Jurisdictional disagreement arises when two or more legal authorities claim the right to govern or adjudicate a particular case or issue, often leading to conflicts and delays in legal proceedings. Resolving these disputes requires understanding the boundaries and powers of each jurisdiction involved to ensure fair and lawful outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how jurisdictional disagreements are addressed and their impact on the legal system.
Table of Comparison
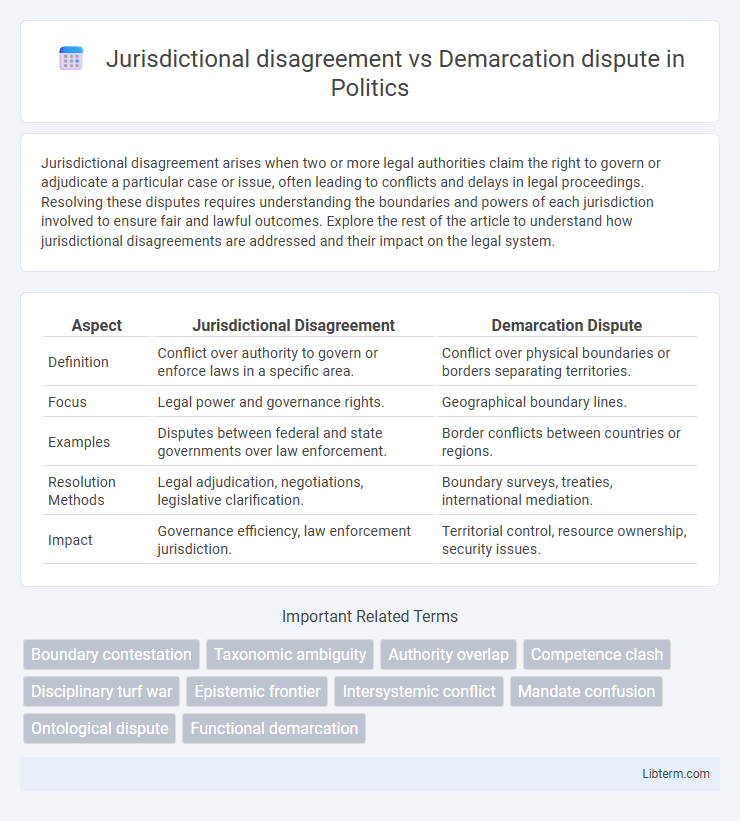
| Aspect | Jurisdictional Disagreement | Demarcation Dispute |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conflict over authority to govern or enforce laws in a specific area. | Conflict over physical boundaries or borders separating territories. |
| Focus | Legal power and governance rights. | Geographical boundary lines. |
| Examples | Disputes between federal and state governments over law enforcement. | Border conflicts between countries or regions. |
| Resolution Methods | Legal adjudication, negotiations, legislative clarification. | Boundary surveys, treaties, international mediation. |
| Impact | Governance efficiency, law enforcement jurisdiction. | Territorial control, resource ownership, security issues. |
Understanding Jurisdictional Disagreement
Jurisdictional disagreement arises when two or more authorities claim legal power over the same matter or area, creating conflicts in authority and decision-making. This type of disagreement primarily involves questions of legal competence, often leading to challenges in enforcement and governance. Understanding jurisdictional disagreement requires analyzing the scope of authority granted by law to each party and the implications for administrative control and resource allocation.
Defining Demarcation Dispute
Demarcation dispute refers to conflicts arising from unclear or overlapping boundaries between organizational roles, departments, or professional territories, leading to disagreements over responsibilities and authority. Unlike jurisdictional disagreements that focus on legal authority or geographic control, demarcation disputes center on internal divisions of labor and functional boundaries within an entity or institution. Resolving these disputes requires precise role definitions and clear communication to prevent operational inefficiencies and employee conflicts.
Key Differences Between Jurisdictional and Demarcation Issues
Jurisdictional disagreement primarily involves conflicts over legal authority or control between governmental or organizational bodies, often concerning the right to enforce laws or regulations within a certain area. Demarcation dispute centers on disagreements regarding physical boundaries or territorial limits, typically involving the precise marking or delineation of borders between regions or properties. The key difference lies in jurisdictional disputes focusing on authority and governance, while demarcation disputes focus on geographic boundaries and their exact placement.
Historical Contexts of Jurisdictional Disagreements
Jurisdictional disagreements historically arise when overlapping legal or administrative authorities claim control over the same territory or issue, often rooted in colonial boundaries or evolving state sovereignties. These disputes frequently emerge from ambiguous treaties or poorly defined borders, leading to prolonged conflicts between nations or subnational entities. Demarcation disputes, in contrast, typically focus narrowly on the physical marking of boundaries, whereas jurisdictional disagreements encompass broader questions of legal authority and governance rights tied to historical claims.
Classic Examples of Demarcation Disputes
Classic examples of demarcation disputes often arise between labor unions competing over the right to represent specific job classifications within the same industry, such as the historic clashes between electricians' and ironworkers' unions regarding construction site responsibilities. These disputes center on the precise allocation of tasks and work boundaries, differing from jurisdictional disagreements that typically involve authority or control over decision-making powers. Understanding the nuanced distinctions between demarcation disputes and jurisdictional disagreements is critical for addressing labor conflict resolution and collective bargaining challenges effectively.
Legal Frameworks Governing Jurisdiction
Jurisdictional disagreements arise when multiple legal authorities claim the right to exercise power over the same matter, often leading to conflicts under overlapping legal frameworks such as federal, state, or international law. Demarcation disputes specifically involve disagreements over geographical boundaries and are governed by treaties, statutes, or judicial rulings that define territorial limits and jurisdictional authority. Legal frameworks governing jurisdiction prioritize clarity in authority through constitutional provisions, international agreements, and judicial interpretations to resolve conflicts between competing jurisdictions efficiently.
Philosophical Perspectives on Demarcation
Jurisdictional disagreement involves conflicts over authority or control between entities, while demarcation disputes focus on defining clear boundaries or limits, often in scientific or philosophical contexts. Philosophical perspectives on demarcation emphasize the criteria that distinguish science from non-science, debating the nature and limits of knowledge classification. These perspectives critically analyze how demarcation shapes epistemological boundaries, impacting the legitimacy and authority attributed to various fields.
Resolving Jurisdictional Conflicts
Resolving jurisdictional conflicts requires clear legal frameworks that define the authority boundaries between different governmental or administrative entities, minimizing overlapping claims. Effective dispute resolution mechanisms such as arbitration, mediation, or adjudication by higher courts help address jurisdictional disagreements before they escalate into demarcation disputes involving physical boundary conflicts. Prioritizing cooperation and communication among parties ensures timely resolution and maintains governance stability.
Addressing Demarcation Disputes in Practice
Addressing demarcation disputes in practice requires clear legal frameworks that define boundary lines between jurisdictions, reducing ambiguities that often lead to conflicts. Effective resolution involves joint surveys, mediation, and enforcement of agreements through recognized authorities to ensure cooperation and compliance. Utilizing geographic information systems (GIS) and cadastral mapping enhances accuracy and transparency in demarcation processes, minimizing potential jurisdictional disagreements.
Implications for Policy and Governance
Jurisdictional disagreements often result in overlapping authority among governmental agencies, complicating policy implementation and leading to inefficiencies in governance. Demarcation disputes, involving unclear boundaries between administrative units, hinder resource allocation and service delivery, thereby affecting public satisfaction and trust. Effective resolution mechanisms are essential to maintain clear governance structures and ensure coherent policy enforcement.
Jurisdictional disagreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com