The principle of humanity emphasizes the inherent dignity and respect owed to every individual, guiding ethical behavior and decision-making in various fields, including humanitarian aid and international relations. It requires prioritizing human welfare and rights above political, economic, or strategic interests. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this principle shapes policies and actions worldwide.
Table of Comparison
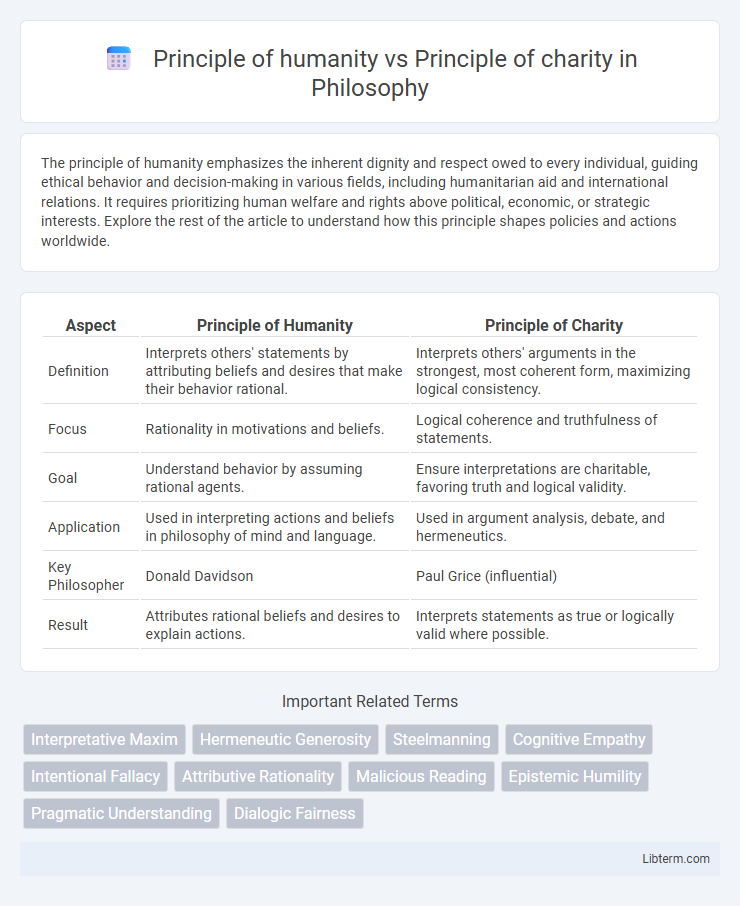
| Aspect | Principle of Humanity | Principle of Charity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interprets others' statements by attributing beliefs and desires that make their behavior rational. | Interprets others' arguments in the strongest, most coherent form, maximizing logical consistency. |
| Focus | Rationality in motivations and beliefs. | Logical coherence and truthfulness of statements. |
| Goal | Understand behavior by assuming rational agents. | Ensure interpretations are charitable, favoring truth and logical validity. |
| Application | Used in interpreting actions and beliefs in philosophy of mind and language. | Used in argument analysis, debate, and hermeneutics. |
| Key Philosopher | Donald Davidson | Paul Grice (influential) |
| Result | Attributes rational beliefs and desires to explain actions. | Interprets statements as true or logically valid where possible. |
Introduction to the Principle of Humanity and Principle of Charity
The Principle of Humanity emphasizes understanding others by interpreting their statements and actions in the most compassionate and empathetic manner, recognizing their intentions and context. The Principle of Charity requires interpreting another person's argument in the strongest, most rational form possible, often assuming logical coherence and truthfulness to foster constructive dialogue. Together, these principles guide effective communication by balancing empathy with intellectual generosity, enhancing mutual understanding.
Defining the Principle of Humanity
The Principle of Humanity requires interpreting others' statements in a way that assumes their beliefs and desires make sense within their own context, emphasizing empathetic understanding rather than strict logical correctness. This principle guides one to portray an interlocutor's view sympathetically and coherently, acknowledging their intentions and experiences. It contrasts with the Principle of Charity, which focuses more narrowly on reconstructing statements to maximize logical coherence and truthfulness.
