Practical contradiction arises when actions or decisions conflict with established principles or objectives, leading to inefficiency and confusion. Addressing these contradictions requires critical analysis and alignment of behaviors with goals to ensure consistency and effectiveness. Explore this article to better understand how you can identify and resolve practical contradictions in your endeavors.
Table of Comparison
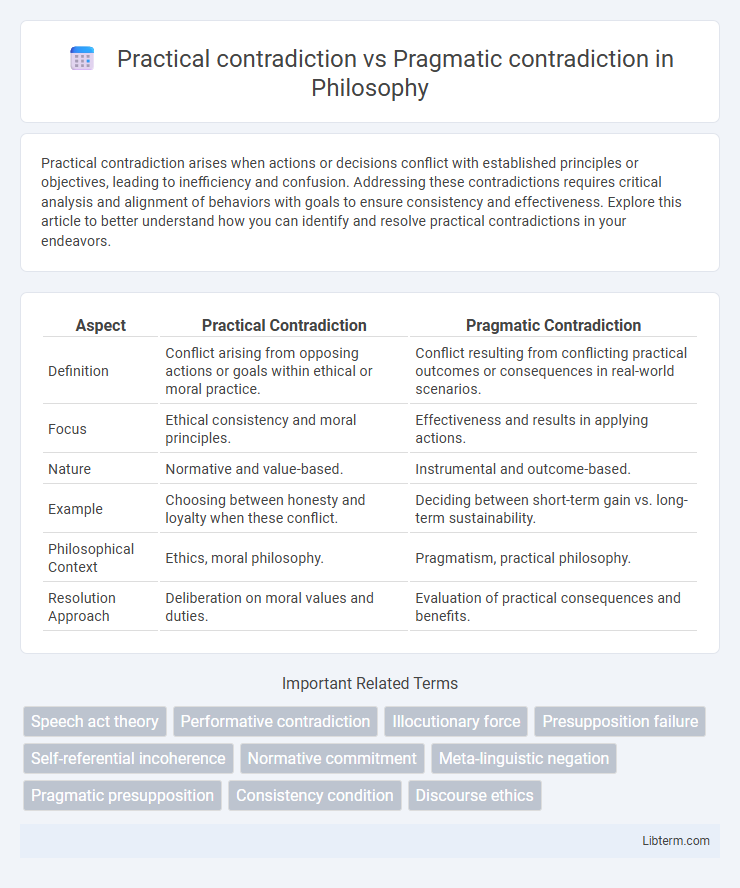
| Aspect | Practical Contradiction | Pragmatic Contradiction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conflict arising from opposing actions or goals within ethical or moral practice. | Conflict resulting from conflicting practical outcomes or consequences in real-world scenarios. |
| Focus | Ethical consistency and moral principles. | Effectiveness and results in applying actions. |
| Nature | Normative and value-based. | Instrumental and outcome-based. |
| Example | Choosing between honesty and loyalty when these conflict. | Deciding between short-term gain vs. long-term sustainability. |
| Philosophical Context | Ethics, moral philosophy. | Pragmatism, practical philosophy. |
| Resolution Approach | Deliberation on moral values and duties. | Evaluation of practical consequences and benefits. |
Understanding Practical Contradiction
Practical contradiction arises when actions or decisions conflict with an individual's or group's intentions or goals, creating a barrier to effective behavior and problem-solving. It reflects inconsistencies between what is aimed for and what is actually done, highlighting gaps in practice versus theory. Recognizing practical contradiction is essential for improving decision-making processes and aligning actions with strategic objectives in various fields such as management, psychology, and conflict resolution.
Defining Pragmatic Contradiction
Pragmatic contradiction arises when a statement's practical application conflicts with the intended communicative purpose or contextual expectations, causing a breakdown in effective communication. Unlike practical contradiction, which involves direct logical or factual inconsistency in actions or outcomes, pragmatic contradiction centers on the mismatch between language use and social context. Understanding pragmatic contradiction is essential for analyzing discourse where meaning is shaped by speaker intention, context, and listener interpretation rather than objective truth conditions.
