studies the meaning and interpretation of symbols within an object-language, which is the formal language used for expressing logical statements. Semantics assigns truth values and models to the object-language, enabling the evaluation of validity and satisfiability of formulas. This distinction ensures precise analysis of logical systems by separating the syntactic structure of object-language from the semantic interpretation in a meta-language.
Common Misconceptions
Semantics involves the study of meaning in languages, whereas the object-language is the language being analyzed or discussed within a meta-language framework. A common misconception is that semantics is merely about dictionary definitions, ignoring its role in interpreting context, pragmatics, and syntactic structures. Confusing the meta-language with the object-language often leads to misunderstandings about language analysis and the scope of semantic theories.
Relevance in Modern Linguistic Theory
Semantics, which studies meaning in natural language, is crucial for interpreting context and intention, while object-language refers to the language being analyzed within a formal system. In modern linguistic theory, the distinction highlights the relevance of semantic frameworks that go beyond syntax to capture pragmatic and cognitive aspects of communication. This focus enables deeper understanding of language use, facilitating advancements in computational linguistics and natural language processing.
Semantics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com