Advocacy coalitions consist of groups of individuals or organizations sharing common policy beliefs who collaborate to influence public policy and decision-making processes. These coalitions leverage collective resources and expertise to effectively advocate for legislative or regulatory changes aligned with their goals. Discover how understanding advocacy coalitions can empower your efforts to shape policy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
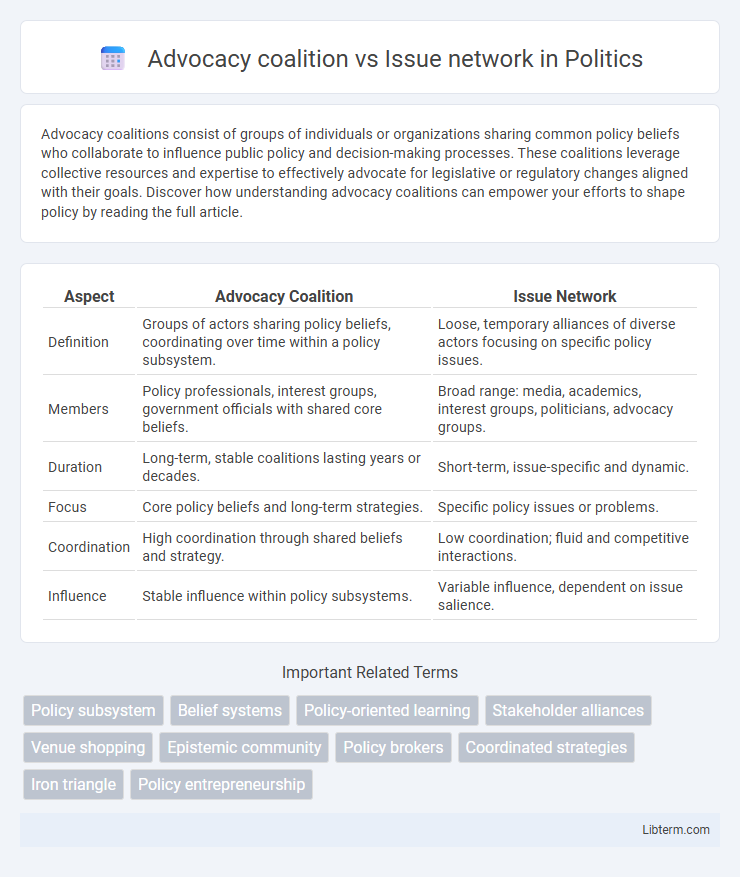
| Aspect | Advocacy Coalition | Issue Network |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Groups of actors sharing policy beliefs, coordinating over time within a policy subsystem. | Loose, temporary alliances of diverse actors focusing on specific policy issues. |
| Members | Policy professionals, interest groups, government officials with shared core beliefs. | Broad range: media, academics, interest groups, politicians, advocacy groups. |
| Duration | Long-term, stable coalitions lasting years or decades. | Short-term, issue-specific and dynamic. |
| Focus | Core policy beliefs and long-term strategies. | Specific policy issues or problems. |
| Coordination | High coordination through shared beliefs and strategy. | Low coordination; fluid and competitive interactions. |
| Influence | Stable influence within policy subsystems. | Variable influence, dependent on issue salience. |
Introduction: Understanding Policy Influence
Advocacy coalitions consist of groups of actors sharing core beliefs and coordinating efforts to influence policy over time, while issue networks are looser, more fluid groupings of diverse stakeholders involved in a specific policy area. Both frameworks highlight the complexity of policy influence but differ in structure and longevity, with advocacy coalitions emphasizing stable alliances and issue networks reflecting shifting relationships. Understanding these distinctions aids in analyzing how policies are shaped within political systems.
Defining Advocacy Coalitions
Advocacy coalitions consist of individuals and organizations that share core beliefs and coordinate efforts over an extended period to influence public policy within a specific domain. These coalitions maintain a stable structure, relying on shared values and long-term collaboration to impact legislative and regulatory processes. In contrast, issue networks are more fluid, encompassing diverse stakeholders focused on particular policy problems without the deep ideological commitment characteristic of advocacy coalitions.
