Empiricism emphasizes the importance of sensory experience and observation as the foundation for knowledge acquisition, asserting that all ideas originate from what we perceive through our senses. This philosophical approach challenges innate ideas and highlights empirical evidence as crucial for scientific inquiry and critical thinking. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how empiricism shapes modern knowledge.
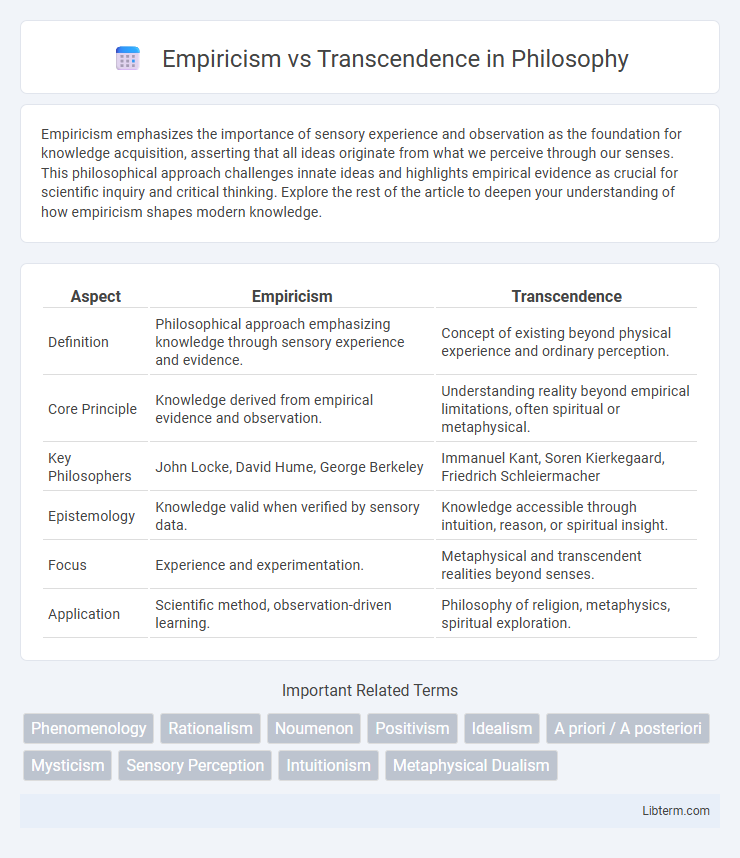
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Empiricism | Transcendence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical approach emphasizing knowledge through sensory experience and evidence. | Concept of existing beyond physical experience and ordinary perception. |
| Core Principle | Knowledge derived from empirical evidence and observation. | Understanding reality beyond empirical limitations, often spiritual or metaphysical. |
| Key Philosophers | John Locke, David Hume, George Berkeley | Immanuel Kant, Soren Kierkegaard, Friedrich Schleiermacher |
| Epistemology | Knowledge valid when verified by sensory data. | Knowledge accessible through intuition, reason, or spiritual insight. |
| Focus | Experience and experimentation. | Metaphysical and transcendent realities beyond senses. |
| Application | Scientific method, observation-driven learning. | Philosophy of religion, metaphysics, spiritual exploration. |
Understanding Empiricism: Foundation and Key Principles
Empiricism is founded on the principle that knowledge originates primarily from sensory experience and observation, emphasizing evidence gathered through experimentation. Key empiricist thinkers such as John Locke and David Hume argue that the mind begins as a blank slate, acquiring ideas and concepts through interaction with the external world. This approach contrasts with transcendence-based philosophies by rejecting innate ideas and focusing on empirical data as the basis for understanding reality.
The Essence of Transcendence in Philosophy
The essence of transcendence in philosophy lies in the quest to understand realities beyond empirical observation, emphasizing experiences, concepts, and entities that surpass sensory data. Transcendence challenges empiricism by positing that knowledge derives not solely from sensory input but from innate structures, metaphysical principles, or spiritual dimensions. This philosophical approach explores the limits of human cognition and the possibility of accessing ultimate truths that exist independently of empirical verification.
