Dogmatism restricts open-minded thinking by rigidly adhering to established beliefs without considering alternative perspectives. This inflexible mindset can hinder personal growth and critical reasoning by dismissing contradictory evidence or ideas. Explore the rest of this article to understand how overcoming dogmatism can enhance Your intellectual flexibility and decision-making skills.
Table of Comparison
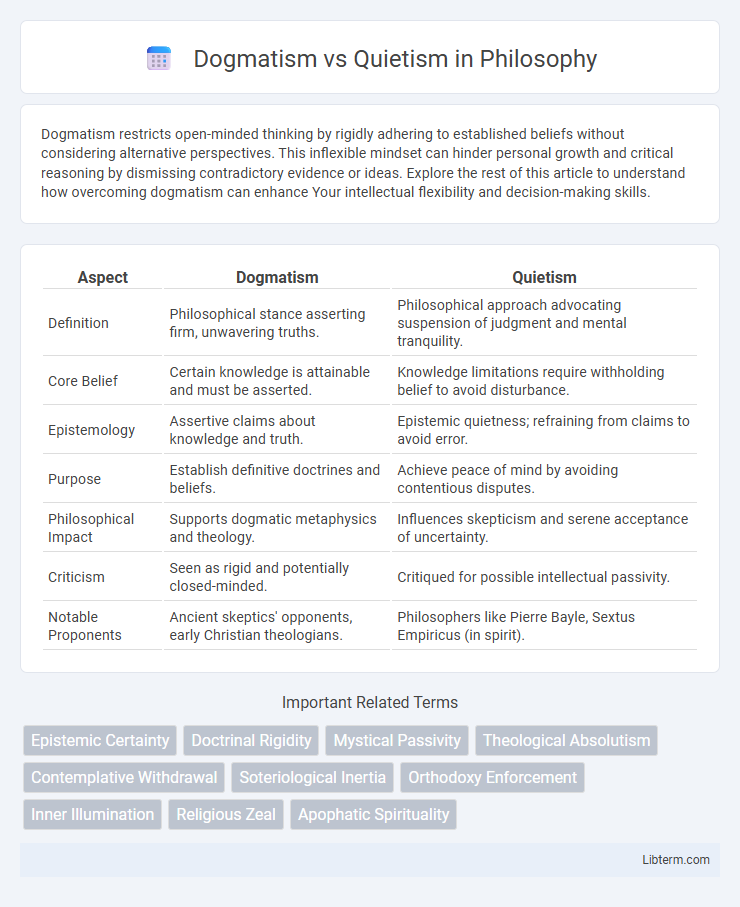
| Aspect | Dogmatism | Quietism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical stance asserting firm, unwavering truths. | Philosophical approach advocating suspension of judgment and mental tranquility. |
| Core Belief | Certain knowledge is attainable and must be asserted. | Knowledge limitations require withholding belief to avoid disturbance. |
| Epistemology | Assertive claims about knowledge and truth. | Epistemic quietness; refraining from claims to avoid error. |
| Purpose | Establish definitive doctrines and beliefs. | Achieve peace of mind by avoiding contentious disputes. |
| Philosophical Impact | Supports dogmatic metaphysics and theology. | Influences skepticism and serene acceptance of uncertainty. |
| Criticism | Seen as rigid and potentially closed-minded. | Critiqued for possible intellectual passivity. |
| Notable Proponents | Ancient skeptics' opponents, early Christian theologians. | Philosophers like Pierre Bayle, Sextus Empiricus (in spirit). |
Understanding Dogmatism: Definition and Origins
Dogmatism refers to the unwavering adherence to beliefs or doctrines without critical examination, often rooted in historical philosophical or religious contexts. Originating from ancient Greek philosophy, particularly linked to the Stoics and later developed through medieval scholasticism, dogmatism emphasizes authoritative knowledge that resists skepticism. This rigidity in thought contrasts with the flexible, non-assertive stance of quietism, highlighting dogmatism's insistence on definitive truth claims.
