Aesthetic virtues enhance the perception of beauty and harmony in art, design, and everyday life, promoting a deeper appreciation of form, color, and balance. These qualities reflect values such as elegance, simplicity, and creativity, influencing emotional responses and enriching cultural experiences. Explore the rest of the article to discover how cultivating aesthetic virtues can transform Your surroundings and enrich Your life.
Table of Comparison
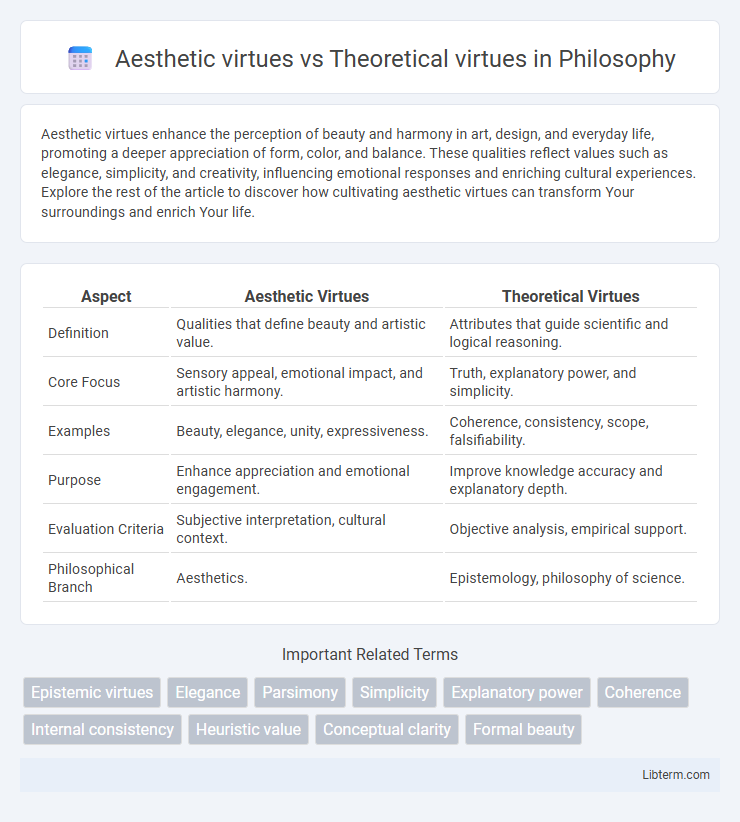
| Aspect | Aesthetic Virtues | Theoretical Virtues |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Qualities that define beauty and artistic value. | Attributes that guide scientific and logical reasoning. |
| Core Focus | Sensory appeal, emotional impact, and artistic harmony. | Truth, explanatory power, and simplicity. |
| Examples | Beauty, elegance, unity, expressiveness. | Coherence, consistency, scope, falsifiability. |
| Purpose | Enhance appreciation and emotional engagement. | Improve knowledge accuracy and explanatory depth. |
| Evaluation Criteria | Subjective interpretation, cultural context. | Objective analysis, empirical support. |
| Philosophical Branch | Aesthetics. | Epistemology, philosophy of science. |
Defining Aesthetic Virtues
Aesthetic virtues refer to the qualities that make an artwork or object perceptually pleasing, emphasizing attributes such as harmony, balance, and expressiveness. These virtues are distinct from theoretical virtues, which prioritize explanatory power, simplicity, and coherence in scientific or philosophical theories. Defining aesthetic virtues involves understanding their role in evoking emotional responses and enhancing sensory experience, rather than validating truth or logical consistency.
Understanding Theoretical Virtues
Theoretical virtues, such as simplicity, explanatory power, and coherence, play a critical role in evaluating scientific theories by ensuring they align closely with empirical evidence and logical consistency. These virtues help scientists choose theories that are not only descriptive but also predictive and unifying within their respective domains. Understanding theoretical virtues enables a more rigorous assessment of hypotheses, fostering the development of robust scientific knowledge.
