An exclusive experience offers unparalleled access to unique benefits and privileges that are not available to the general public. This level of exclusivity ensures personalized attention and a sense of prestige that elevates your overall experience. Discover how this exclusive opportunity can transform your expectations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
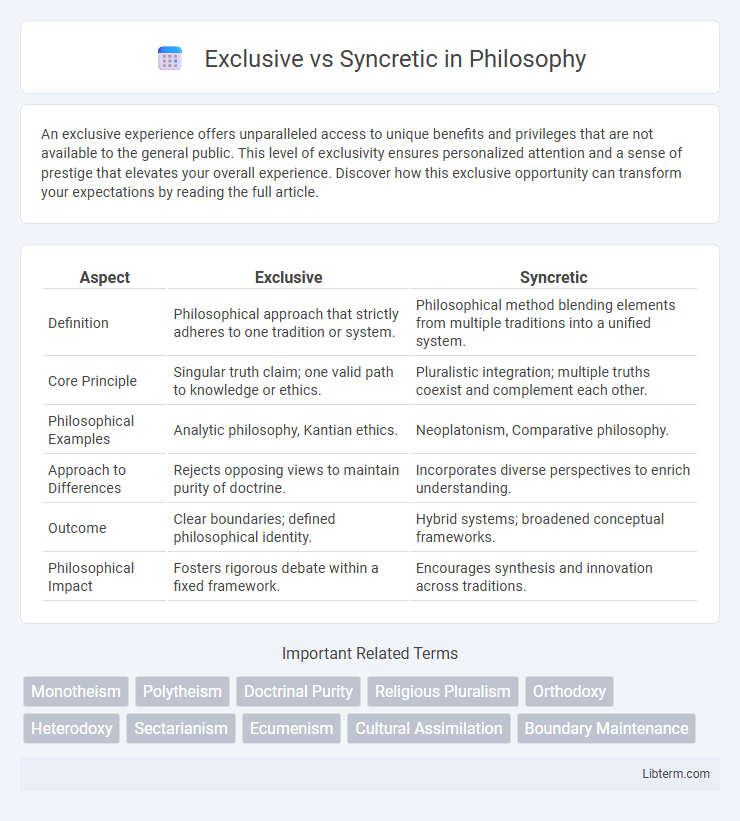
| Aspect | Exclusive | Syncretic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical approach that strictly adheres to one tradition or system. | Philosophical method blending elements from multiple traditions into a unified system. |
| Core Principle | Singular truth claim; one valid path to knowledge or ethics. | Pluralistic integration; multiple truths coexist and complement each other. |
| Philosophical Examples | Analytic philosophy, Kantian ethics. | Neoplatonism, Comparative philosophy. |
| Approach to Differences | Rejects opposing views to maintain purity of doctrine. | Incorporates diverse perspectives to enrich understanding. |
| Outcome | Clear boundaries; defined philosophical identity. | Hybrid systems; broadened conceptual frameworks. |
| Philosophical Impact | Fosters rigorous debate within a fixed framework. | Encourages synthesis and innovation across traditions. |
Understanding Exclusive vs Syncretic Approaches
Exclusive approaches maintain clear boundaries between belief systems, emphasizing the uniqueness and superiority of one tradition without integrating external practices. Syncretic approaches blend elements from multiple religions or philosophies, creating hybrid systems that reflect a fusion of diverse cultural and spiritual influences. Understanding these approaches is crucial for analyzing how societies navigate religious identity, cultural exchange, and the evolution of spiritual practices.
Defining Exclusivism: Key Characteristics
Exclusivism is defined by the belief that only one religion or worldview holds the absolute truth, rejecting the validity of other faiths or perspectives. Key characteristics include a rigid doctrinal adherence, the exclusivity of salvation or ultimate truth, and often a clear boundary between insiders and outsiders. This perspective emphasizes the necessity of specific beliefs and practices for spiritual legitimacy, resulting in minimal theological overlap with syncretic or pluralistic approaches.
Syncretism Explained: Core Features
Syncretism explained focuses on blending distinct religious or cultural beliefs into a cohesive system, emphasizing inclusivity and adaptability. Core features include the integration of diverse rituals, symbols, and doctrines, allowing for new interpretations and coexistence of different traditions. This approach contrasts with exclusivism by promoting harmony and shared values rather than strict adherence to a single belief system.
Historical Roots of Exclusive and Syncretic Thinking
Exclusive thinking has historical roots in early religious and ideological movements that emphasized strict adherence to a singular truth or doctrine, often to maintain social cohesion and authority. Syncretic thinking emerged in pluralistic societies where cultural and religious interactions fostered the blending of beliefs and practices, exemplified by Hellenistic influence on early Christianity and the fusion of indigenous traditions with colonial religions. These contrasting cognitive approaches reflect different responses to cultural diversity and the challenges of preserving identity versus embracing transformation.
Exclusive vs Syncretic: Major Differences
Exclusive belief systems emphasize strict adherence to a single set of doctrines, rejecting contradictory viewpoints and practices. Syncretic systems blend elements from multiple traditions, creating a hybrid belief structure that accommodates diverse influences. The major difference lies in exclusivity versus inclusivity, where exclusive frameworks demand loyalty to one ideology, while syncretic approaches integrate various cultural or religious ideas.
Impact on Religion and Spirituality
Exclusive religious beliefs emphasize a singular truth, often fostering strong group identity but sometimes leading to division and conflict between different faith communities. Syncretic approaches blend elements from multiple religious traditions, promoting inclusiveness and adaptability that can enhance spiritual growth and cross-cultural understanding. The impact on spirituality varies, with exclusivity potentially limiting dialogue while syncretism encourages diverse expressions and personal meaning-making within religious practices.
Cultural Implications of Exclusiveness and Syncretism
Exclusive cultural practices often emphasize distinct identity markers, leading to strong group cohesion but can foster social divisions and resistance to external influences. Syncretic cultures blend elements from various traditions, promoting inclusivity, adaptability, and intercultural dialogue, yet may face challenges in maintaining unique heritage and authenticity. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating multicultural societies and addressing tensions between preservation and integration.
Exclusive Perspectives: Pros and Cons
Exclusive perspectives emphasize a clear distinction between in-group and out-group beliefs, fostering strong group identity and cohesion. This approach can lead to unwavering commitment and clarity of purpose but may also result in social divisiveness and limited openness to alternative ideas. The rigidity of exclusive views often hinders dialogue and cooperation across diverse cultural or religious backgrounds.
Syncretic Practices: Benefits and Challenges
Syncretic practices blend elements from multiple religious or cultural traditions, fostering inclusivity and promoting cross-cultural understanding. These practices enhance social cohesion by integrating diverse beliefs, yet they may also face challenges such as doctrinal conflicts, identity dilution, and resistance from purist groups. Embracing syncretism requires balancing respect for original traditions while adapting to new, hybrid expressions of faith or culture.
Navigating Exclusivity and Syncretism in a Globalized World
Navigating exclusivity and syncretism in a globalized world requires understanding the dynamics between exclusive belief systems that maintain distinct identities and syncretic approaches that blend diverse cultural or religious elements. Exclusive frameworks often emphasize clear boundaries and unique traditions, while syncretism fosters integration and cross-cultural dialogue, promoting adaptability and innovation. Global interconnectedness challenges societies to balance preserving heritage with embracing pluralism, facilitating coexistence amid increasing cultural exchange.
Exclusive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com