Historical Roots of Empiricism
Empiricism traces its roots to ancient Greek philosophers such as Aristotle, who emphasized observation and experience as the foundation of knowledge. During the 17th century, thinkers like John Locke and David Hume further developed empiricism by arguing that all ideas originate from sensory experience rather than innate concepts. This historical foundation contrasts sharply with transcendence, which is grounded in the belief of knowledge acquired through intuition or spiritual insight beyond empirical evidence.
Transcendence through Spiritual and Metaphysical Lenses
Transcendence through spiritual and metaphysical lenses emphasizes the experience of realities beyond empirical observation, highlighting concepts such as inner awakening, universal consciousness, and the soul's journey. This perspective prioritizes intuition, mystical experiences, and the interconnectedness of all existence as pathways to knowledge and truth. Metaphysical transcendence often challenges the limits of sensory data, advocating for a deeper, non-material understanding of reality that surpasses empirical boundaries.
Comparing Epistemological Approaches: Empiricism vs. Transcendence
Empiricism emphasizes knowledge acquisition through sensory experience and empirical evidence, relying on observation and experimentation as primary sources of understanding. In contrast, transcendence prioritizes intuitive and metaphysical insights that go beyond sensory data, asserting that certain truths exist independently of empirical validation. These opposing epistemological approaches reveal fundamental differences in how knowledge is justified, with empiricism grounded in tangible evidence and transcendence in abstract reasoning and spiritual cognition.
Empirical Evidence and the Limits of Experience
Empiricism centers on knowledge derived from sensory experience and empirical evidence, emphasizing observation and experimentation as the foundations of understanding. However, the limits of experience reveal that not all truths or concepts can be fully grasped through empirical data alone, highlighting gaps in knowledge that transcend sensory input. This tension underscores debates in epistemology regarding the scope of human cognition and the validity of metaphysical or abstract principles beyond empirical verification.
Transcendent Knowledge: Beyond Sensory Perception
Transcendent knowledge surpasses empirical data by accessing truths beyond sensory perception and material experience, emphasizing metaphysical insight and spiritual understanding. It draws from intuitive revelation, mystical experience, and a priori reasoning to grasp realities that empirical methods cannot validate. This approach challenges the limits of sensory-based knowledge, proposing that certain existential and universal truths are inherently inaccessible through observation alone.
Major Thinkers: Empiricists and Transcendentalists
Empiricism, championed by John Locke and David Hume, argues that knowledge originates from sensory experience and empirical evidence, emphasizing observation and experimentation as foundations of understanding. Transcendentalism, led by thinkers like Immanuel Kant and Ralph Waldo Emerson, posits that knowledge transcends sensory experience through innate ideas and intuition, highlighting the role of a priori concepts and the self's connection to a higher reality. These contrasting philosophies delineate empiricism's reliance on observable data versus transcendentalism's focus on inherent knowledge and spiritual insight.
Modern Implications in Science and Spirituality
Empiricism, grounded in sensory experience and scientific method, drives advancements in technology, medicine, and cognitive neuroscience by emphasizing observable data and reproducibility. Transcendence, rooted in spiritual and metaphysical traditions, influences contemporary explorations in consciousness studies, quantum physics interpretations, and holistic healing practices that address non-material dimensions of existence. The modern interplay between empiricism and transcendence fosters integrative approaches, bridging empirical rigor with spiritual insights to expand understanding in both scientific inquiry and personal transformation.
Bridging Empiricism and Transcendence: Is Reconciliation Possible?
Bridging empiricism and transcendence involves integrating sensory-based knowledge with metaphysical insights to create a comprehensive understanding of reality. Empirical methods emphasize observation and experimentation, while transcendence explores phenomena beyond empirical evidence, such as spirituality and consciousness. Reconciliation is possible through interdisciplinary approaches that utilize scientific inquiry alongside philosophical and theological frameworks to address phenomena beyond immediate sensory experience.
Empiricism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com