Ego shapes the core of your identity, influencing how you perceive yourself and interact with the world around you. Understanding the dynamics between ego and self-awareness can lead to personal growth and healthier relationships. Explore the article to discover how managing your ego improves emotional intelligence and well-being.
Table of Comparison
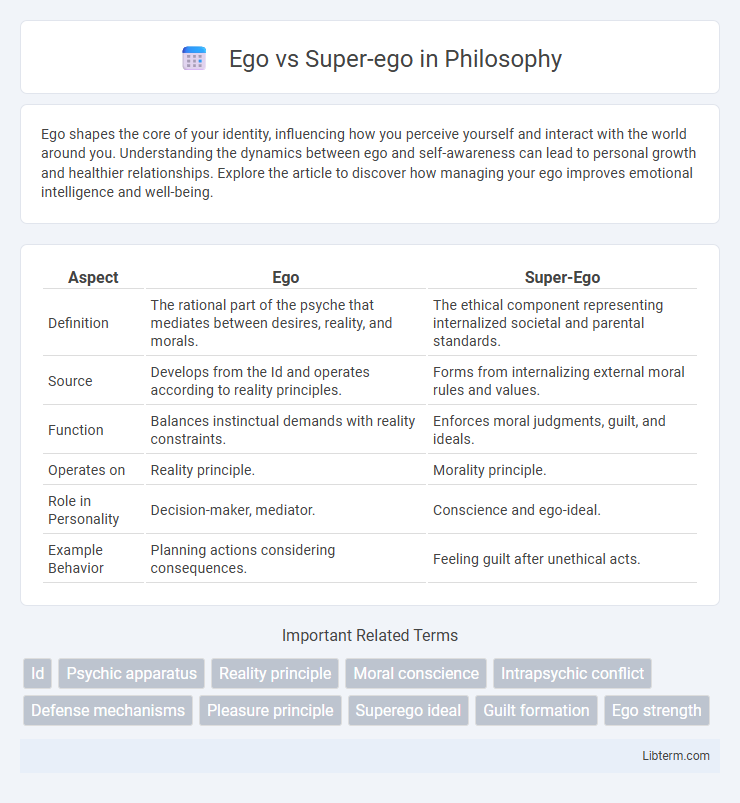
| Aspect | Ego | Super-Ego |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The rational part of the psyche that mediates between desires, reality, and morals. | The ethical component representing internalized societal and parental standards. |
| Source | Develops from the Id and operates according to reality principles. | Forms from internalizing external moral rules and values. |
| Function | Balances instinctual demands with reality constraints. | Enforces moral judgments, guilt, and ideals. |
| Operates on | Reality principle. | Morality principle. |
| Role in Personality | Decision-maker, mediator. | Conscience and ego-ideal. |
| Example Behavior | Planning actions considering consequences. | Feeling guilt after unethical acts. |
Understanding the Ego and Super-ego
The ego functions as the rational part of the psyche, mediating between primal desires and moral constraints by balancing the demands of the id and the superego. The super-ego represents internalized societal norms and ideals, enforcing ethical standards and guilt to guide behavior. Understanding the ego and super-ego is crucial for analyzing how individuals regulate impulses and conform to social expectations.
Historical Origins in Freudian Theory
The concepts of Ego and Super-ego were introduced by Sigmund Freud as part of his structural model of the psyche, initially developed in the early 20th century. The Ego emerged as the rational mediator between the primitive desires of the Id and the moral constraints imposed by the Super-ego, which itself evolved from the internalization of parental and societal norms. Freud's historical development of these entities marked a shift from his earlier topographical model, emphasizing dynamic interactions within the mind and contributing to psychoanalytic theory's foundation.
Core Functions of the Ego
The core functions of the ego include reality testing, impulse control, and judgment, which allow it to mediate between the primitive desires of the id and the moral constraints of the super-ego. The ego operates according to the reality principle, delaying gratification and finding realistic ways to satisfy the id's demands while maintaining social appropriateness. It also employs defense mechanisms like repression and rationalization to manage internal conflicts and reduce anxiety.
The Role of the Super-ego
The role of the super-ego is to serve as the moral conscience, guiding behavior by internalizing societal rules and ethical standards. It acts to counterbalance the primitive desires of the id by imposing guilt and striving for perfection. In Freud's psychoanalytic theory, the super-ego helps individuals navigate complex social environments by promoting values, ideals, and self-discipline.
Differences Between Ego and Super-ego
The ego and super-ego are distinct components of Freud's psychoanalytic theory, where the ego operates as the rational mediator balancing primitive desires and reality, while the super-ego embodies internalized moral standards and ideals. The ego functions based on the reality principle, making pragmatic decisions to satisfy the id's impulses in socially acceptable ways, whereas the super-ego imposes guilt and strives for perfection through adherence to societal norms. This dynamic creates a psychological tension between the ego's practical approach and the super-ego's ethical imperatives, shaping individual behavior and conscience.
Ego vs Super-ego in Personality Development
Ego plays a crucial role in personality development by mediating between the impulsive desires of the id and the moral constraints of the super-ego. The super-ego contributes to personality formation by internalizing societal norms and ideals, guiding ethical behavior and self-criticism. Balanced interaction between ego and super-ego fosters mature personality traits, including self-control, social responsibility, and realistic decision-making.
How Ego Balances Reality
The ego functions as the rational mediator between the impulsive desires of the id and the moral constraints of the super-ego, employing realistic thinking to navigate external world demands. It operates based on the reality principle, seeking practical and socially acceptable ways to satisfy instinctual drives while minimizing negative consequences. This balancing act ensures psychological stability by integrating internal urges and ethical standards with real-world conditions.
The Moral Influence of the Super-ego
The super-ego exerts a powerful moral influence by internalizing societal norms and parental standards, guiding the ego through feelings of guilt and pride. It functions as the ethical component of personality, constantly evaluating actions against an internalized code of conduct to enforce moral behavior. This regulatory role helps maintain social order by motivating individuals to align their desires with collective values and ideals.
Conflicts Between Ego and Super-ego
Conflicts between the ego and the super-ego arise when the ego's realistic desires clash with the super-ego's strict moral standards, leading to internal tension and anxiety. The super-ego imposes conscience-driven judgments that can cause the ego to experience guilt or shame when impulses do not align with ethical ideals. This dynamic often results in psychological conflict requiring defense mechanisms like repression or rationalization to maintain mental balance.
Impact on Mental Health and Behavior
The dynamic between ego and superego critically shapes mental health by balancing realistic self-perceptions with moral standards, influencing anxiety levels and self-esteem. An overpowering superego can lead to guilt and perfectionism, contributing to anxiety disorders, while a weak ego may result in poor impulse control and increased risk of behavioral problems. Effective ego functioning promotes adaptive coping strategies, emotional regulation, and healthy decision-making, essential for psychological resilience and overall well-being.
Ego Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com