Tracking voter registration count provides crucial insights into electoral engagement and potential voter turnout during elections. It reflects the level of political participation within a community and helps identify trends in voter demographics that can influence election outcomes. Explore the rest of this article to understand how voter registration count impacts your voting power and the overall democratic process.
Table of Comparison
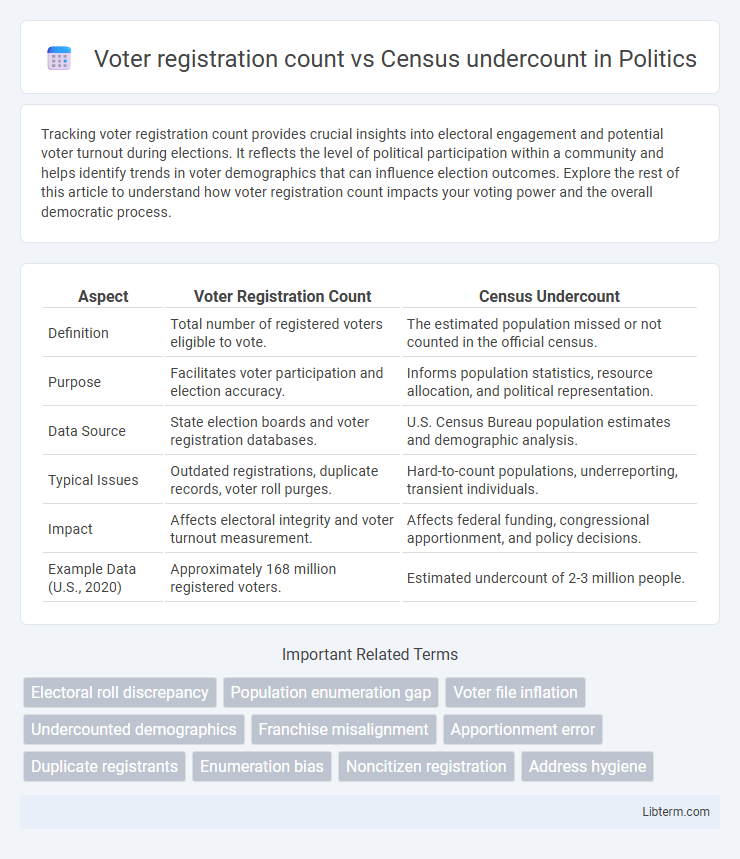
| Aspect | Voter Registration Count | Census Undercount |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total number of registered voters eligible to vote. | The estimated population missed or not counted in the official census. |
| Purpose | Facilitates voter participation and election accuracy. | Informs population statistics, resource allocation, and political representation. |
| Data Source | State election boards and voter registration databases. | U.S. Census Bureau population estimates and demographic analysis. |
| Typical Issues | Outdated registrations, duplicate records, voter roll purges. | Hard-to-count populations, underreporting, transient individuals. |
| Impact | Affects electoral integrity and voter turnout measurement. | Affects federal funding, congressional apportionment, and policy decisions. |
| Example Data (U.S., 2020) | Approximately 168 million registered voters. | Estimated undercount of 2-3 million people. |
Understanding Voter Registration Count
Understanding voter registration count involves analyzing the total number of individuals officially registered to vote, which is critical for assessing electoral participation and resource allocation. Comparing voter registration counts to census data reveals discrepancies often caused by census undercount, where certain populations, such as minorities and low-income groups, are underrepresented. Accurate voter registration data improves election management by ensuring all eligible voters are accounted for and addressing gaps highlighted by census undercount patterns.
What is the Census Undercount?
The Census undercount refers to the number of people missed or not counted during the official population tally, affecting the accuracy of demographic data used for voter registration and political representation. Undercounting disproportionately impacts marginalized communities, leading to fewer resources and reduced political influence in those areas. Accurate voter registration relies on comprehensive census data to ensure fair districting and equitable allocation of government services.
Key Differences Between Voter Registration and Census Data
Voter registration data captures the number of individuals registered to vote, often reflecting active political participation, while census data aims to count every resident regardless of citizenship or voter eligibility. Census undercounts frequently occur in hard-to-reach populations, such as minorities, immigrants, and transient individuals, leading to discrepancies when compared to voter registration totals. These key differences highlight how voter registration numbers can underestimate or overestimate the eligible voting population compared to more comprehensive, though sometimes incomplete, census counts.
Factors Leading to Census Undercounts
Census undercounts often stem from factors such as transient populations, language barriers, and distrust of government, which result in incomplete responses and inaccurate population data. These undercounts affect voter registration counts by excluding eligible individuals from official records, skewing demographic representation and resource allocation. Addressing challenges like housing instability, outreach to marginalized communities, and enhancing data collection methods can reduce discrepancies between voter registration and census figures.
Causes of Inflated Voter Registration Rolls
Inflated voter registration rolls often result from outdated records, including deceased individuals, people who have relocated, and duplicates created by inconsistent data entry across jurisdictions. The Census undercount disproportionately affects marginalized communities, leading to discrepancies between the actual population and registered voters, as some residents remain unregistered due to lack of outreach or identification barriers. Addressing these issues requires regular auditing and cross-referencing of voter databases with updated census data to ensure accuracy and integrity in election processes.
Implications for Electoral Representation
Discrepancies between voter registration counts and census undercounts significantly impact electoral representation by skewing district population data used for redistricting and resource allocation. Undercounted populations, often marginalized communities, lead to fewer representative allocations and diminished political influence, undermining democratic fairness. Accurate alignment of voter registration data with comprehensive census counts is essential to ensure equitable political representation and uphold the principle of one person, one vote.
Impact on Resource Allocation and Funding
Discrepancies between voter registration counts and census undercounts significantly affect resource allocation and funding, as government programs rely heavily on census data to distribute billions in federal and state funds. Undercounted populations lead to undervaluation of community needs, resulting in decreased funding for essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure development. Accurate reconciliation of voter registration data with census figures is crucial to ensure equitable resource distribution and effective policy planning.
Addressing Data Discrepancies: Solutions and Challenges
Addressing data discrepancies between voter registration counts and census undercount requires implementing enhanced data integration techniques and improving outreach to marginalized communities who are often underrepresented. Employing advanced statistical matching algorithms and leveraging administrative records can help reconcile inconsistencies in population estimates. Challenges include privacy concerns, resource limitations, and ensuring equitable data collection across diverse demographic groups.
Case Studies Comparing Voter Rolls and Census Data
Case studies comparing voter registration counts with census data reveal significant discrepancies that highlight challenges in data accuracy and population representation. In several regions, voter rolls often exceed census counts due to outdated records, duplicate entries, or migration patterns, complicating electoral logistics and resource allocation. These mismatches underscore the need for integrated data management systems and regular updates to ensure both voter registration and census data reflect true population demographics.
Recommendations for More Accurate Population Measurement
To improve accuracy in population measurement, integrating voter registration data with advanced statistical modeling can help address Census undercount issues, especially in hard-to-reach communities. Implementing targeted outreach and data verification protocols enhances the inclusiveness of both Census and voter rolls, reducing disparities in demographic representation. Leveraging geospatial analysis and cross-referencing administrative records further refines population estimates, enabling policymakers to allocate resources more equitably.
Voter registration count Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com