Self-identity shapes how you perceive yourself, encompassing personal beliefs, values, and experiences that define your unique individuality. Social identity arises from the groups and communities you belong to, influencing your behavior and sense of belonging through shared norms and roles. Explore the interplay between these identities to understand how they impact your interactions and self-perception in various social contexts.
Table of Comparison
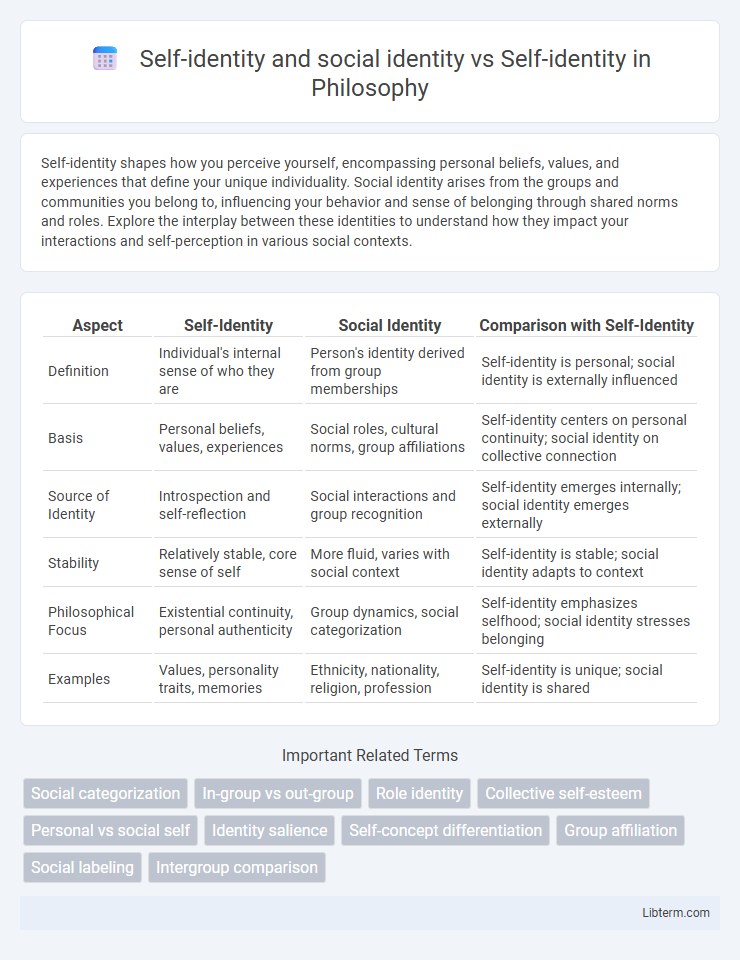
| Aspect | Self-Identity | Social Identity | Comparison with Self-Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual's internal sense of who they are | Person's identity derived from group memberships | Self-identity is personal; social identity is externally influenced |
| Basis | Personal beliefs, values, experiences | Social roles, cultural norms, group affiliations | Self-identity centers on personal continuity; social identity on collective connection |
| Source of Identity | Introspection and self-reflection | Social interactions and group recognition | Self-identity emerges internally; social identity emerges externally |
| Stability | Relatively stable, core sense of self | More fluid, varies with social context | Self-identity is stable; social identity adapts to context |
| Philosophical Focus | Existential continuity, personal authenticity | Group dynamics, social categorization | Self-identity emphasizes selfhood; social identity stresses belonging |
| Examples | Values, personality traits, memories | Ethnicity, nationality, religion, profession | Self-identity is unique; social identity is shared |
Understanding Self-Identity: Definition and Core Concepts
Self-identity refers to an individual's conscious understanding and perception of their own unique characteristics, beliefs, values, and experiences that define who they are independently. Social identity, by contrast, is derived from group memberships and social categories such as nationality, ethnicity, or occupation, influencing how individuals relate to others and see their place within societal structures. Understanding self-identity involves exploring core concepts like self-concept, self-esteem, and personal agency, emphasizing internal coherence and self-reflection beyond external social affiliations.
