Logical form structures arguments by representing their abstract patterns, ensuring clarity and validity in reasoning processes. It focuses on how propositions connect through logical operators, enabling you to analyze and evaluate the soundness of arguments effectively. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of logical form and its applications.
Table of Comparison
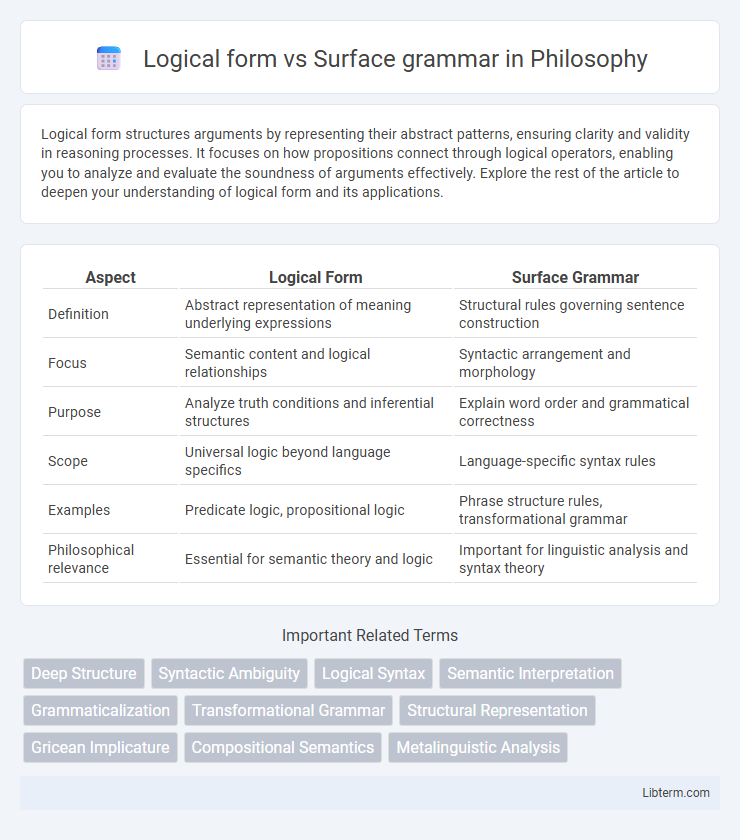
| Aspect | Logical Form | Surface Grammar |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abstract representation of meaning underlying expressions | Structural rules governing sentence construction |
| Focus | Semantic content and logical relationships | Syntactic arrangement and morphology |
| Purpose | Analyze truth conditions and inferential structures | Explain word order and grammatical correctness |
| Scope | Universal logic beyond language specifics | Language-specific syntax rules |
| Examples | Predicate logic, propositional logic | Phrase structure rules, transformational grammar |
| Philosophical relevance | Essential for semantic theory and logic | Important for linguistic analysis and syntax theory |
Introduction to Logical Form and Surface Grammar
Logical form represents the underlying syntactic and semantic structure of a sentence, capturing meaning beyond the surface arrangement of words. Surface grammar refers to the observable syntax and morphology--the arrangement of words and phrases as they appear in spoken or written language. Understanding the distinction between logical form and surface grammar is crucial for accurate parsing, semantic interpretation, and computational linguistics applications.
Defining Logical Form in Linguistics
Logical form in linguistics represents the underlying syntactic and semantic structure of a sentence that captures its true meaning beyond surface variations. It abstracts the deep relations between elements, such as quantifiers and operators, enabling precise interpretation in formal semantics and natural language understanding. This form contrasts surface grammar, which concerns the literal word order and syntactic rules without directly encoding meaning.
Understanding Surface Grammar Structures
Surface grammar structures refer to the observable syntactic patterns and word arrangements in sentences, essential for parsing and language comprehension. These structures emphasize the literal construction of sentences without delving into the underlying logical relationships or meanings they may represent. Mastery of surface grammar facilitates accurate sentence interpretation and effective communication by ensuring clarity in form and function.
The Relationship Between Logical Form and Surface Grammar
Logical form represents the underlying semantic structure of a sentence, capturing its meaning independent of syntactic variations. Surface grammar refers to the observable syntactic arrangement of words and phrases in actual speech or writing. The relationship between logical form and surface grammar lies in how surface grammar maps onto logical form, enabling the interpretation of meaning through the syntactic structures present in language.
Key Differences: Logical Form vs Surface Grammar
Logical form represents the underlying semantic structure of a sentence, capturing meaning through abstract relations and roles, while surface grammar pertains to the syntactic arrangement of words and phrases as they appear in discourse. Logical form abstracts from linguistic variations, enabling consistent interpretation in formal semantics, whereas surface grammar reflects language-specific rules and variability in sentence construction. Key differences lie in logical form's focus on meaning representation beyond syntactic patterns, compared to surface grammar's emphasis on correct word order and morphological agreement.
Role of Syntax in Surface Grammar
Surface grammar governs the arrangement of words and phrases according to syntactic rules, ensuring coherent sentence structures that convey meaning effectively. Syntax in surface grammar determines how subject-verb-object configurations and phrase order impact clarity and emphasis in communication. This structural framework supports the interpretation of logical forms by providing the necessary grammatical context for semantic analysis.
Semantic Interpretation Through Logical Form
Logical form captures the underlying semantic structure of a sentence by abstracting away from surface grammar, enabling precise interpretation of meaning regardless of syntactic variation. Semantic interpretation through logical form relies on formal representations such as predicate logic to map natural language expressions to their truth-conditional content. This process facilitates disambiguation, quantifier scope resolution, and inference by focusing on the logical relationships rather than the surface linguistic configuration.
Ambiguity Resolution: Logical Form or Surface Grammar?
Ambiguity resolution in natural language processing relies heavily on logical form rather than surface grammar, as logical form captures the deep semantic relationships and intended meaning beyond syntactic structure. Surface grammar can present multiple interpretations due to syntactic ambiguity, but logical form provides a unique, unambiguous representation by mapping sentences to their semantic roles and propositions. Therefore, logical form serves as a more robust tool for disambiguating meaning in complex sentence constructions.
Applications in Computational Linguistics
Logical form represents the underlying semantic structure of sentences, enabling precise interpretation and reasoning in computational linguistics. Surface grammar deals with syntactic rules and word order, crucial for natural language parsing and generation algorithms. Applications such as semantic parsing, machine translation, and question answering rely on integrating logical form with surface grammar to improve accuracy and contextual understanding.
Conclusion: Bridging Logical Form and Surface Grammar
Bridging logical form and surface grammar enhances natural language understanding by aligning deep semantic structures with syntactic representations. Integrating these layers enables more accurate parsing and interpretation of complex sentences, improving computational linguistics applications. Emphasizing this connection supports advancements in natural language processing and artificial intelligence systems.
Logical form Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com