The Core Principles of Quietism
Quietism centers on the core principles of inner peace, spiritual passivity, and complete surrender to divine will, emphasizing detachment from worldly desires and ego-driven actions. It advocates for a contemplative life where the individual refrains from intrusive reasoning or dogmatic assertions, seeking instead to align with a higher, ineffable truth through silence and stillness. This approach contrasts sharply with dogmatism, which rigidly adheres to fixed doctrines and asserts absolute certainty in beliefs.
Historical Context: Dogmatism vs Quietism
Dogmatism emerged prominently during the Enlightenment as a rigid adherence to established doctrines, often resisting new ideas and critical inquiry. Quietism developed in the 17th century as a spiritual movement emphasizing inner tranquility and passive contemplation, rejecting active theological debate and external religious authority. The historical conflict between Dogmatism and Quietism reflects the broader tension between assertive doctrinal certainty and the pursuit of inner spiritual peace.
Philosophical Foundations of Dogmatism
Dogmatism in philosophy is grounded in the belief that certain foundational truths are known with certainty and must be accepted without doubt, often relying on a priori reasoning and established doctrines. This stance asserts that knowledge is attainable through definitive principles, contrasting with skeptical approaches that question the possibility of certainty. Dogmatism upholds metaphysical and epistemological commitments that serve as the basis for further philosophical inquiry and knowledge claims.
Roots and Influences of Quietism in Philosophy
Quietism in philosophy, emerging primarily through the works of Pierre Bayle and later Ludwig Wittgenstein, roots itself in skepticism and the rejection of contentious metaphysical speculation. It emphasizes the suspension of judgment and advocates for intellectual tranquility by avoiding dogmatic assertions. This philosophical stance contrasts with dogmatism, which upholds absolute, rigid beliefs, often influenced by earlier rationalist and scholastic traditions.
Key Differences Between Dogmatism and Quietism
Dogmatism asserts firm beliefs and principles often resistant to change, emphasizing certainty and unwavering conviction. Quietism advocates for passive acceptance and suspension of judgment, promoting inner peace through detachment from contentious debates or rigid doctrines. The key difference lies in dogmatism's active affirmation of specific truths versus quietism's deliberate avoidance of definitive stances to maintain tranquility.
Impact on Religious and Ethical Thought
Dogmatism enforces strict adherence to established religious doctrines, often limiting open interpretation and hindering ethical pluralism, which can result in rigid moral frameworks. Quietism encourages spiritual passivity and inward contemplation, promoting a more individualized and flexible approach to ethics but sometimes leading to disengagement from active moral discourse. The tension between dogmatism and quietism shapes religious thought by balancing authoritative teaching with personal spiritual experience, impacting how ethical principles are internalized and practiced.
Dogmatism in Contemporary Debates
Dogmatism in contemporary debates is characterized by an unwavering adherence to beliefs despite counterarguments, often hindering constructive dialogue and intellectual progress. It manifests in political polarization, where rigid ideologies prevent compromise and deepen societal divisions. This inflexibility contrasts with quietism, which advocates for restraint and acceptance, though critics argue dogmatism exacerbates conflicts by rejecting alternative perspectives.
Quietism’s Relevance in Modern Society
Quietism's relevance in modern society emerges from its emphasis on inner tranquility and acceptance amidst contemporary stress and rapid change. By promoting detachment from external controversies and rigid beliefs, Quietism encourages mental clarity and emotional resilience. This philosophical approach offers practical strategies for reducing anxiety and fostering well-being in an increasingly polarized and fast-paced world.
Striking a Balance: Navigating Between Dogmatism and Quietism
Striking a balance between dogmatism and quietism involves maintaining strong convictions while remaining open to alternative perspectives and constructive dialogue. Embracing a flexible mindset prevents the rigidity of dogmatism and counters the passivity of quietism, fostering critical thinking and meaningful engagement. Navigating this middle path enhances personal growth, promotes tolerance, and supports effective decision-making in complex situations.
Dogmatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com