Internationalism promotes cooperation and understanding among nations to address global challenges collaboratively. Embracing diverse cultures and shared values strengthens peace, economic development, and human rights worldwide. Discover how internationalism impacts your world and why it matters by reading the full article.
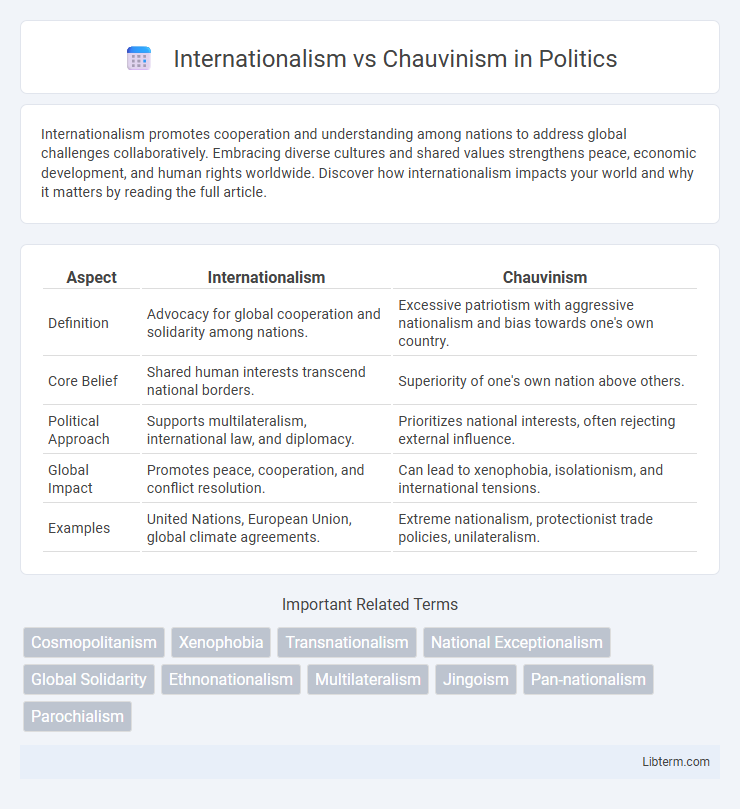
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Internationalism | Chauvinism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advocacy for global cooperation and solidarity among nations. | Excessive patriotism with aggressive nationalism and bias towards one's own country. |
| Core Belief | Shared human interests transcend national borders. | Superiority of one's own nation above others. |
| Political Approach | Supports multilateralism, international law, and diplomacy. | Prioritizes national interests, often rejecting external influence. |
| Global Impact | Promotes peace, cooperation, and conflict resolution. | Can lead to xenophobia, isolationism, and international tensions. |
| Examples | United Nations, European Union, global climate agreements. | Extreme nationalism, protectionist trade policies, unilateralism. |
Understanding Internationalism: A Global Perspective
Internationalism promotes cooperation and solidarity across nations, emphasizing shared human values and global problem-solving for issues like climate change, poverty, and security. It supports multinational institutions such as the United Nations and advocates for policies that prioritize collective well-being over national interests. This approach contrasts sharply with chauvinism, which centers on extreme national pride and exclusionary attitudes that hinder global collaboration and peace-building efforts.
Defining Chauvinism: Roots and Ramifications
Chauvinism originates from excessive patriotism and blind loyalty to one's nation, often linked to Nicolas Chauvin, a soldier known for fervent nationalism. It manifests in aggressive superiority and prejudice against other groups, fostering conflict and social division. The ramifications include impaired international cooperation and the perpetuation of xenophobia, undermining global unity and peace efforts.
Historical Evolution of Internationalism
Internationalism evolved prominently in the 19th and 20th centuries, driven by the rise of global movements advocating peace, cooperation, and solidarity beyond national borders, as seen in the formation of the League of Nations and later the United Nations. The concept gained momentum through socialist and labor movements that emphasized class solidarity over national loyalty, challenging chauvinistic nationalism which prioritized national superiority and aggressive patriotism. Key historical events such as the World Wars and decolonization further shaped internationalism by highlighting the dangers of chauvinism and promoting frameworks for global governance and human rights.
The Rise of Chauvinism in Modern Politics
The rise of chauvinism in modern politics manifests through nationalist rhetoric, xenophobic policies, and exclusionary identity politics that challenge the principles of internationalism promoting global cooperation and multiculturalism. Increasing political movements emphasize ethnic, cultural, or national superiority, undermining efforts toward international solidarity and collective problem-solving. This shift has intensified geopolitical tensions, weakened international institutions, and fostered divisive public discourse worldwide.
Key Differences: Internationalism vs. Chauvinism
Internationalism emphasizes global cooperation, mutual respect, and the prioritization of collective human interests beyond national borders, fostering cultural exchange and shared progress. Chauvinism, in contrast, asserts an aggressive, often unquestioning superiority of one's own nation or group, promoting exclusionary practices and undermining international solidarity. The key difference lies in internationalism's inclusive approach to global unity versus chauvinism's exclusive, nationalistic fervor.
Internationalism and Global Cooperation
Internationalism promotes global cooperation by emphasizing shared human values and collective problem-solving across borders. It fosters diplomatic relations, cultural exchange, and multilateral institutions to address challenges such as climate change, poverty, and security. This approach strengthens economic interdependence and peaceful coexistence, contrasting with the exclusionary nationalism of chauvinism.
Chauvinism's Impact on Societal Division
Chauvinism fosters intense loyalty to one's own group, often leading to exclusion and discrimination against others, which deepens societal divisions. This tribal mindset exacerbates conflicts between communities by promoting superiority and intolerance, undermining social cohesion and harmony. Such divisions hinder cooperative efforts necessary for addressing common challenges in multicultural societies.
Case Studies: Internationalism and Chauvinism in Action
The case studies of internationalism versus chauvinism reveal contrasting approaches to global cooperation and nationalist fervor. Internationalism promotes cross-border solidarity, exemplified by the European Union's collaborative policies fostering peace and economic stability, while chauvinism is evident in Brexit, where nationalist priorities led to the UK's withdrawal from the EU. These case studies highlight the impact of inclusive international policies versus exclusionary nationalist agendas on global diplomacy and socio-economic development.
Balancing National Identity and Global Responsibility
Balancing national identity with global responsibility requires recognizing the importance of cultural heritage while embracing international cooperation for shared challenges like climate change and human rights. Internationalism promotes collaboration across borders, fostering peace and sustainable development, whereas chauvinism emphasizes aggressive nationalism that can undermine global solidarity and exacerbate conflicts. Effective policy frameworks must integrate respect for sovereignty with commitments to multilateralism to achieve equitable progress worldwide.
The Future of Internationalism vs. Chauvinism
The future of internationalism hinges on expanding global cooperation through institutions like the United Nations and multilateral trade agreements, promoting shared economic growth and peace. Chauvinism, characterized by extreme nationalism and protectionist policies, risks fragmenting international relations and escalating conflicts. Sustainable progress depends on balancing national interests with global solidarity to address challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and transnational security threats.
Internationalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com