Self-identity shapes how you perceive yourself and influences your interactions with others, while otherness highlights differences that distinguish groups and individuals. Understanding the dynamics between self-identity and otherness is crucial for fostering empathy and social cohesion. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your insight into these complex concepts and their impact on human relationships.
Table of Comparison
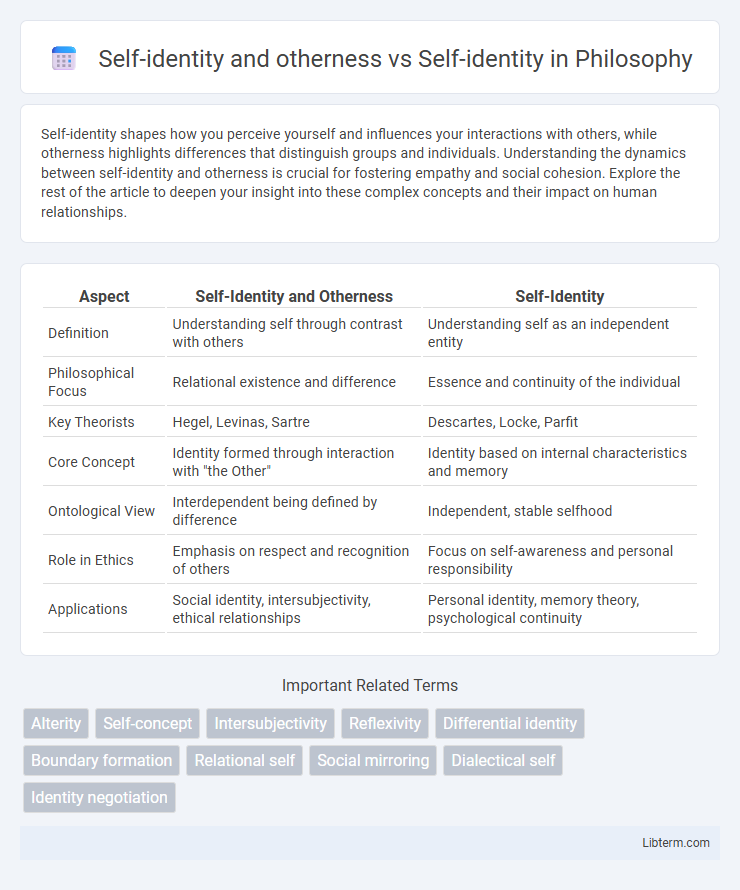
| Aspect | Self-Identity and Otherness | Self-Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding self through contrast with others | Understanding self as an independent entity |
| Philosophical Focus | Relational existence and difference | Essence and continuity of the individual |
| Key Theorists | Hegel, Levinas, Sartre | Descartes, Locke, Parfit |
| Core Concept | Identity formed through interaction with "the Other" | Identity based on internal characteristics and memory |
| Ontological View | Interdependent being defined by difference | Independent, stable selfhood |
| Role in Ethics | Emphasis on respect and recognition of others | Focus on self-awareness and personal responsibility |
| Applications | Social identity, intersubjectivity, ethical relationships | Personal identity, memory theory, psychological continuity |
Understanding Self-Identity: Core Concepts
Self-identity encompasses an individual's sense of who they are, shaped by personal beliefs, values, and experiences that create a coherent self-concept. Understanding self-identity involves exploring how internal perceptions and external social interactions affirm or challenge this self-concept. The concept of otherness highlights differences perceived between oneself and others, which plays a crucial role in defining and negotiating one's self-identity through contrast and relational dynamics.
Defining Otherness in Personal Development
Defining otherness in personal development involves recognizing and embracing differences that distinguish the self from others, fostering deeper self-awareness and growth. This process highlights how encountering otherness challenges fixed self-identity, prompting critical reflection and adaptive change. Understanding otherness as a dynamic relational concept enriches personal identity by integrating diverse perspectives into self-construction.
Self-Identity vs Otherness: Key Differences
Self-identity refers to an individual's perception and understanding of their own unique characteristics, beliefs, and values, forming a coherent sense of self. Otherness denotes the recognition of difference, highlighting qualities that distinguish oneself from others or groups, often shaping social dynamics and interpersonal relationships. The key difference lies in self-identity's internal focus on self-definition, while otherness emphasizes external comparison and distinction between the self and the "other.
The Role of Society in Shaping Self-Identity
Society plays a crucial role in shaping self-identity by influencing individuals through cultural norms, social expectations, and group affiliations, which contribute to a sense of belonging or otherness. Social institutions such as family, education, and media help construct identity by reinforcing certain values and roles while marginalizing others, creating clear distinctions between self and other. This dynamic interaction shapes personal identity by negotiating acceptance within social frameworks and managing the experience of otherness as a counterpoint to self-recognition.
Interpersonal Relationships and the Concept of Otherness
Self-identity in interpersonal relationships shapes how individuals perceive themselves in relation to others, influencing communication and empathy. The concept of otherness highlights differences that affect social connection and can either create barriers or foster understanding. Recognizing otherness within self-identity promotes deeper interpersonal bonds and social cohesion.
Self-Identity in the Age of Social Media
Self-identity in the age of social media is shaped by the continuous interaction between personal expression and public perception, where curated online personas influence self-concept and self-worth. The digital environment amplifies the tension between authentic self-identity and the fragmented selves presented across multiple platforms, often leading to identity negotiation and redefinition. This dynamic process highlights the impact of social validation, peer feedback, and algorithm-driven content on the construction and evolution of self-identity.
Navigating Self-Perception and External Influence
Navigating self-perception and external influence involves balancing one's internal sense of self-identity against perceptions imposed by others, highlighting the dynamic interplay between personal authenticity and social recognition. The concept of otherness challenges individuals to reconcile differences and stereotypes that shape external judgments, which can either affirm or distort self-identity. Understanding this tension is crucial in identity formation, as it affects psychological well-being and social integration within diverse communities.
Embracing Diversity: The Value of Otherness
Self-identity is shaped through the recognition of otherness, highlighting the importance of diverse experiences and perspectives in defining the self. Embracing diversity fosters empathy and broadens understanding, allowing individuals to appreciate cultural, social, and personal differences. This dynamic interaction between self-identity and otherness enriches personal growth and promotes inclusive communities.
Challenges in Balancing Self-Identity and Otherness
Balancing self-identity and otherness presents challenges such as negotiating personal authenticity while respecting cultural and social differences. Individuals often face internal conflicts when their sense of self clashes with external expectations or stereotypes imposed by others. These tensions can lead to identity fragmentation, requiring continuous reflection and adaptation to maintain psychological coherence and social harmony.
Building Resilient Identities in a Diverse World
Building resilient identities in a diverse world requires integrating self-identity with an understanding of otherness, fostering empathy and adaptability across cultural boundaries. Recognizing the dynamic interplay between personal values and external perspectives enhances psychological resilience and social cohesion. Strategies emphasizing inclusive self-awareness support individuals in navigating diversity while maintaining a strong, coherent sense of self.
Self-identity and otherness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com