Historical Roots of Aesthetic and Theoretical Values
Aesthetic virtues, rooted in classical philosophy, emphasize qualities such as beauty, harmony, and emotional resonance derived from ancient Greek thinkers like Plato and Aristotle. Theoretical virtues, grounded in the philosophy of science and epistemology, highlight attributes like simplicity, coherence, and explanatory power, tracing back to medieval scholars and early modern philosophers such as Aquinas and Newton. Historically, these values evolved through distinct intellectual traditions, with aesthetics focusing on sensory and artistic appreciation while theoretical virtues guided the pursuit of knowledge and scientific understanding.
Criteria for Evaluating Scientific Theories
Aesthetic virtues in scientific theories emphasize simplicity, elegance, and coherence, often guiding researchers toward intuitively appealing models. Theoretical virtues focus on predictive accuracy, explanatory power, and consistency with empirical data, serving as objective criteria for theory evaluation. Prioritizing theoretical virtues over aesthetic ones ensures scientific robustness by grounding theory choice in measurable performance rather than subjective appeal.
The Role of Beauty in Scientific Explanation
The role of beauty in scientific explanation bridges aesthetic virtues such as simplicity, elegance, and harmony with theoretical virtues like explanatory power and coherence. Scientists often judge theories not only by empirical adequacy but also by how beautifully these theories unify disparate phenomena, reflecting a deep interplay between aesthetic appreciation and scientific rigor. This synthesis suggests that aesthetic virtues guide the development and acceptance of theories by highlighting patterns that resonate with both intellectual clarity and sensory appeal.
Simplicity: Aesthetic or Theoretical Virtue?
Simplicity serves as both an aesthetic and a theoretical virtue, emphasizing clarity, elegance, and efficiency in explanation or design. In aesthetics, simplicity appeals to the human preference for minimalism and coherence, enhancing the beauty and harmony of an object or concept. Theoretically, simplicity promotes parsimony, reducing assumptions and complexity in scientific theories, thus increasing their explanatory power and testability.
Case Studies Illustrating Virtue Conflicts
Case studies illustrating conflicts between aesthetic virtues and theoretical virtues reveal how priorities in scientific theory choice can diverge between explanatory power and simplicity or beauty. For example, tension arises when a theory is elegant (an aesthetic virtue) yet lacks predictive accuracy (a theoretical virtue), as seen in debates over string theory's mathematical beauty versus empirical testability. These cases underscore how philosophers analyze trade-offs between virtues like coherence, simplicity, and empirical adequacy in scientific model evaluation.
Philosophical Debates: Which Virtue Prevails?
Philosophical debates on aesthetic virtues versus theoretical virtues center on the question of which type holds greater epistemic value and influence on human understanding. Aesthetic virtues, such as beauty, simplicity, and elegance, are praised for enhancing the intuitive appeal and cognitive accessibility of theories, while theoretical virtues like explanatory power, coherence, and empirical adequacy ensure rigorous truth-tracking and scientific reliability. Scholars remain divided, with some arguing that theoretical virtues ultimately prevail due to their role in objective knowledge acquisition, whereas others emphasize the indispensability of aesthetic virtues in guiding theory choice and fostering creativity.
Impact on Scientific Progress and Discovery
Aesthetic virtues such as simplicity and elegance guide scientists in creating hypotheses that are not only appealing but also easier to test, accelerating the formulation of innovative theories. Theoretical virtues like explanatory power and predictive accuracy directly influence the acceptance and refinement of scientific models, driving empirical validation and cumulative knowledge growth. Balancing aesthetic appeal with rigorous theoretical criteria optimizes scientific progress and enhances the robustness of discoveries.
Integrating Aesthetic and Theoretical Virtues: Future Perspectives
Integrating aesthetic and theoretical virtues enhances the robustness of scientific theories by balancing explanatory power with elegance and simplicity. Future perspectives emphasize developing interdisciplinary frameworks that quantify aesthetic criteria alongside empirical adequacy, fostering models that are both intellectually satisfying and empirically reliable. Advances in machine learning and philosophy of science increasingly facilitate this integration, promoting holistic approaches to theory evaluation and development.
Aesthetic virtues Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com