Defining Issue Networks
Issue networks consist of a broad, diverse group of stakeholders including interest groups, government officials, and experts who collaborate loosely around specific policy issues, often lacking the tight coordination seen in advocacy coalitions. These networks are characterized by fluid relationships and shifting alliances, enabling flexible responses to evolving policy environments. Defining issue networks involves identifying their open, dynamic nature and their role in shaping policy through dispersed influence rather than centralized coordination.
Structure and Composition Comparison
Advocacy coalitions consist of groups with shared policy core beliefs and stable relationships, typically formed within a hierarchical framework that integrates government officials, experts, and interest groups. Issue networks feature more fluid, diverse, and loosely connected participants, including media, think tanks, and public interest groups, with a less formal structure that allows for dynamic interaction across multiple sectors. The structured alignment of advocacy coalitions contrasts with the broad, decentralized composition of issue networks that facilitate varied influence on policymaking.
Goals and Motivations: Advocacy Coalitions vs Issue Networks
Advocacy coalitions consist of groups of actors who share core beliefs and long-term policy goals, working collaboratively to influence policy over extended periods. Issue networks are more fluid, comprising diverse stakeholders motivated by specific, short-term issues, often aligning temporarily to address immediate policy concerns. While advocacy coalitions focus on sustained policy change driven by shared ideological commitments, issue networks prioritize flexibility and responsiveness to particular policy problems.
Strategies for Policy Change
Advocacy coalitions employ coordinated strategies such as leveraging shared beliefs, mobilizing resources, and engaging in long-term policy learning to influence legislative agendas and regulatory frameworks. Issue networks utilize more fluid tactics by fostering diverse stakeholder participation, forming temporary alliances, and capitalizing on media and public opinion to create immediate pressure for policy shifts. Both approaches integrate targeted lobbying and expert testimony but differ in coalition permanence and scope of policy influence.
Examples in Policy-Making
Advocacy coalitions such as the climate change coalition, composed of environmental groups, scientists, and government agencies, work collectively over long periods to influence energy and environmental policies. In contrast, Issue networks, like the healthcare reform network, consist of diverse actors including lobbyists, interest groups, and media who form temporary alliances to impact specific legislative efforts. Both play critical roles in policy-making by shaping agendas, providing expertise, and mobilizing stakeholders around shared policy goals.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Advocacy coalitions bring together groups of actors who share core beliefs, enabling sustained policy influence through coordinated strategies and long-term commitment, but their rigid belief systems can limit flexibility and inclusion of diverse perspectives. Issue networks provide broader participation from varied stakeholders, enhancing adaptability and responsiveness to policy changes, yet their loose structure often results in weaker cohesion and difficulty in maintaining consistent policy goals. Both approaches balance the trade-off between focused influence and inclusive dialogue, affecting their effectiveness in complex policymaking environments.
Impact on Legislative Outcomes
Advocacy coalitions drive legislative outcomes through coordinated, long-term strategies involving actors sharing core beliefs, enhancing policy stability and continuity. Issue networks, comprising diverse stakeholders with varied interests, create more fluid and dynamic legislative impacts, often resulting in short-term or incremental policy changes. The sustained influence of advocacy coalitions contrasts with the episodic, dispersed effects typical of issue networks on lawmaking processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Policy Influence Model
Selecting the appropriate policy influence model depends on the complexity and scope of the issue; advocacy coalitions excel in long-term, value-driven policy environments, uniting stakeholders around shared beliefs to drive systemic change. Issue networks offer greater flexibility and inclusivity, incorporating diverse perspectives and expertise for dynamic, issue-specific policymaking processes. Understanding the policy context and desired outcomes ensures effective engagement and strategic influence within the policymaking arena.
Advocacy coalition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com