Digital governance ensures efficient management of technology resources, data security, and regulatory compliance within organizations. Strong digital governance frameworks enable transparency, accountability, and risk mitigation in your digital transformation efforts. Explore the rest of the article to discover how effective digital governance can enhance your organization's success.
Table of Comparison
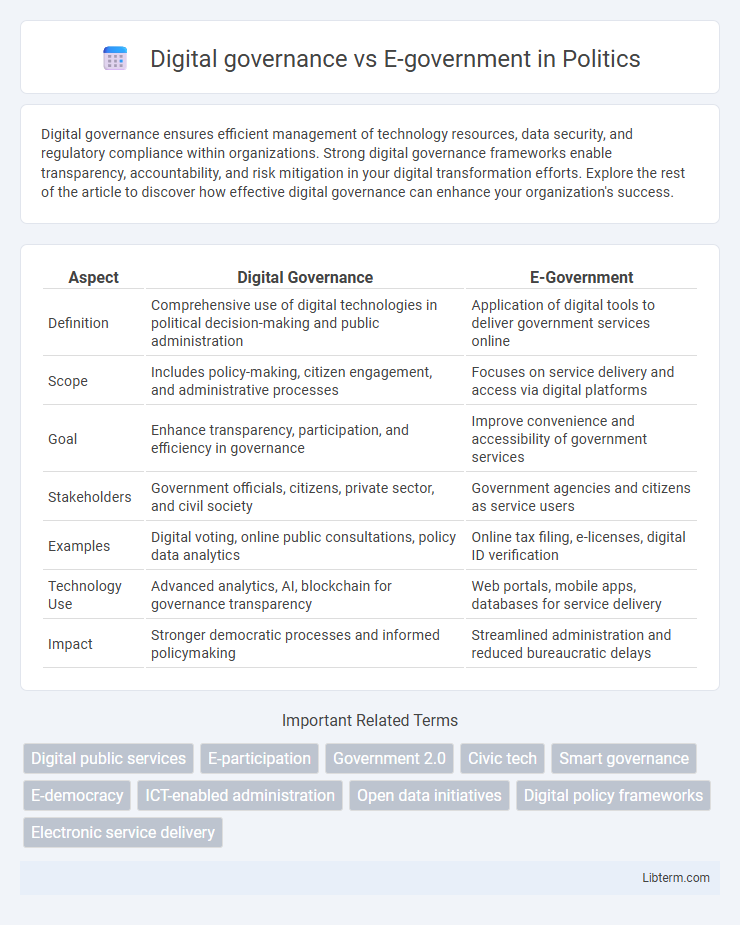
| Aspect | Digital Governance | E-Government |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive use of digital technologies in political decision-making and public administration | Application of digital tools to deliver government services online |
| Scope | Includes policy-making, citizen engagement, and administrative processes | Focuses on service delivery and access via digital platforms |
| Goal | Enhance transparency, participation, and efficiency in governance | Improve convenience and accessibility of government services |
| Stakeholders | Government officials, citizens, private sector, and civil society | Government agencies and citizens as service users |
| Examples | Digital voting, online public consultations, policy data analytics | Online tax filing, e-licenses, digital ID verification |
| Technology Use | Advanced analytics, AI, blockchain for governance transparency | Web portals, mobile apps, databases for service delivery |
| Impact | Stronger democratic processes and informed policymaking | Streamlined administration and reduced bureaucratic delays |
Understanding Digital Governance and E-Government
Digital governance refers to the framework and policies that guide the strategic use of digital technologies in public administration to enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen engagement. E-Government specifically focuses on the implementation of digital tools and online services to improve the efficiency and accessibility of government functions for citizens and businesses. Understanding the distinction highlights how digital governance encompasses broader regulatory and organizational aspects, while e-government concentrates on the practical delivery of digital public services.
Core Principles: Digital Governance vs E-Government
Digital governance emphasizes inclusive decision-making, transparency, and accountability by integrating digital technologies into policy and administrative frameworks. E-government focuses on delivering public services efficiently through digital platforms, enhancing accessibility and user experience. Core principles of digital governance prioritize participatory engagement and data-driven strategies, whereas e-government centers on service digitalization and process automation.
Key Technologies Powering Each Approach
Digital governance leverages blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics to enhance transparency, citizen engagement, and decision-making processes. E-government primarily utilizes cloud computing, mobile applications, and online portals to deliver public services and improve administrative efficiency. Both approaches integrate IoT and cybersecurity measures to ensure secure, real-time data exchange and infrastructure resilience.
Scope of Services: Contrasting Digital Governance and E-Government
Digital governance encompasses a broad framework of policies, regulations, and administrative practices designed to manage digital transformation across public and private sectors, emphasizing inclusivity and multi-stakeholder participation. E-government specifically refers to the implementation of digital tools and platforms to deliver public services such as online tax filing, digital identity management, and electronic voting systems directly to citizens. Whereas e-government focuses on service delivery channels, digital governance addresses overarching governance structures, data privacy, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure management.
Stakeholder Involvement and Collaboration
Digital governance emphasizes inclusive stakeholder involvement by integrating diverse public, private, and civil society actors to co-create policies and ensure transparency. E-government primarily focuses on delivering government services efficiently through digital platforms, with limited direct collaboration among stakeholders. Effective digital governance fosters multi-sector collaboration, enhancing accountability and responsiveness beyond traditional e-government service delivery models.
Policy Implications and Regulatory Frameworks
Digital governance emphasizes the integration of digital technologies within the broader policy-making process, requiring adaptive regulatory frameworks that promote transparency, data privacy, and citizen engagement. E-government focuses on the implementation of electronic services and digital platforms to enhance public service delivery, necessitating policies that ensure accessibility, interoperability, and cybersecurity. Policymakers must balance innovation with regulatory oversight to foster trust, empower stakeholders, and enhance the efficiency of governance through digital transformation.
Impact on Citizen Engagement and Participation
Digital governance enhances citizen engagement by integrating advanced data analytics and AI-driven platforms that enable real-time feedback and personalized public services, fostering transparency and accountability. E-government primarily focuses on digitizing existing government processes and services, improving accessibility and efficiency but often maintaining a top-down communication approach. The shift from e-government to digital governance transforms participation from passive consumption to active collaboration, empowering citizens to co-create policies and monitor implementation.
Challenges and Barriers in Implementation
Digital governance faces significant challenges in integrating advanced technologies with traditional governmental frameworks, including data privacy concerns, lack of interoperability, and resistance to organizational change. E-government implementation struggles with digital divide issues, limited infrastructure in rural areas, and inadequate user trust and engagement, hindering widespread adoption. Both models must overcome policy fragmentation and resource constraints to achieve seamless, efficient public service delivery.
Case Studies: Global Best Practices
Digital governance emphasizes policy frameworks, stakeholder engagement, and transparent decision-making processes, while e-government focuses on delivering public services through digital platforms. Case studies from Estonia demonstrate innovative digital identity systems enhancing citizen interactions, whereas Singapore showcases integrated e-government portals improving administrative efficiency. Global best practices reveal the importance of data interoperability, cybersecurity measures, and inclusive access in advancing both digital governance and e-government initiatives.
Future Trends and Innovations in Public Sector Digitization
Digital governance emphasizes strategic frameworks and policies driving the integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and big data analytics to enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen engagement. E-government focuses on the implementation of digital services and platforms, including cloud computing and mobile applications, that streamline public service delivery and improve accessibility. Future trends highlight the convergence of digital governance and e-government through smart city initiatives, automated decision-making, and adaptive infrastructures, fostering resilient, inclusive, and efficient public sector ecosystems.
Digital governance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com