Suspension of the rules allows a legislative body to temporarily set aside standard procedures to expedite urgent or non-controversial matters, enabling faster decision-making. This mechanism is often used to bypass complex debate or procedural delays, ensuring efficient handling of important issues. Discover how this process works and when it can influence your legislative experience.
Table of Comparison
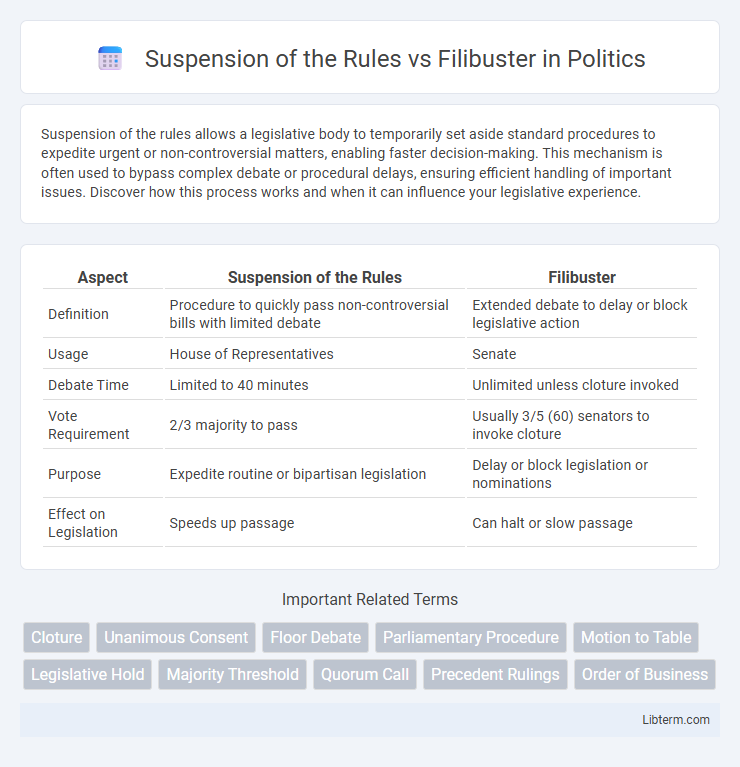
| Aspect | Suspension of the Rules | Filibuster |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Procedure to quickly pass non-controversial bills with limited debate | Extended debate to delay or block legislative action |
| Usage | House of Representatives | Senate |
| Debate Time | Limited to 40 minutes | Unlimited unless cloture invoked |
| Vote Requirement | 2/3 majority to pass | Usually 3/5 (60) senators to invoke cloture |
| Purpose | Expedite routine or bipartisan legislation | Delay or block legislation or nominations |
| Effect on Legislation | Speeds up passage | Can halt or slow passage |
Introduction to Suspension of the Rules and Filibuster
Suspension of the Rules is a legislative procedure in the U.S. House of Representatives designed to quickly pass non-controversial bills by limiting debate to 40 minutes and prohibiting amendments. The filibuster is a Senate tactic allowing extended debate to delay or block a vote, requiring a supermajority of 60 senators to invoke cloture and end the discussion. Both methods influence legislative efficiency but operate under distinct rules and strategic purposes.
Definition and Purpose of Suspension of the Rules
Suspension of the Rules is a legislative procedure in the U.S. House of Representatives designed to quickly pass non-controversial bills and resolutions by limiting debate to 40 minutes and prohibiting amendments. Its primary purpose is to expedite the legislative process for measures with broad bipartisan support, avoiding prolonged discussions and complex amendments. Unlike a filibuster, which is a Senate tactic used to delay or block legislation through extended debate, Suspension of the Rules streamlines approval in a structured, time-efficient manner.
Understanding the Filibuster: Meaning and History
The filibuster is a procedural tactic used in the United States Senate to delay or block legislative action by extending debate, often requiring a supermajority of 60 votes for cloture to end it. Originating in the 19th century, the filibuster allows a minority of senators to exert significant influence over legislation, shaping the balance of power within the chamber. In contrast, suspension of the rules is a quicker process to expedite consideration of non-controversial bills, requiring a two-thirds majority but limiting debate and amendments.
Key Differences Between Suspension of the Rules and Filibuster
Suspension of the Rules is a fast-track legislative procedure in the U.S. House of Representatives allowing debate to be limited to 40 minutes and requiring a two-thirds majority for passage, primarily used for non-controversial bills. In contrast, a filibuster is a tactic in the U.S. Senate where a senator extends debate indefinitely to delay or block a vote, overcome only by invoking cloture, which requires a three-fifths majority of 60 senators. The key difference lies in the chamber-specific rules and majority thresholds: suspension expedites House proceedings with a high supermajority vote, whereas filibusters slow Senate action unless supermajority support ends debate.
Procedural Requirements: How Each Method Works
Suspension of the Rules requires a two-thirds majority vote for approval and is typically used to quickly pass non-controversial bills within limited debate time. Filibuster, unique to the Senate, allows unlimited debate to delay or block a vote until a three-fifths majority (60 senators) votes for cloture to end the debate. The procedural requirement for suspension emphasizes expedited passage with supermajority consent, whereas the filibuster empowers minority senators to extend debate and necessitates a significant bipartisan consensus to overcome.
Impact on Legislative Process and Decision-Making
Suspension of the Rules accelerates the legislative process by allowing expedited consideration of non-controversial bills with a two-thirds majority vote, reducing debate time and limiting amendments. In contrast, the filibuster empowers minority senators to prolong debate and delay or block legislation, requiring a supermajority of 60 votes to invoke cloture and end debate. The suspension mechanism fosters efficiency in decision-making for widely supported measures, while the filibuster introduces a significant hurdle that can stall or reshape legislative outcomes.
Historical Examples in Congress
Suspension of the Rules in Congress allows for expedited consideration of non-controversial bills by limiting debate to 40 minutes and prohibiting amendments, historically used to pass routine legislation efficiently. The filibuster, primarily in the Senate, enables minority senators to extend debate indefinitely, famously employed by Senator Strom Thurmond in 1957 to oppose the Civil Rights Act and by others to delay civil rights legislation in the 1960s. These procedural tools illustrate contrasting approaches to legislative strategy: Suspension of the Rules accelerates consensus-driven bills, while the filibuster protects minority interests and can stall legislation for extended periods.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Tactic
Suspension of the Rules allows for expedited consideration of bills with limited debate, enabling swift passage but requiring a two-thirds majority, which can be challenging to attain. The filibuster permits extended debate in the Senate, protecting minority interests by requiring a 60-vote threshold to end discussion, yet it can lead to legislative gridlock and delays. While suspension streamlines the legislative process by reducing floor time, it limits opportunities for amendment, whereas the filibuster encourages thorough debate at the cost of potential obstruction.
Recent Debates and Reforms
Recent debates over the Suspension of the Rules versus the Filibuster have intensified amid discussions on Senate efficiency and minority rights protection. Reform proposals target the Filibuster's use to block legislation, aiming to streamline approval processes while preserving debate integrity. These efforts reflect ongoing tensions between accelerating legislative action and maintaining procedural fairness in the U.S. Senate.
Conclusion: Implications for Democratic Governance
Suspension of the Rules expedites legislative action by limiting debate and amendments, fostering efficiency in passing non-controversial bills. The filibuster empowers the minority to extend debate and delay proceedings, promoting thorough deliberation but potentially causing legislative gridlock. Balancing these tools is crucial for democratic governance as it influences legislative transparency, minority rights, and the ability to address pressing national issues effectively.
Suspension of the Rules Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com