Isolationism focuses on minimizing a country's involvement in foreign affairs to prioritize domestic interests and avoid entanglements. This policy often aims to protect national sovereignty and reduce the risks associated with international conflicts. Discover how isolationism shapes global relations and impacts your nation's strategic decisions in the full article.
Table of Comparison
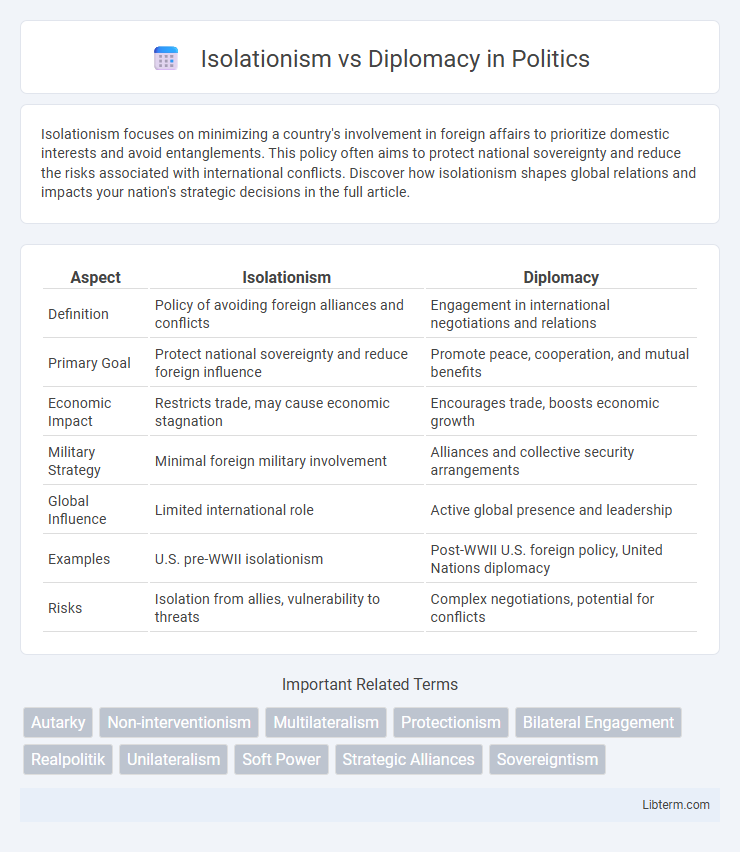
| Aspect | Isolationism | Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policy of avoiding foreign alliances and conflicts | Engagement in international negotiations and relations |
| Primary Goal | Protect national sovereignty and reduce foreign influence | Promote peace, cooperation, and mutual benefits |
| Economic Impact | Restricts trade, may cause economic stagnation | Encourages trade, boosts economic growth |
| Military Strategy | Minimal foreign military involvement | Alliances and collective security arrangements |
| Global Influence | Limited international role | Active global presence and leadership |
| Examples | U.S. pre-WWII isolationism | Post-WWII U.S. foreign policy, United Nations diplomacy |
| Risks | Isolation from allies, vulnerability to threats | Complex negotiations, potential for conflicts |
Defining Isolationism and Diplomacy
Isolationism is a foreign policy approach where a nation minimizes its involvement in international political and economic alliances to preserve sovereignty and avoid external conflicts. Diplomacy involves managing international relations through negotiation, dialogue, and collaboration to resolve conflicts and promote mutual interests. Defining these concepts highlights isolationism's emphasis on self-reliance and non-intervention, contrasting with diplomacy's focus on engagement and cooperation among states.
Historical Roots of Isolationism
Isolationism in U.S. history traces back to the early 19th century, rooted in the Monroe Doctrine of 1823, which warned European powers against further colonization in the Americas while advocating minimal involvement in European conflicts. This policy reflected a desire to protect national sovereignty and avoid entangling alliances, emphasizing autonomous economic and political development. The interwar period reinforced isolationist sentiments as the United States sought to recover from World War I's devastation, leading to restrictive immigration policies and trade barriers that underscored a preference for non-interventionism.
The Evolution of Diplomatic Engagement
The evolution of diplomatic engagement reflects a shift from strict isolationism to proactive international collaboration, emphasizing bilateral and multilateral treaties, global governance institutions, and conflict resolution mechanisms. Key historical milestones include the Treaty of Westphalia establishing state sovereignty, the Congress of Vienna creating a balance of power, and the United Nations promoting collective security and diplomacy. This progression underscores the growing recognition that sustained peace and economic stability depend on open dialogue, negotiation, and cooperation across nations.
Key Advantages of Isolationist Policies
Isolationist policies prioritize national sovereignty and reduce entanglement in foreign conflicts, minimizing military expenses and avoiding the risks of international wars. By focusing on domestic development and self-sufficiency, isolationism strengthens internal economic stability and preserves cultural identity. This approach also limits exposure to global political instability and foreign influence, enhancing security and control over national affairs.
The Benefits of Active Diplomacy
Active diplomacy fosters international cooperation, enabling countries to address global challenges such as climate change and security threats effectively. By engaging in diplomatic dialogues, nations can prevent conflicts, build economic partnerships, and promote cultural exchange. This proactive approach strengthens global stability and enhances national interests through collaborative problem-solving.
Major Case Studies: Isolationism in Practice
Japan's Sakoku policy (1633-1853) exemplified isolationism by severely restricting foreign trade and contact to maintain political stability and cultural purity. The United States' pre-World War II stance reflected isolationism by avoiding entanglements in European conflicts despite rising global tensions. North Korea continues strict isolationism through limited foreign interactions to preserve regime control and resist external influences.
Diplomatic Success Stories in International Relations
Diplomatic success stories in international relations highlight the effectiveness of dialogue and negotiation, such as the Camp David Accords between Egypt and Israel in 1978, which established a lasting peace framework. The Treaty of Versailles, despite its flaws, exemplified post-World War I efforts to prevent future global conflicts through collective diplomacy. These cases demonstrate that proactive diplomacy often resolves disputes and fosters cooperation, contrasting with isolationism's tendency to exacerbate tensions by ignoring global issues.
Economic Impacts: Isolationism vs Diplomacy
Isolationism often leads to reduced trade volumes, limiting economic growth and access to foreign investment, while diplomacy fosters international partnerships that enhance trade opportunities and economic stability. Countries practicing diplomacy benefit from negotiated trade agreements, increased market access, and foreign direct investment inflows, driving innovation and job creation. Economic isolation can result in supply chain disruptions and higher costs for consumers, whereas diplomatic engagement supports global integration and competitive advantage.
National Security: Balancing Independence and Cooperation
Isolationism emphasizes national security through strict self-reliance and minimal foreign entanglements, aiming to avoid external threats by limiting international commitments. Diplomacy prioritizes strategic alliances and international cooperation to address global security challenges, enhance intelligence sharing, and promote collective defense. Balancing independence and cooperation requires a nuanced approach that safeguards sovereignty while engaging selectively in multilateral efforts to mitigate transnational risks.
The Future of Isolationism and Diplomacy in a Globalized World
The future of isolationism in a globalized world faces diminishing viability as economic interdependence and transnational challenges demand cooperative diplomacy. Nations increasingly rely on multilateral institutions and strategic alliances to address issues such as climate change, trade, and security. Diplomatic engagement remains essential for sustaining global stability and fostering innovation across interconnected societies.
Isolationism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com