Self-contradictory statements create confusion by asserting two opposing ideas simultaneously, undermining the clarity and reliability of the message. Recognizing these contradictions is essential for effective communication and critical thinking. Explore the rest of this article to understand how to identify and avoid self-contradictory expressions in your writing.
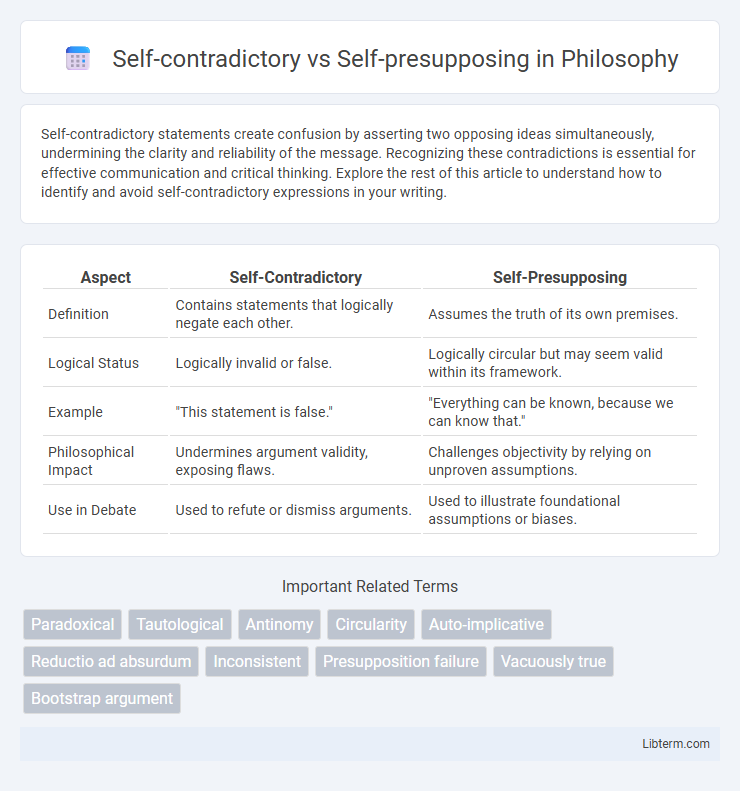
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Self-Contradictory | Self-Presupposing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contains statements that logically negate each other. | Assumes the truth of its own premises. |
| Logical Status | Logically invalid or false. | Logically circular but may seem valid within its framework. |
| Example | "This statement is false." | "Everything can be known, because we can know that." |
| Philosophical Impact | Undermines argument validity, exposing flaws. | Challenges objectivity by relying on unproven assumptions. |
| Use in Debate | Used to refute or dismiss arguments. | Used to illustrate foundational assumptions or biases. |
Understanding Self-Contradictory Statements
Self-contradictory statements contain inherent logical conflicts that render them impossible to be true under any interpretation, such as "This statement is false." Understanding self-contradictory statements involves identifying contradictions within the statement itself that violate basic principles of logic, leading to inconsistency and meaninglessness. Unlike self-presupposing statements, which require certain assumptions to hold true for the statement to make sense, self-contradictory statements negate their own validity by simultaneously affirming and denying the same proposition.
Defining Self-Presupposing Statements
Self-presupposing statements inherently assume the truth of a proposition within the statement itself, creating a backdrop that must be accepted for the statement to hold meaning. Unlike self-contradictory statements, which contain internal logical inconsistencies rendering them false, self-presupposing statements depend on implicit assumptions that are taken for granted by the speaker and listener. Understanding this distinction is crucial in fields like linguistics and logic, where analyzing language structure and meaning hinges on identifying such presuppositions.
Key Differences Between Self-Contradictory and Self-Presupposing
Self-contradictory statements inherently negate themselves, creating a logical impossibility, such as "I am both alive and not alive." Self-presupposing statements assume the truth of a condition without explicitly stating it, like "Jane stopped smoking," which presupposes that Jane once smoked. The key difference lies in self-contradiction invalidating the statement outright, whereas self-presupposition embeds implicit assumptions critical for understanding the statement's meaning.
Common Examples of Self-Contradictory Sentences
Self-contradictory sentences contain inherently conflicting elements that make them logically impossible, such as "I always lie" or "This sentence is false." These sentences cannot be true under any interpretation because their statements negate themselves. In contrast, self-presupposing sentences assume the truth of certain conditions or background information, maintaining internal coherence without logical impossibility.
Illustrative Cases of Self-Presupposing Propositions
Self-presupposing propositions inherently assume the truth of a subordinate statement within their structure, such as "The king of France is bald," which presupposes the existence of a king of France. Illustrative cases include statements like "John stopped smoking," presupposing that John previously smoked, highlighting how meaning depends on accepted background information. These cases contrast with self-contradictory propositions, which contain elements that directly negate each other, making their truth conditions logically impossible.
The Role of Logic in Identifying Contradictions
Self-contradictory statements contain inherent logical inconsistencies, making them universally false under any interpretation, while self-presupposing statements depend on assumptions that must hold true for the statement to be meaningful. Logic plays a crucial role in identifying contradictions by applying formal rules and semantic analysis to detect statements that violate the principle of non-contradiction. Through techniques such as truth tables and predicate logic, logical frameworks systematically reveal inconsistencies, ensuring clarity and coherence in argumentation.
Implications of Self-Presupposition in Reasoning
Self-presupposition in reasoning implies that certain assumptions are inherently accepted before any argument progresses, impacting the validity and soundness of conclusions drawn. Unlike self-contradictory statements which invalidate an argument by presenting opposing ideas simultaneously, self-presupposing premises shape the framework within which reasoning occurs, potentially limiting objectivity and introducing bias. Recognizing self-presuppositions is crucial for critical thinking, as it reveals underlying beliefs that affect interpretation and assessment of evidence in logical discourse.
How Self-Contradictions Undermine Arguments
Self-contradictions occur when statements within an argument oppose each other, leading to logical inconsistencies that invalidate the overall claim. This undermining effect damages the argument's credibility, making it difficult for audiences to accept conclusions that are based on contradictory premises. In contrast, self-presupposing statements assume certain conditions without contradiction, allowing arguments to build coherently on an accepted foundation.
Recognizing Presuppositions in Everyday Language
Recognizing presuppositions in everyday language involves identifying statements that inherently assume certain facts or beliefs are true before the main assertion is made, distinguishing them from self-contradictory statements that negate their own claims and create logical inconsistency. Self-presupposing utterances rely on implicit background assumptions, such as "John stopped smoking," presupposing John once smoked, while self-contradictory expressions, like "I always lie," undermine their own validity by introducing paradoxes. Effective language comprehension requires differentiating these concepts to understand implicit meanings and avoid misinterpretations in communication.
Practical Applications: Avoiding Logical Pitfalls
Self-contradictory statements inherently conflict with themselves, making them logically untenable and easy to identify and avoid in practical reasoning or debate. Self-presupposing statements, however, rely on background assumptions that must be accepted for the statement to hold true, requiring careful analysis to uncover implicit biases or hidden premises. Recognizing and differentiating these logical pitfalls enhances critical thinking skills and improves decision-making in fields such as law, philosophy, and artificial intelligence.
Self-contradictory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com