Democratization involves the transition from authoritarian regimes to democratic governance, emphasizing citizen participation, rule of law, and political accountability. It fosters inclusive institutions and protects individual freedoms, enabling societies to flourish politically and economically. Explore this article to understand the complexities and impacts of democratization in today's world.
Table of Comparison
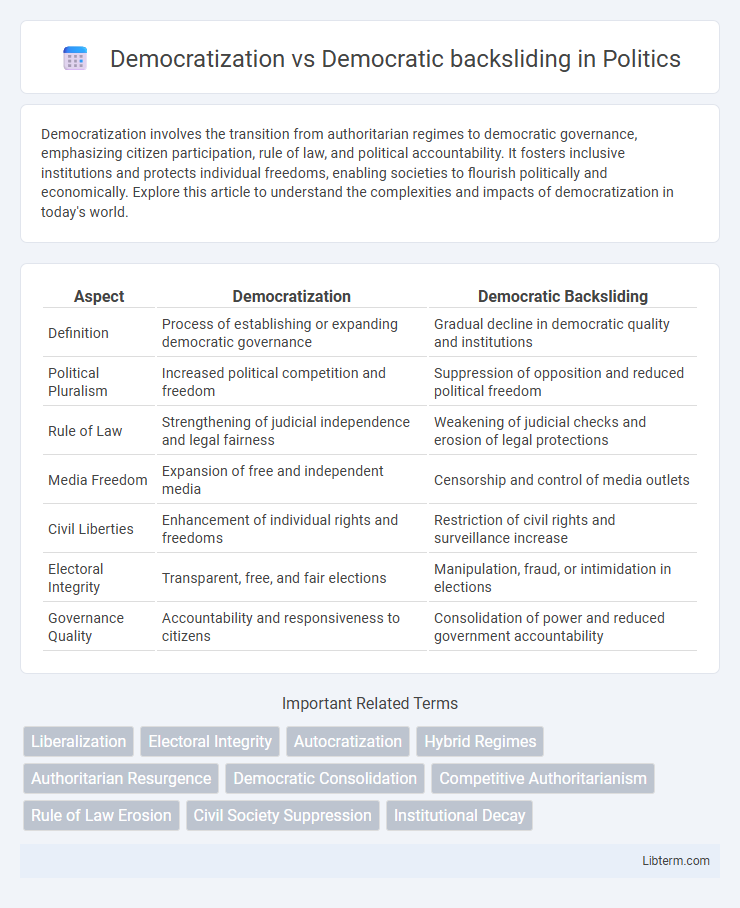
| Aspect | Democratization | Democratic Backsliding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of establishing or expanding democratic governance | Gradual decline in democratic quality and institutions |
| Political Pluralism | Increased political competition and freedom | Suppression of opposition and reduced political freedom |
| Rule of Law | Strengthening of judicial independence and legal fairness | Weakening of judicial checks and erosion of legal protections |
| Media Freedom | Expansion of free and independent media | Censorship and control of media outlets |
| Civil Liberties | Enhancement of individual rights and freedoms | Restriction of civil rights and surveillance increase |
| Electoral Integrity | Transparent, free, and fair elections | Manipulation, fraud, or intimidation in elections |
| Governance Quality | Accountability and responsiveness to citizens | Consolidation of power and reduced government accountability |
Understanding Democratization: Definition and Key Components
Democratization refers to the transition from non-democratic to democratic governance characterized by free and fair elections, political pluralism, and the protection of civil liberties. Key components include the establishment of rule of law, active participation of citizens in political processes, and institutional accountability. These elements collectively foster a political environment where power is derived from the will of the people, ensuring transparency and safeguarding human rights.
What is Democratic Backsliding? Core Features and Indicators
Democratic backsliding refers to the gradual decline in the quality and functioning of democratic institutions, characterized by the erosion of political pluralism, weakening of checks and balances, and the undermining of civil liberties. Core features include the concentration of executive power, decreased judicial independence, restrictions on media freedom, and manipulation of electoral processes. Indicators of democratic backsliding often involve increased authoritarian practices such as political repression, reduced transparency, and curtailed opposition participation in governance.
Historical Overview: Waves of Democratization and Regression
The historical waves of democratization trace back to the early 19th century with the expansion of suffrage in Europe and the Americas, notably during the First Wave (1828-1926) and the Third Wave (1974-1990) which saw significant democratic transitions worldwide. Periods of democratic regression, or backsliding, often correspond to economic crises, authoritarian revivals, or military coups, as observed in the Interwar Period and post-Cold War era. These waves illustrate the cyclical and fragile nature of democracy, emphasizing the need for robust institutions to sustain democratic governance.
Causes and Drivers of Democratization
Economic development, increased education levels, and the expansion of civil society are primary causes driving democratization by fostering political participation and accountability. International influences such as foreign aid, diplomatic pressure, and the spread of democratic norms also promote democratic transitions. Technological advancements and social media enhance citizen mobilization and transparency, further facilitating the consolidation of democratic regimes.
Common Triggers of Democratic Backsliding
Common triggers of democratic backsliding include political polarization, erosion of judicial independence, and the weakening of institutional checks and balances. Undermining press freedom and increasing executive power often facilitate authoritarian tendencies within democracies. Economic instability and social unrest can also create fertile ground for leaders to curtail democratic norms and consolidate personal power.
Political Institutions: Strengthening Democracy vs Weakening Safeguards
Robust political institutions are essential for democratization, providing checks and balances that uphold the rule of law and protect civil liberties. Weakening these safeguards through authoritarian practices or corruption accelerates democratic backsliding, eroding trust and enabling power concentration. Strengthening judiciary independence, free press, and transparent electoral systems remains critical to sustaining democratic resilience and preventing institutional decay.
Role of Civil Society in Advancing or Resisting Change
Civil society plays a crucial role in both democratization and resisting democratic backsliding by mobilizing public participation, advocating for transparency, and holding governments accountable. Non-governmental organizations, grassroots movements, and independent media contribute to fostering inclusive political environments and defending democratic norms. In contrast, weakening or co-opting civil society organizations often facilitates authoritarian entrenchment and undermines democratic progress.
Case Studies: Countries Experiencing Democratization and Backsliding
Countries like Tunisia and Myanmar exemplify democratization efforts, where initial political reforms and increased electoral participation reflect progress toward democratic governance. Conversely, Hungary and Turkey illustrate democratic backsliding through measures such as weakening judicial independence, restricting media freedom, and consolidating executive power. These case studies highlight the dynamic spectrum of political change, emphasizing that democratization and backsliding often coexist within global political landscapes.
Global Impacts: Consequences of Democratic Trends
Democratization fosters political stability, economic growth, and increased human rights protection globally, reinforcing international cooperation and peace. Democratic backsliding, evident in countries such as Hungary and Turkey, results in weakened institutions, erosion of civil liberties, and reduced foreign investment, undermining global governance structures. These divergent trends influence regional security, economic development, and the effectiveness of international organizations like the United Nations and the European Union.
Strategies to Promote Democratization and Counter Democratic Backsliding
Effective strategies to promote democratization include strengthening institutions such as independent judiciaries and free press, ensuring transparent electoral processes, and fostering civic education to empower citizen participation. Countering democratic backsliding requires implementing robust checks and balances, monitoring political actors for authoritarian tendencies, and supporting civil society organizations that defend human rights and democratic norms. International cooperation and targeted sanctions also play key roles in deterring anti-democratic behaviors and reinforcing democratic resilience.
Democratization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com