Please provide the subject or topic you want the semantic-optimized text for.
Table of Comparison
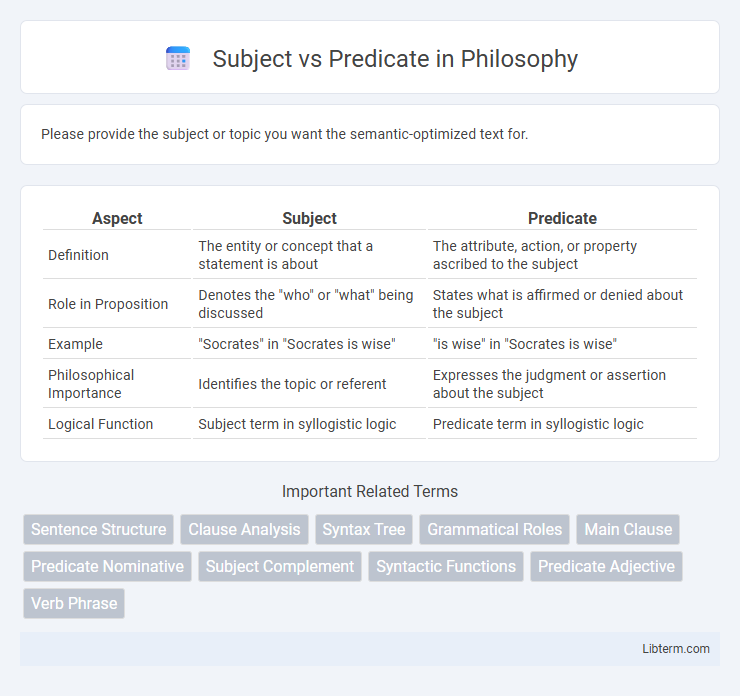
| Aspect | Subject | Predicate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The entity or concept that a statement is about | The attribute, action, or property ascribed to the subject |
| Role in Proposition | Denotes the "who" or "what" being discussed | States what is affirmed or denied about the subject |
| Example | "Socrates" in "Socrates is wise" | "is wise" in "Socrates is wise" |
| Philosophical Importance | Identifies the topic or referent | Expresses the judgment or assertion about the subject |
| Logical Function | Subject term in syllogistic logic | Predicate term in syllogistic logic |
Understanding Subject and Predicate
The subject of a sentence identifies who or what performs the action or is being described, while the predicate conveys the action or state of the subject. Understanding the subject involves recognizing the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that the sentence is about, and comprehending the predicate requires identifying the verb and any accompanying information that completes the idea. Mastery of subject and predicate structure is essential for analyzing sentence construction and improving grammatical accuracy.
Definition of Subject
The subject in a sentence is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that performs the action or is described by the predicate. It answers the question "who" or "what" the sentence is about, serving as the main topic around which the predicate provides information. Understanding the subject is essential for identifying the core meaning and structure of a sentence.
Definition of Predicate
The predicate in a sentence conveys information about the subject, typically including a verb and any objects or modifiers. It expresses what the subject does, what happens to the subject, or the condition of the subject. Predicates are essential for forming complete thoughts by providing action or state of being linked to the subject.
Types of Subjects
Types of subjects in grammar include simple, compound, and complete subjects, each playing a crucial role in sentence structure. A simple subject consists of a single noun or pronoun, while a compound subject contains two or more nouns or pronouns joined by a conjunction. The complete subject includes the simple subject along with all its modifiers, providing a full description necessary for understanding the predicate's action or state.
Types of Predicates
Predicates can be classified into simple, compound, and complex types based on their structure and function within a sentence. A simple predicate consists of a single verb or verb phrase that expresses the action or state of the subject, while a compound predicate contains two or more verbs sharing the same subject. Complex predicates include additional elements such as objects, complements, or modifiers that provide more information about the action or state described by the verb.
Subject-Predicate Agreement
Subject-predicate agreement requires the subject and predicate in a sentence to match in number and person, ensuring grammatical consistency. Singular subjects pair with singular predicates, while plural subjects demand plural predicates to maintain clarity and coherence. Proper agreement between subject and predicate is essential for effective communication and syntactic accuracy.
How to Identify Subject and Predicate
Identify the subject by locating the noun or pronoun that performs the action or is described in the sentence. The predicate contains the verb and provides information about what the subject does or is. Analyzing sentence structure helps distinguish the subject as the performer and the predicate as the descriptor or action.
Common Errors with Subjects and Predicates
Common errors with subjects and predicates include subject-verb agreement mistakes, where the verb does not correctly correspond in number with the subject, and misplaced modifiers that cause confusion about which part of the sentence is being described. Another frequent issue is the presence of sentence fragments lacking either a clear subject or predicate, resulting in incomplete thoughts. Correct identification of compound subjects and predicates also poses challenges, often leading to improper comma usage or run-on sentences.
Importance of Subjects and Predicates in Sentences
Subjects and predicates form the foundation of sentence structure, with subjects identifying the main topic and predicates providing essential information about the subject's actions or state. The clarity and meaning of sentences depend on the precise relationship between subjects and predicates, enabling effective communication and comprehension. Mastery of subjects and predicates is crucial for constructing grammatically correct and semantically rich sentences in English grammar.
Subject and Predicate Examples in Sentences
The subject in a sentence represents who or what the sentence is about, while the predicate explains what the subject does or is. For example, in the sentence "The cat sleeps on the couch," "The cat" is the subject and "sleeps on the couch" is the predicate. Another example is "She reads books," where "She" serves as the subject and "reads books" is the predicate.
Subject Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com