Constitutive refers to something that forms an essential part or aspect of a system, structure, or concept, often implying that it is a fundamental element without which the whole cannot exist. In biology, it describes genes or enzymes that are continually active, regardless of environmental conditions. Explore this article to uncover how constitutive functions shape various fields and influence your understanding.
Table of Comparison
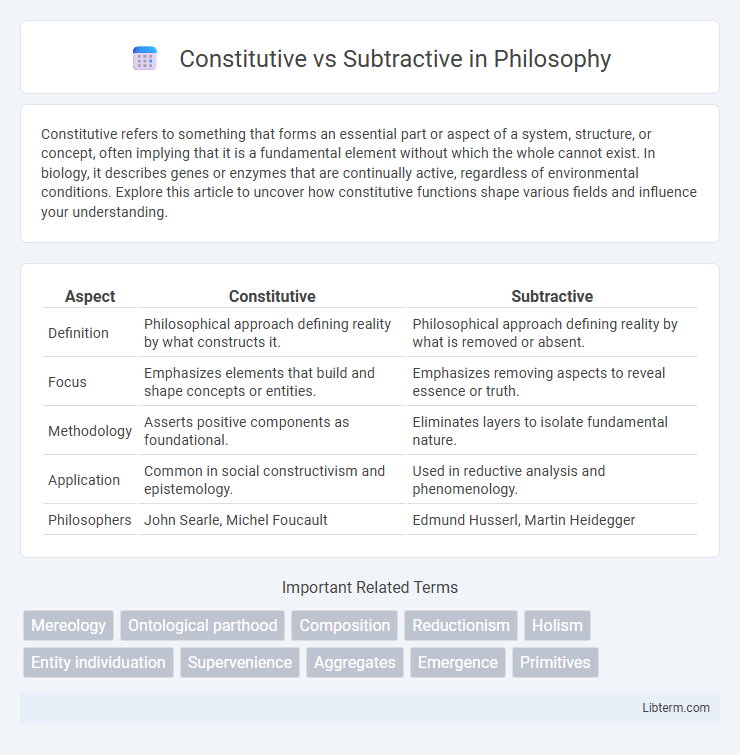
| Aspect | Constitutive | Subtractive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical approach defining reality by what constructs it. | Philosophical approach defining reality by what is removed or absent. |
| Focus | Emphasizes elements that build and shape concepts or entities. | Emphasizes removing aspects to reveal essence or truth. |
| Methodology | Asserts positive components as foundational. | Eliminates layers to isolate fundamental nature. |
| Application | Common in social constructivism and epistemology. | Used in reductive analysis and phenomenology. |
| Philosophers | John Searle, Michel Foucault | Edmund Husserl, Martin Heidegger |
Introduction to Constitutive and Subtractive Approaches
Constitutive and subtractive approaches represent two fundamental methods in system design and analysis, where constitutive focuses on building systems by defining core components and their interactions, while subtractive involves simplifying existing systems by removing elements to understand essential functions. The constitutive approach emphasizes the creation and integration of parts to form a coherent whole, often used in disciplines like biology, engineering, and cognitive science. In contrast, the subtractive approach aids in isolating critical features by systematically eliminating non-essential components, facilitating deeper insights into system mechanics and behavior.
Defining Constitutive Processes
Constitutive processes involve the formation and continuous development of social or organizational structures through ongoing interactions and practices that give meaning and shape to the entity. These processes establish the foundational components and norms that define the existence and identity of the system over time. Understanding constitutive processes provides insight into how entities are actively created and maintained rather than passively altered.
Understanding Subtractive Processes
Subtractive processes involve removing material from a solid block using techniques such as milling, turning, or drilling to shape the final product. These methods rely on computer numerical control (CNC) machines for precision and are commonly used in manufacturing industries for metal, plastic, and wood components. Understanding subtractive manufacturing requires knowledge of tool paths, cutting speeds, and material properties to optimize efficiency and surface finish quality.
Key Differences Between Constitutive and Subtractive
Constitutive and subtractive methods differ primarily in their approach to material formation: constitutive processes build up material layers to create an object, such as 3D printing, while subtractive processes involve removing material from a solid block, like CNC machining. Constitutive techniques offer greater flexibility and complexity in design, whereas subtractive methods provide higher precision and surface finish quality. Understanding these distinctions is critical for selecting the optimal manufacturing strategy based on project requirements, material properties, and production volume.
Examples of Constitutive Approaches in Practice
Constitutive approaches emphasize the role of rules and norms in shaping social and political orders, exemplified by treaty agreements like the United Nations Charter, which establishes principles guiding member states' behavior. In international relations, constitutive practices manifest through the creation of institutions such as the European Union, where shared norms and legal frameworks define member interactions. These examples illustrate how constitutive methods form the foundation for collective identity and governance by establishing essential rules rather than merely limiting actions.
Real-World Applications of Subtractive Methods
Subtractive methods are widely applied in manufacturing processes such as CNC machining, where material is precisely removed from a solid block to create intricate components used in aerospace and automotive industries. These techniques support high accuracy and repeatability, essential for producing parts with tight tolerances like turbine blades and engine components. The ability to fabricate complex geometries from metal, plastic, and composite materials through milling, turning, and drilling underscores subtractive methods' critical role in industrial production.
Advantages of Constitutive Approaches
Constitutive approaches offer advantages by emphasizing the formation and identity of entities through specific defining features, enabling clearer classification and understanding of complex systems. These approaches enhance semantic precision and facilitate consistent categorization in knowledge representation frameworks, supporting more accurate reasoning and interoperability in artificial intelligence applications. By focusing on intrinsic properties, constitutive methods reduce ambiguity and improve the robustness of data modeling, especially in ontology development and concept formalization.
Benefits and Limitations of Subtractive Approaches
Subtractive approaches in design and manufacturing focus on removing material to create a final product, offering benefits such as high precision, suitability for hard materials, and established industry standards. Limitations include material waste, longer production times for complex geometries, and restrictions in creating internal features compared to additive methods. Efficient use of subtractive techniques requires balancing these advantages with considerations of cost, design complexity, and material properties.
Choosing Between Constitutive and Subtractive
Choosing between constitutive and subtractive approaches depends on the desired outcome in design and manufacturing processes. Constitutive methods add material or elements, enabling the creation of complex, customized structures, while subtractive methods remove material for precision and efficiency. Evaluating factors such as material properties, production speed, cost, and design complexity helps determine the optimal method for specific project requirements.
Conclusion: Implications for Future Developments
Constitutive and subtractive approaches each offer unique advantages that shape the future of design and manufacturing technologies. Constitutive methods enable precise control over material properties at the molecular level, fostering innovations in nanotechnology and bioprinting, while subtractive techniques remain essential for rapid prototyping and large-scale production with consistent quality. Understanding the complementary strengths of these processes will drive advancements in hybrid manufacturing systems, enhancing efficiency, customization, and sustainability across industries.
Constitutive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com