Subject and predicate form the foundation of every complete sentence by establishing who or what performs the action and what action or state is described. Understanding how the subject identifies the main focus while the predicate provides essential information enables clearer and more effective communication. Explore the rest of this article to master the essential components of sentence structure and enhance your writing skills.
Table of Comparison
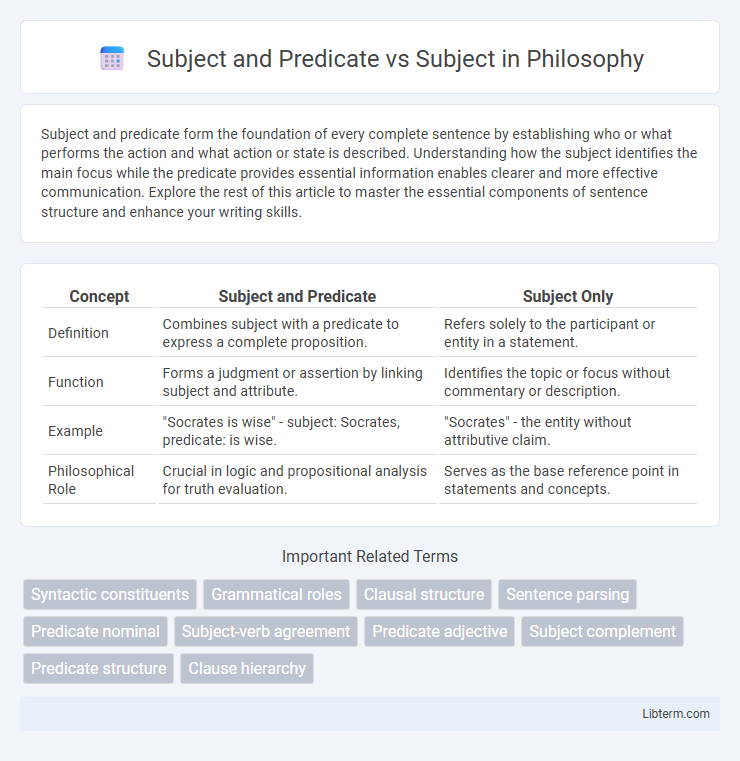
| Concept | Subject and Predicate | Subject Only |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines subject with a predicate to express a complete proposition. | Refers solely to the participant or entity in a statement. |
| Function | Forms a judgment or assertion by linking subject and attribute. | Identifies the topic or focus without commentary or description. |
| Example | "Socrates is wise" - subject: Socrates, predicate: is wise. | "Socrates" - the entity without attributive claim. |
| Philosophical Role | Crucial in logic and propositional analysis for truth evaluation. | Serves as the base reference point in statements and concepts. |
Understanding Subjects and Predicates
Subjects identify who or what the sentence is about, serving as the sentence's main focus, while predicates describe the action or state of the subject. Understanding the distinction between subject and predicate is crucial for mastering sentence structure and grammar. Clear recognition of subjects and predicates enhances comprehension and effective communication in English.
Defining the Subject in a Sentence
The subject in a sentence is the noun, pronoun, or phrase that performs the action or is described by the predicate, serving as the sentence's main focus. Understanding the subject involves identifying who or what the sentence is about, which is essential for grasping the sentence's meaning and structure. Clear subject identification supports accurate sentence analysis and effective communication in English grammar.
What is a Predicate?
A predicate is the part of a sentence that expresses what is said about the subject, including the verb and any objects or modifiers. It provides essential information such as actions, states, or descriptions related to the subject. Understanding the predicate is crucial for sentence structure analysis, as it complements the subject to convey complete meaning.
Subject vs. Subject and Predicate: Key Differences
Subject identifies who or what performs the action or is described, while Subject and Predicate together form the complete thought, with the predicate providing information about the subject's action or state. The subject alone can be a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase, whereas the predicate always contains a verb that conveys the action or condition. Understanding the distinction is crucial for constructing clear and grammatically correct sentences in English syntax.
The Role of the Subject in Sentence Structure
The subject functions as the central element in sentence structure, representing the person, place, thing, or idea performing the action or being described. It establishes the basis for agreement with the predicate, which provides information about the subject's action or state of being. Understanding the distinct roles of the subject and predicate is essential for constructing clear, grammatically accurate sentences that convey precise meaning.
The Role of the Predicate in Sentence Structure
The predicate plays a crucial role in sentence structure by providing essential information about the subject, such as actions, states, or attributes. Unlike the subject, which identifies who or what the sentence is about, the predicate conveys what the subject does or is. Understanding the predicate's function improves sentence clarity and grammatical accuracy in both simple and complex sentences.
Examples: Identifying Subjects and Predicates
In the sentence "The cat sleeps," "The cat" is the subject, and "sleeps" is the predicate, illustrating the basic division of a sentence into who or what performs the action and what is said about the subject. For more complex examples, "The smart student studies diligently" highlights "The smart student" as the subject and "studies diligently" as the predicate, demonstrating how predicates can include verbs and modifiers to provide more information. Understanding how to identify subjects and predicates helps in analyzing sentence structure, improving grammar skills, and constructing clear, meaningful sentences.
Common Errors with Subjects and Predicates
Confusing the subject with the complete predicate or failing to identify the subject correctly leads to common grammatical errors such as subject-verb disagreement. Omitting the subject in sentences, especially in imperative moods, can create ambiguity, while including extraneous information mistakenly as part of the subject affects clarity. Mastery of distinguishing the subject (the doer or focus of the sentence) from the predicate (the action or description about the subject) ensures proper sentence structure and improves overall writing precision.
Importance of Both Elements for Complete Sentences
The subject and predicate are essential components of a complete sentence, where the subject identifies who or what the sentence is about, and the predicate provides information about the subject's action or state. Without a predicate, a subject cannot form a meaningful statement, and without a subject, the predicate lacks clarity about whom or what it describes. Both elements work together to convey a complete thought, making their presence vital for grammatical accuracy and effective communication.
Tips for Teaching Subjects and Predicates
Clear emphasis on distinguishing subjects and predicates helps students grasp sentence structure fundamentals. Using visual aids and sentence diagramming clarifies how subjects identify "who" or "what" the sentence is about, while predicates describe actions or states of being related to the subject. Interactive exercises focusing separately on subject identification and predicate recognition enhance comprehension and create stronger language foundation.
Subject and Predicate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com