Generalism allows individuals to develop versatile skills across multiple disciplines, enhancing adaptability in dynamic environments. Embracing a broad knowledge base supports innovative problem-solving and collaboration across diverse fields. Discover how cultivating generalist abilities can elevate your career and personal growth by reading the full article.
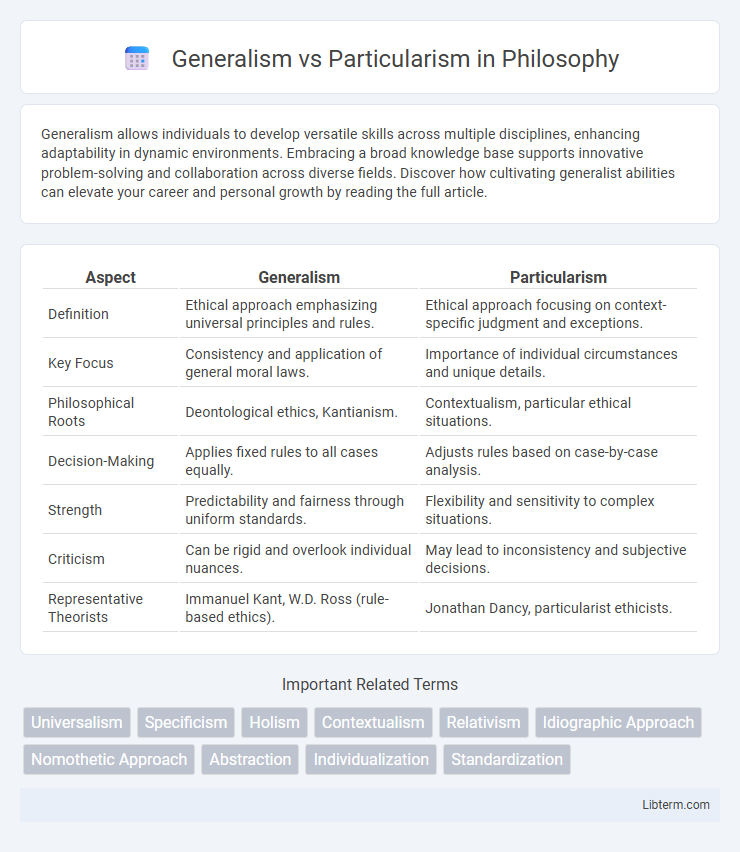
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Generalism | Particularism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ethical approach emphasizing universal principles and rules. | Ethical approach focusing on context-specific judgment and exceptions. |
| Key Focus | Consistency and application of general moral laws. | Importance of individual circumstances and unique details. |
| Philosophical Roots | Deontological ethics, Kantianism. | Contextualism, particular ethical situations. |
| Decision-Making | Applies fixed rules to all cases equally. | Adjusts rules based on case-by-case analysis. |
| Strength | Predictability and fairness through uniform standards. | Flexibility and sensitivity to complex situations. |
| Criticism | Can be rigid and overlook individual nuances. | May lead to inconsistency and subjective decisions. |
| Representative Theorists | Immanuel Kant, W.D. Ross (rule-based ethics). | Jonathan Dancy, particularist ethicists. |
Understanding Generalism and Particularism
Generalism emphasizes universal rules and standards that apply broadly across situations, prioritizing consistency and fairness in decision-making processes. Particularism focuses on context-specific factors, valuing relationships, unique circumstances, and individual cases over fixed rules. Understanding these cultural dimensions helps in navigating social interactions and organizational behavior by recognizing how people prioritize norms versus personal connections.
Historical Perspectives on Generalism vs Particularism
Historical perspectives on generalism versus particularism highlight how ancient societies favored particularism, emphasizing local customs and personal relationships in decision-making processes. Over time, the rise of centralized states and bureaucracies promoted generalism, advocating for universal laws and standardized practices to ensure fairness and efficiency. This shift reflects broader socio-political transformations from segmented communities towards integrated nation-states driven by Enlightenment ideals and modern governance structures.
Core Principles of Generalism
Generalism emphasizes broad knowledge and skills applicable across diverse fields, promoting adaptability and problem-solving in various contexts. Core principles include versatility, interdisciplinary understanding, and the ability to synthesize information from multiple domains to create innovative solutions. This approach values holistic perspective over specialized expertise, enabling individuals to navigate complex, dynamic environments effectively.
Key Features of Particularism
Particularism emphasizes context-specific rules and relationships over universal principles, highlighting the importance of individualized judgments in decision-making. It prioritizes personal connections, flexibility, and adapting to unique situations rather than strict adherence to standardized procedures. This approach often leads to varied outcomes based on specific circumstances and interpersonal dynamics.
Advantages of a Generalist Approach
A generalist approach offers versatility by enabling professionals to adapt across diverse industries and roles, enhancing problem-solving through broad knowledge integration. This adaptability fosters innovation by allowing the application of varied perspectives and skills to complex challenges. Generalists often excel in leadership and project management by connecting interdisciplinary teams and synthesizing information for strategic decision-making.
Benefits of Embracing Particularism
Embracing particularism fosters strong interpersonal relationships by emphasizing context-specific understanding and flexibility in decision-making. This approach enhances trust and cooperation within diverse teams, leading to tailored solutions that address unique cultural and situational nuances. Organizations adopting particularism often experience improved conflict resolution and increased adaptability in dynamic environments.
Generalism vs Particularism in the Workplace
Generalism in the workplace emphasizes broad skills and adaptable knowledge, enabling employees to handle diverse tasks and roles efficiently. Particularism prioritizes specialized expertise and context-specific relationships, fostering deep trust and tailored decision-making within teams. Balancing generalist versatility with particularist depth enhances organizational agility and fosters effective collaboration.
Impact on Education and Learning
Generalism fosters a broad knowledge base that promotes adaptability and interdisciplinary thinking in education, enabling students to connect concepts across various fields. Particularism emphasizes specialized knowledge and tailored learning pathways, enhancing deep expertise and skill mastery in specific subjects. The balance between generalism and particularism shapes curriculum design, influencing students' critical thinking abilities and readiness for diverse professional environments.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Generalism faces challenges in addressing specific cultural contexts, often oversimplifying complex social dynamics and leading to misinterpretations in diverse settings. Particularism is criticized for its potential to foster relativism, making consistent policy application and ethical standards difficult across different groups. Both approaches struggle with balancing universal principles and cultural specificity, complicating effective cross-cultural communication and decision-making.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between generalism and particularism depends on factors such as the complexity of the task, the need for specialized knowledge, and the context of decision-making. Generalism suits dynamic environments where adaptability and broad skill sets enable effective problem-solving across diverse situations. Particularism thrives in specialized fields where deep expertise and tailored solutions offer precision and efficiency.
Generalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com