Key Differences Between Practical and Pragmatic Contradictions
Practical contradictions arise from conflicts between actions and goals, emphasizing real-world implementation challenges, whereas pragmatic contradictions involve inconsistencies in language use or communication context affecting interpretation and meaning. Practical contradictions focus on tangible problems in decision-making and behavior, while pragmatic contradictions highlight the impact of situational factors and speaker intentions on discourse coherence. Understanding these key differences helps in resolving issues by addressing either operational feasibility or linguistic and contextual clarity.
Origins and Theoretical Backgrounds
Practical contradiction originates from everyday reasoning where actions or decisions clash with stated goals, rooted in ethical and moral philosophy emphasizing consistency between beliefs and behaviors. Pragmatic contradiction emerges from linguistic and communication theories, particularly pragmatics and speech act theory, analyzing how utterances conflict with context-based expectations or intentions. Both concepts derive from distinct intellectual traditions, with practical contradiction grounded in normative ethics and pragmatic contradiction in the study of language use and meaning in social interaction.
Real-world Examples of Practical Contradiction
Practical contradictions arise when individuals face incompatible goals or actions in real-world scenarios, such as trying to increase productivity while simultaneously reducing working hours, leading to conflicting priorities. An example of practical contradiction can be seen in urban planning, where efforts to expand road infrastructure to ease traffic congestion clash with environmental sustainability goals that prioritize green spaces. These contradictions highlight the challenges in balancing competing interests and the need for strategic decision-making to navigate conflicting practical demands.
Real-world Examples of Pragmatic Contradiction
Pragmatic contradictions occur when a statement undermines its own purpose or context, such as someone saying, "I am not speaking," while speaking, demonstrating a real-world example of language contradicting usage. Another example is a "Do not enter" sign placed on an open door easily bypassed, where the action contradicts the intended instruction, highlighting practical communication conflicts. These contradictions emphasize the importance of context and interpretation in everyday discourse and decision-making scenarios.
Implications in Logic and Reasoning
Practical contradiction occurs when an agent's actions conflict with their intentions or beliefs, revealing inconsistencies in decision-making processes, whereas pragmatic contradiction arises from contextual or conversational misunderstandings that do not necessarily imply logical inconsistency. In logic and reasoning, practical contradictions impact the coherence of an agent's behavior and undermine rational agency, while pragmatic contradictions affect communication effectiveness and interpretation in natural language contexts. Understanding these distinctions aids in developing robust formal systems for modeling belief dynamics and context-sensitive reasoning frameworks.
Practical Contradiction in Ethical Decision-Making
Practical contradiction in ethical decision-making occurs when an individual's actions directly conflict with their moral principles, revealing an inconsistency between belief and practice. This form of contradiction challenges the coherence of ethical commitments by demonstrating how intentions fail to translate into responsible conduct. Addressing practical contradictions requires critical reflection and behavioral adjustment to ensure alignment between ethical values and real-world decisions.
Pragmatic Contradiction in Communication
Pragmatic contradiction in communication occurs when the intended meaning of a message conflicts with the contextual cues or social norms, leading to misunderstandings or ambiguity. Unlike practical contradiction, which involves direct logical inconsistency in actions or statements, pragmatic contradiction centers on the incongruity between what is said and how it is interpreted within a specific communicative context. Recognizing pragmatic contradictions enhances effective communication by addressing the subtle interplay of language, context, and listener perception.
Resolving Contradictions: Methods and Approaches
Resolving practical contradictions involves systematic application of problem-solving techniques such as TRIZ, which emphasizes inventive principles and analysis of technical systems to eliminate conflicts without compromise. Pragmatic contradictions require context-sensitive negotiation and adaptive strategies that balance conflicting stakeholder interests by prioritizing real-world constraints and desired outcomes. Both approaches benefit from iterative evaluation, stakeholder engagement, and flexible frameworks to achieve optimal, sustainable solutions.
Practical contradiction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com