Reality shapes our perception and understanding of the world around us, influencing every decision and interaction we have. Exploring its layers reveals the complex interplay between objective facts and subjective experiences that define our existence. Dive into the article to uncover how reality impacts your life and perspectives.
Table of Comparison
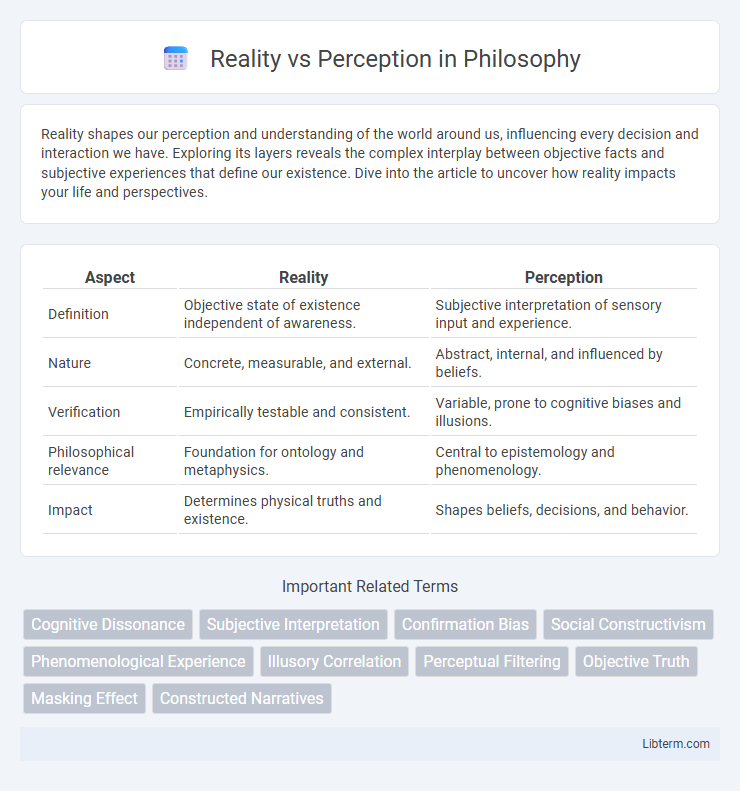
| Aspect | Reality | Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Objective state of existence independent of awareness. | Subjective interpretation of sensory input and experience. |
| Nature | Concrete, measurable, and external. | Abstract, internal, and influenced by beliefs. |
| Verification | Empirically testable and consistent. | Variable, prone to cognitive biases and illusions. |
| Philosophical relevance | Foundation for ontology and metaphysics. | Central to epistemology and phenomenology. |
| Impact | Determines physical truths and existence. | Shapes beliefs, decisions, and behavior. |
Defining Reality and Perception
Reality consists of objective facts and phenomena that exist independently of individual thoughts or feelings, grounded in measurable evidence and physical existence. Perception involves the subjective interpretation of those facts through sensory input, cognitive processing, and personal experiences, often leading to varied understandings among different individuals. Defining reality requires examining empirical data, while defining perception focuses on the mental and emotional frameworks shaping individual viewpoints.
The Psychological Basis of Perception
The psychological basis of perception involves how the brain processes sensory information to construct an individual's experience of reality, which often differs from objective truth. Cognitive factors such as attention, memory, and prior knowledge shape perceptual interpretation, leading to subjective realities. Studies in cognitive psychology highlight that perception is an active process influenced by neural mechanisms and psychological biases, underscoring the divergence between reality and perception.
How Beliefs Shape Our View of Reality
Beliefs act as cognitive filters that shape an individual's interpretation of reality, often leading to selective perception where information aligning with existing beliefs is favored. Neural mechanisms such as confirmation bias reinforce these beliefs, influencing decision-making and emotional responses. This interplay between belief and perception highlights the subjective nature of reality, demonstrating that what one perceives is often a constructed narrative rather than an objective truth.
Cognitive Biases and Distorted Perception
Cognitive biases such as confirmation bias, anchoring, and availability heuristic significantly influence how individuals interpret reality, often distorting perception by filtering information through preconceived beliefs or emotions. Distorted perception arises when mental shortcuts lead to misjudgments, causing a discrepancy between objective facts and subjective experience. Understanding these biases is crucial for improving decision-making accuracy and fostering clearer, more rational interpretations of the environment.
Social Influences on Perception
Social influences significantly shape individual perception by filtering experiences through cultural norms, peer pressure, and media representation, which often distort reality. Group dynamics and social conformity drive people to interpret events and behaviors in ways that align with collective beliefs rather than objective facts. This interplay between social context and cognitive processing results in perception that can diverge substantially from actual reality.
Media, Misinformation, and Perceived Reality
Media plays a crucial role in shaping perceived reality by selectively presenting information and often amplifying misinformation, which distorts public understanding. Algorithms prioritize sensational content, creating echo chambers that reinforce biased perceptions and hinder objective truth. The proliferation of fake news and manipulated media further blurs the line between reality and perception, challenging individuals to critically evaluate the authenticity of information they consume.
The Role of Experience in Shaping Perception
Experience fundamentally shapes perception by filtering sensory input through memories, beliefs, and prior knowledge, creating a subjective interpretation of reality. Neural plasticity allows repeated experiences to rewire the brain's perceptual pathways, enhancing familiar patterns while diminishing novel or contradictory information. This dynamic underscores how individual differences in experience lead to diverse and sometimes conflicting perceptions of the same objective reality.
When Perception Diverges from Objective Reality
When perception diverges from objective reality, cognitive biases such as confirmation bias and illusion of control often distort individual understanding. Neuroscientific studies reveal that the brain constructs subjective experiences influenced by prior knowledge, emotions, and social context, leading to discrepancies between actual events and perceived truths. This divergence impacts decision-making, memory accuracy, and interpersonal communication, highlighting the importance of critical thinking and empirical verification.
Bridging the Gap: Aligning Perception with Reality
Bridging the gap between reality and perception requires aligning individual beliefs with objective facts through critical thinking and evidence-based evaluation. Cognitive biases and misinformation often distort perception, making it essential to cultivate awareness and seek diverse perspectives for accurate understanding. Effective communication and education foster alignment by encouraging openness to new information and challenging preconceived notions.
The Impact of Reality vs Perception on Decision-Making
Reality shapes decision-making through objective facts and tangible outcomes, while perception influences choices based on individual beliefs and biases. Misalignment between reality and perception can lead to flawed judgments, affecting personal and professional decisions. Understanding the disparity enhances critical thinking, allowing for more accurate evaluations and improved strategic planning.
Reality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com