Exploring Social Identity: Meaning and Key Components
Social identity refers to the part of an individual's self-concept derived from membership in social groups such as nationality, ethnicity, or profession, emphasizing group belonging and shared characteristics. Key components of social identity include categorization, identification, and comparison, which influence how individuals perceive themselves and others within a social context. Self-identity, in contrast, encompasses a broader sense of personal uniqueness and individual traits beyond group affiliations.
Key Differences Between Self-Identity and Social Identity
Self-identity refers to an individual's internal perception and understanding of their own unique characteristics, values, and beliefs, while social identity is derived from group memberships and the social categories one belongs to, such as ethnicity, nationality, or profession. Key differences include the source of identity construction: self-identity is shaped by personal experiences and introspection, whereas social identity is influenced by external social contexts and group dynamics. Self-identity emphasizes individuality and personal continuity, whereas social identity highlights collective membership and social roles.
The Interplay Between Self-Identity and Social Identity
The interplay between self-identity and social identity shapes individual behavior by linking personal beliefs and values with social roles and group memberships. Self-identity encompasses personal traits and self-concepts, while social identity derives from affiliations such as ethnicity, gender, and cultural groups. This dynamic interaction influences how individuals perceive themselves and are perceived by others, affecting social interactions, group cohesion, and psychological well-being.
How Self-Identity Shapes Personal Experiences
Self-identity profoundly shapes personal experiences by influencing individual perceptions, decisions, and emotional responses, as it encompasses the core beliefs and values defining who one is. Unlike social identity, which is derived from group affiliations and societal roles, self-identity centers on internal self-concept and personal agency. This intrinsic sense of self guides behavior and interpretation of events, making personal experiences unique and deeply subjective.
The Influence of Social Identity on Group Behaviors
Social identity significantly shapes group behaviors by influencing individuals' sense of belonging and adherence to group norms, which reinforces collective cohesion and drives cooperative actions. Self-identity interacts dynamically with social identity, as personal values and beliefs are often aligned or contrasted with group expectations to maintain social harmony or assert individuality. This interaction affects decision-making, conformity, and intergroup relations, highlighting the powerful role of social identity in guiding behavior within group contexts.
Factors Shaping Self-Identity vs Social Identity
Self-identity is primarily shaped by internal factors such as personal values, beliefs, and individual experiences, while social identity is influenced by external factors including group memberships, cultural norms, and social roles. Psychological processes like self-reflection and cognitive development contribute to self-identity formation, whereas social identity emerges from interaction with societal structures and collective affiliations. The dynamic interplay between internal self-perceptions and social categorization processes underscores the complexity of how individuals perceive themselves within both personal and communal contexts.
Challenges in Balancing Self-Identity and Social Identity
Balancing self-identity and social identity presents significant challenges as individuals navigate personal values alongside societal expectations. Conflicts often arise when social roles demand conformity, risking the suppression of authentic self-expressions which can lead to identity confusion and reduced psychological well-being. Effective strategies for maintaining this balance include developing self-awareness and resilience while fostering social support systems that respect individual differences.
The Role of Culture in Identity Formation
Culture plays a pivotal role in shaping both self-identity and social identity by providing shared beliefs, values, and practices that influence how individuals perceive themselves and relate to others. Self-identity is formed through personal experiences and introspection, yet it is deeply embedded in the cultural context that frames individual meaning and self-concept. Social identity emerges from group memberships and cultural affiliations, reflecting collective norms and fostering a sense of belonging within cultural communities.
Strengthening Self-Identity Within Social Contexts
Strengthening self-identity within social contexts involves integrating personal values and beliefs while navigating external social roles and expectations. This process enhances psychological resilience by fostering a coherent sense of self that adapts yet remains authentic amid diverse social interactions. Research in social psychology emphasizes the importance of reflective self-awareness and meaningful group affiliations for developing a stable self-identity that supports mental well-being and social connectedness.
Self-identity and social identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com