Defining the Principle of Charity
The Principle of Charity requires interpreting a speaker's statements in the most rational and coherent way possible, attributing to them the strongest possible argument to avoid misunderstanding. It aims to reconstruct arguments to ensure they are logically consistent and reflect the speaker's intended meaning, often filling gaps in incomplete reasoning. This principle contrasts with the Principle of Humanity, which emphasizes attributing beliefs and desires similar to our own to others, but the Principle of Charity specifically focuses on enhancing argumentative clarity and logical strength.
Origins and Philosophical Background
The Principle of Humanity originates from a moral philosophy tradition emphasizing empathic understanding by interpreting others' statements in the most rational and coherent way possible, acknowledging their beliefs and intentions. In contrast, the Principle of Charity stems from analytic philosophy and hermeneutics, particularly rooted in the work of philosophers like David Hume and Donald Davidson, advocating for interpreting others' arguments in the strongest, most persuasive form to avoid misunderstandings. Both principles serve to promote constructive dialogue by assuming others' rationality, yet they differ in focus--humanity prioritizes sincere comprehension, while charity emphasizes intellectual generosity.
Key Differences Between Humanity and Charity Principles
The Principle of Humanity emphasizes interpreting others' statements to reveal their true beliefs and intentions, aiming to avoid misrepresentation of their viewpoint. In contrast, the Principle of Charity instructs interpreters to adopt the most rational and coherent understanding of a statement, often attributing logical consistency and truth to the speaker's claims. Key differences include that humanity focuses on understanding the speaker's actual perspective based on context, while charity prioritizes maximizing rationality and truthfulness to foster constructive interpretation.
Applications in Argument Interpretation
The Principle of Humanity in argument interpretation emphasizes attributing rationality and coherence to the speaker's beliefs and intentions, ensuring their argument is understood in the most reasonable light. The Principle of Charity requires interpreting arguments by maximizing truth and logical consistency to avoid misunderstanding and unfair critique. Applying these principles enhances constructive dialogue by fostering empathy and clarity, facilitating more accurate and fair evaluations of opposing viewpoints.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Principle
The Principle of Humanity emphasizes understanding an argument by considering the intentions and beliefs of the speaker, promoting empathy and reducing misinterpretation but risks subjective bias and overlooking logical flaws. The Principle of Charity aims to interpret arguments in their strongest, most rational form, enhancing clarity and constructive critique while potentially attributing undue strength to weak or flawed positions. Both principles support effective communication and rational analysis but require careful balance to avoid distortion or misrepresentation of the original argument.
Real-world Examples and Case Studies
The principle of humanity requires interpreting others' statements in a way that acknowledges their beliefs and intentions as reasonable and coherent, often applied in diplomatic negotiations where understanding an adversary's perspective prevents escalation. Case studies in intercultural communication demonstrate that applying the principle of charity--interpreting arguments in their strongest, most persuasive form--facilitates conflict resolution by fostering mutual respect and accurate comprehension. Real-world examples include legal disputes where judges use the principle of charity to fairly assess the strength of opposing arguments, ensuring just outcomes based on fair interpretation rather than adversarial bias.
Impact on Effective Communication and Discourse
The Principle of Humanity enhances effective communication by encouraging empathy and understanding of others' intentions, fostering a respectful and constructive dialogue. The Principle of Charity improves discourse quality by interpreting arguments in their strongest, most coherent form, reducing misunderstandings and promoting intellectual honesty. Together, these principles create a balanced framework that supports meaningful exchanges and minimizes conflict in discussions.
Conclusion: Balancing Humanity and Charity in Interpretation
Balancing the Principle of Humanity and the Principle of Charity in interpretation requires recognizing the speaker's intentions while ensuring their arguments are as rational and coherent as possible. Applying the Principle of Humanity involves attributing beliefs and desires similar to our own to understand the speaker sincerely, while the Principle of Charity demands interpreting statements in their strongest, most logical form. Effective interpretation hinges on harmonizing these principles to foster accurate, empathetic understanding without distorting the original meaning.
Principle of humanity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com