Regulation shapes how industries operate by setting clear standards and ensuring compliance to protect consumers and maintain market fairness. Effective regulatory frameworks adapt to new challenges, fostering innovation while minimizing risks. Explore the rest of this article to understand how regulations impact your business and daily life.
Table of Comparison
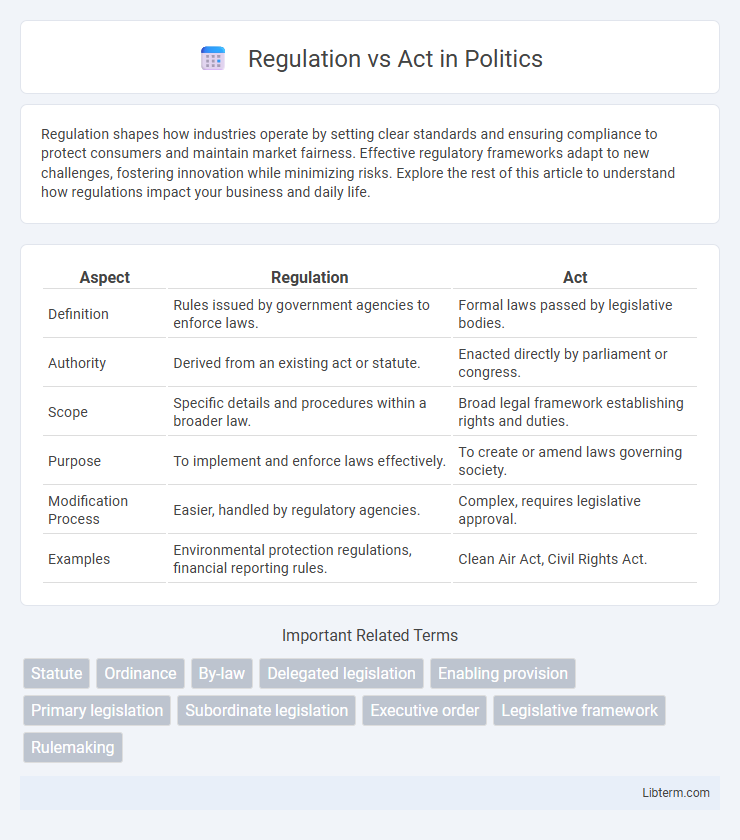
| Aspect | Regulation | Act |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules issued by government agencies to enforce laws. | Formal laws passed by legislative bodies. |
| Authority | Derived from an existing act or statute. | Enacted directly by parliament or congress. |
| Scope | Specific details and procedures within a broader law. | Broad legal framework establishing rights and duties. |
| Purpose | To implement and enforce laws effectively. | To create or amend laws governing society. |
| Modification Process | Easier, handled by regulatory agencies. | Complex, requires legislative approval. |
| Examples | Environmental protection regulations, financial reporting rules. | Clean Air Act, Civil Rights Act. |
Definition of Regulation
Regulation refers to a rule or directive made and maintained by an authority to control or govern conduct within a specific area, often issued by government agencies based on legislation. Regulations have the force of law and are detailed provisions that specify how broader statutes, or Acts, should be implemented and enforced. Unlike Acts, which are laws passed by legislative bodies, regulations provide the practical guidelines necessary to ensure compliance and operationalize legislative intent.
Definition of Act
An Act is a formal statute enacted by a legislative body, serving as a primary source of law that establishes legal rights and obligations. It provides a comprehensive framework for governance, often detailing specific provisions, penalties, and enforcement mechanisms. Unlike regulations, which are more detailed rules created by executive agencies to implement Acts, an Act holds higher legal authority and establishes broad mandates.
Key Differences Between Regulations and Acts
Regulations are detailed rules issued by government agencies based on authority granted by an Act, providing specific guidelines for implementing and enforcing legislation. Acts are formal laws passed by legislative bodies, establishing broad legal principles and frameworks. Key differences include that Acts require legislative approval, while Regulations are created by agencies to operationalize and enforce the Acts without needing new legislation.
Purpose and Scope of Acts
Acts serve as formal legislative statutes enacted by a governing body to establish laws with broad applicability and enduring authority across various sectors. Their primary purpose is to define legal frameworks, rights, and obligations while addressing public policy issues comprehensively. The scope of Acts encompasses wide-ranging societal and regulatory matters, ensuring uniformity and consistency in legal interpretation and enforcement.
Purpose and Scope of Regulations
Regulations are detailed directives issued by governmental agencies to implement and enforce laws established by an Act, specifying the procedures and standards necessary for compliance. The primary purpose of regulations is to provide clarity and operational guidelines that ensure consistent application within the scope defined by the Act. Unlike Acts, which set broad legal frameworks, regulations address specific technical and administrative aspects within particular industries or sectors.
Legal Authority and Hierarchy
Regulations derive their legal authority from Acts, serving as detailed rules formulated by government agencies to implement and enforce the broader provisions of legislation. Acts, passed by legislative bodies, hold supreme authority within the legal hierarchy, establishing fundamental rights, duties, and frameworks. In the hierarchy of law, Acts sit above Regulations, which must comply with and operate within the boundaries set by their enabling Acts.
Creation and Implementation Process
Regulations are detailed directives created by executive agencies based on authority granted by an existing Act, focusing on practical application and enforcement of the law. Acts, or statutes, are laws formally enacted by the legislative body through a structured process involving proposal, debate, and ratification, establishing broader legal frameworks. The implementation of Acts relies heavily on regulations to specify procedures, compliance requirements, and enforcement mechanisms.
Examples of Acts and Regulations
The Clean Air Act exemplifies an Act that establishes broad legislative frameworks to control air pollution across the United States, while the Environmental Protection Agency's Clean Air Regulations provide detailed rules and standards for emission limits under this Act. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a key example of an Act ensuring civil rights for individuals with disabilities, whereas the Department of Justice's ADA Standards for Accessible Design represent regulations that specify technical requirements for accessibility. Acts serve as primary legislation passed by Congress or governing bodies, and regulations are the enforceable rules developed by agencies to implement and interpret those Acts effectively.
Impact on Businesses and Individuals
Regulations impose specific requirements that businesses must follow, often resulting in increased compliance costs and operational adjustments to avoid penalties. Acts, as broader legislative frameworks, establish legal standards that shape industry practices and protect individual rights, influencing market behavior and consumer confidence. Both regulations and acts drive organizational accountability and individual protections, but regulations tend to have a more immediate and detailed impact on day-to-day business operations.
Importance of Understanding Regulation vs Act
Understanding the difference between regulations and acts is crucial for effective legal compliance and policy implementation. Acts, passed by legislative bodies, establish broad legal frameworks, while regulations provide detailed rules necessary to enforce those acts. Grasping this distinction ensures accurate interpretation, application, and adherence to the law, reducing risks of legal violations and improving governance.
Regulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com