Single-party government centralizes political power within one dominant party, often eliminating opposition and limiting political pluralism. This system can lead to streamlined decision-making but may also hinder democratic processes and reduce governmental accountability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how single-party governments impact your country's political landscape and social development.
Table of Comparison
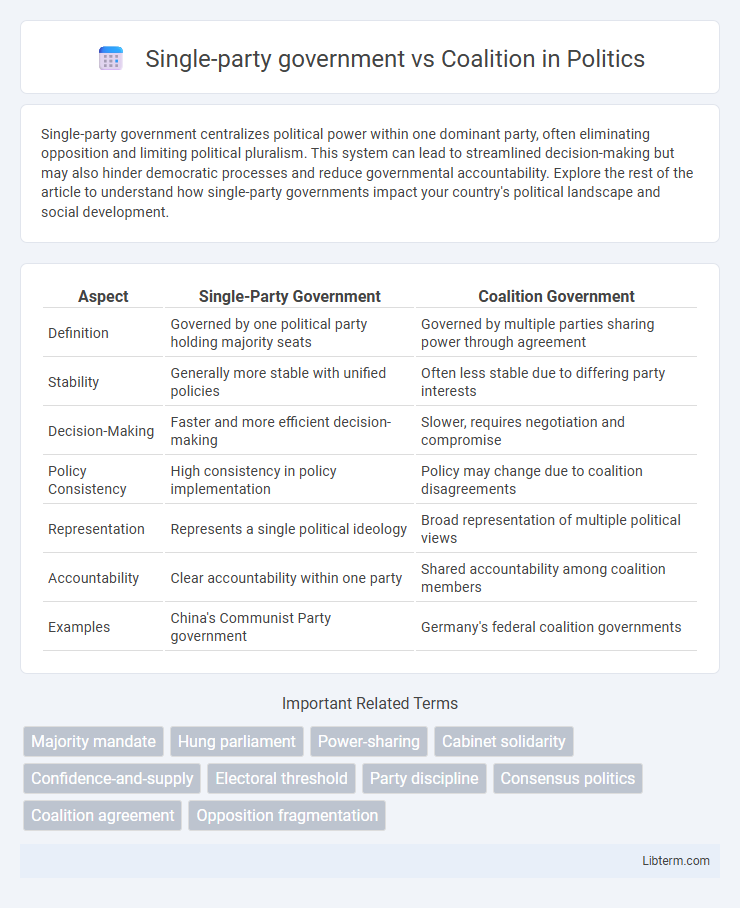
| Aspect | Single-Party Government | Coalition Government |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governed by one political party holding majority seats | Governed by multiple parties sharing power through agreement |
| Stability | Generally more stable with unified policies | Often less stable due to differing party interests |
| Decision-Making | Faster and more efficient decision-making | Slower, requires negotiation and compromise |
| Policy Consistency | High consistency in policy implementation | Policy may change due to coalition disagreements |
| Representation | Represents a single political ideology | Broad representation of multiple political views |
| Accountability | Clear accountability within one party | Shared accountability among coalition members |
| Examples | China's Communist Party government | Germany's federal coalition governments |
Understanding Single-Party Government
Single-party government occurs when one political party holds a clear majority in the legislature, allowing for streamlined decision-making and policy implementation without the need for consensus from other parties. This system often results in greater political stability and coherent governance, as the ruling party can push its agenda more efficiently. However, it may also reduce political diversity and limit opposition influence within the legislative process.
Defining Coalition Government
Coalition government is a political arrangement where multiple parties cooperate, sharing executive power to form a majority in the legislature. Unlike single-party governments, coalitions require negotiation and compromise to develop policies that reflect diverse party agendas. This system promotes broader representation but can result in slower decision-making due to the need for consensus.
Historical Contexts of Both Systems
Single-party governments have historically emerged in contexts where centralized authority was prioritized to enforce uniform policies, often seen in authoritarian regimes such as the Soviet Union under Stalin or China under Mao Zedong. Coalition governments, by contrast, are typical in parliamentary democracies like post-World War II Italy and India, where multiple parties collaborate to achieve political stability and represent diverse societal interests. The historical trajectory of these systems reflects differing approaches to governance, with single-party rule emphasizing ideological conformity and coalitions promoting pluralism and compromise.
Efficiency in Decision-Making
Single-party governments often achieve higher efficiency in decision-making due to centralized power and streamlined policy implementation, reducing negotiation delays. Coalition governments require consensus among multiple parties, which can slow down decision processes and complicate policy formulation. The balance between diverse representation and decisiveness frequently impacts the speed and clarity of legislative actions in democratic systems.
Political Stability: Single-Party vs Coalition
Single-party governments often provide greater political stability by enabling swift decision-making and consistent policy implementation without the need for compromise among multiple parties. Coalition governments can face challenges in maintaining stability due to differing party agendas and the necessity for negotiation, which may lead to policy gridlocks or government collapses. Empirical studies indicate single-party administrations experience fewer votes of no confidence and longer uninterrupted terms compared to coalition counterparts.
Representation and Inclusivity
Single-party governments often enable decisive policy implementation but may limit diverse representation, consolidating power within one political entity. Coalition governments increase inclusivity by combining multiple parties, ensuring broader representation of varied social, ethnic, and political groups. This fosters consensus-building and reflects a wider range of societal interests in decision-making processes.
Policy Consistency and Continuity
Single-party governments often ensure greater policy consistency and continuity due to unified party control, enabling streamlined decision-making and implementation of long-term goals. Coalition governments frequently face challenges in maintaining consistent policies as compromises between diverse parties can lead to fragmented or shifting agendas. The stability of single-party governments typically supports sustained economic and social reforms, whereas coalitions may experience policy volatility driven by varying party priorities.
Risks of Power Concentration
Single-party governments often face heightened risks of power concentration, leading to reduced checks and balances and potential authoritarianism. The lack of political pluralism can result in decision-making dominated by a single entity, increasing vulnerability to corruption and policy stagnation. In contrast, coalitions distribute power among multiple parties, fostering negotiation and accountability that mitigate such risks.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Governance
Single-party governments offer streamlined decision-making processes, enabling rapid policy implementation and greater flexibility during crises. Coalition governments, while often slower due to negotiation and compromise among multiple parties, tend to be more adaptable by incorporating diverse perspectives and balancing interests. The trade-off between swift action and inclusive deliberation shapes the governance style and responsiveness of each system.
Impact on Voter Choice and Democracy
Single-party governments streamline decision-making by consolidating power, potentially limiting voter choice by presenting fewer ideological alternatives. Coalition governments enhance democratic representation by incorporating diverse viewpoints and encouraging compromise, which can increase voter engagement and satisfaction. However, coalitions may also introduce policy gridlock and instability, affecting governance effectiveness and public trust.
Single-party government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com